Stroke – Cerebrovascular accident
Description of stroke
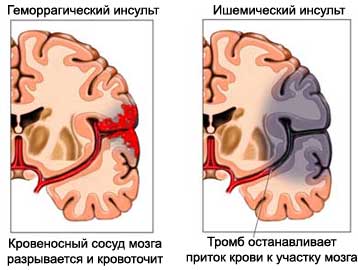
Stroke – brain damage. It arises, when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted. Without oxygen and nutrients, coming from the blood, brain tissue quickly dies (less than 10 minutes). This results in sudden loss of normal brain function.
Causes of stroke
A stroke occurs, When the blood flow in the brain is blocked (the so-called ischemic stroke). This is caused by one of the following reasons:
- A sudden decrease in blood flow;
- Damage to blood vessels, supplying blood to the brain. The reason may be:
- Trauma;
- Blood clot, which is formed and comes off from the other parts of the body (eg, heart or neck);
- Certain disorders, that predispose to the formation of blood clots:
- Cancer;
- Pregnancy;
- Atrial fibrillation;
- Some autoimmune diseases;
- Damage to blood vessels, supplying blood to the brain. The reason may be:
- Local blood clot;
- Capacity of fatty substances (atherosclerotic plaques) on the inner wall of the artery, then it may be:
- Arteriostenosis;
- Reduced elasticity;
- Local inflammation;
- Defect blood proteins increases its coagulation;
- Reduced blood flow in the artery;
- Capacity of fatty substances (atherosclerotic plaques) on the inner wall of the artery, then it may be:
- A clot in an artery, nourish the brain;
- Inflammatory diseases of the blood vessels (vasculitis).
A stroke may also occur, If the blood vessels of the brain bleeds razryvaetsyai. This is called a hemorrhagic stroke.
Risk factors for stroke
Risk factors increase the likelihood of stroke.
Risk factors, that can be influenced:
- High blood pressure (the main risk factor for ischemic stroke);
- High levels of homocysteine in the blood;
- Drug abuse (heroin, cocaine, amfetaminы);
- Arteriostenosis, supplying the brain with blood due to atherosclerosis;
- High cholesterol (in particular, high levels of "bad" cholesterol);
- Smoking;
- Diabetes mellitus or impaired glucose tolerance;
- Atrial fibrillation (abnormalities of cardiac rhythm);
- The use of birth control pills after 35 years, together with smoking;
- Long-term use of hormone replacement therapy;
Risk factors, that can not affect:
- Previous stroke or cardiovascular disease, such as heart attack;
- Previous transient ischemic attack (TIA) – some people experience “predinsult” or TIA. This is a temporary cessation of the blood supply to the brain (mini-stroke). These stroke symptoms completely resolve within a few minutes. They may indicate a very high risk of a full stroke in the near future;
- Age: 60 and older;
- Family members, who suffered a stroke;
- Paul: Men are at greater risk;
- Blood diseases, that increase its coagulation, eg, serpovidnokletochnaya anemia and polycythemia;
- Valvular heart, Such As mytralnыy stenosis.
Symptoms of stroke
Symptoms occur suddenly. They vary depending on the affected part of the brain. Besides, may occur simultaneously several symptoms. If you notice any of the following symptoms, immediately seek medical advice. Emergency assistance is very important, because brain tissue dies quickly in the absence of oxygen. Characteristic signs of stroke:
- Sudden weakness or numbness of the face, hands or feet, especially on one side of the body;
- Sudden confusion;
- Sudden problems with speech and understanding;
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes;
- Sudden dizziness, problems with walking, loss of balance or coordination;
- Sudden severe headache of unknown cause.
Diagnosis of Stroke
The presence of a stroke is an emergency. Diagnosis includes:
- Neurological tests;
- Electrocardiogram – test, that records heart activity by measuring electrical current, passing through the heart muscle;
- Tests for medical imaging of the brain and blood vessels:
- CT – type of X-ray, which uses computer, to make pictures of the brain. This helps your doctor distinguish between hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke;
- MRT – examination, which uses magnetic waves, to make pictures of the brain;
- US – examination, which uses sound waves to study the blood vessels, supplying the brain;
- Blood tests, especially for homocysteine, prothrombin time and other coagulation tests.
Some tests may include:
- Arteriography (angiography) – into a blood vessel in the groin catheter, which is supplied to the brain, and then take pictures of the brain arteries;
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) – conducted study blood flow in blood vessels in the brain;
- CT angiography – test uses a CT scanner, which carries images of blood vessels in the brain after administration of a radiopaque dye into them;
- Functional MRI – It shows the activity of the brain while changing various factors (body movement, changing the level of oxygen in blood, etc.);
- Doppler ultrasound – It allows you to see the narrowing of the arteries (carotid and vertebral), supplying the brain, evaluate blood flow to the brain;
- Echocardiography – test, which uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound), to examine the size, shape and motion of the heart, to determine the presence of a blood clot in the heart chambers.
Stroke care
Immediate treatment is needed, that:
- Rastvoritь clot, that causes an ischemic stroke;
- Stop the bleeding during a hemorrhagic stroke.
Further treatment is aimed at, that:
- Reduce the risk of stroke in the future;
- To improve the functioning of the brain;
- To overcome the limited ability after stroke.
Medication for the treatment of stroke
- Fibrinolytic agents (to dissolve blood clots):
- Available shortly after the onset of symptoms, usually given for 4,5 hours intravenously, or intra-six hours;
- Provided carefully examined patients;
- Antiagregantы:
- Aspirin;
- Clopidogrel and dipyridamole / aspirin;
- Blood-thinning drugs (antykoahulyantы):
- Heparin, injected into a vein;
- Peroralynыe drugs (eg, warfarin), subject to long-term treatment with blood thinners;
- Kleksan / Lovenoks (enoxaparin sodium) or other medicines, subcutaneously.
Other drugs used to treat stroke:
- Medications to control blood pressure (labetalol, sodium nitroprusside);
- Medicines, allowing to reduce the likelihood of further blood clots (aspirin or similar drugs);
- Drugs to reduce brain swelling;
- Drugs to control abnormal heart rhythm (atrial fibrillation).
Other events, recommended during acute stroke:
- Ensure victim a sufficient amount of oxygen;
- It is necessary to take precautions, to prevent choking;
- It is necessary to carry out frequent neurological examinations.
The operation for the treatment of stroke
They can be assigned to certain procedures, prevents damage or restore blood flow in the affected area after a stroke:
- Эkstrakranialynыy / vnutricherepnoy bypass – blood supply is redirected around the blocked artery. Used healthy scalp artery;
- Craniotomy – held, to relieve pressure on the brain, cause swelling;
- Embolectomy – through the blood vessels to clot supplied catheter; with a special device doctor or mechanically remove blood clot, or drugs used for dissolving.
Other operations can be performed after a stroke or TIA, to prevent the recurrence of stroke:
- Carotid endarterectomy – of the carotid arteries (major arteries in the neck) removes fat deposits;
- Karotidnaja Angioplasty and stenting – minimally invasive procedures, carotid artery expands and fits into it to expand the mesh tube.
Even, that endarterectomy is more invasive, for some patients it may be preferable to, Cem angioplasty. Angioplasty may be an option for patients, who are at high risk of complications of carotid endarterectomy.
Methods of recovery after stroke
- Physiotherapy, to recover maximum mobility;
- Occupational therapy, to assist in everyday tasks and self-service;
- Speech therapy to improve swallowing and speech;
- Psychological therapy to improve mood and reduce depression.
Stroke Prevention
To reduce the chance of stroke, Follow these steps::
- Exercise regularly;
- Eat more fruits, vegetables and cereals. Limit your intake of salt and fat;
- Quit smoking;
- Eat more fish;
- Drink alcohol only in moderation (50-100 grams per day);
- Maintain a healthy weight;
- Frequently check blood pressure. Follow your doctor's recommendations for keeping it in a safe range;
- Take low-dose aspirin (50-325 mg per day), if the doctor says, it's safe;
- Control chronic diseases – high cholesterol and diabetes;
- Ask your doctor about the possibility of the use of statins. These medications can help prevent certain kinds of strokes;
- Seek medical advice, If you experience symptoms of a stroke, even if they have disappeared;
- We need to stop taking drugs (eg, cocaine, heroin, marijuana, amfetaminы).
