Atherosclerosis
Description of atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis – reduction in blood vessel elasticity from accumulating on the inner part of plaque (plaques), consisting of Body Fat, cholesterol and calcium. This leads to, artery to narrow and harden. It affects large and medium arteries.
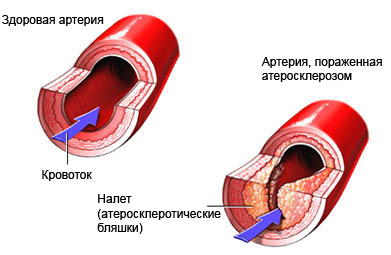
As the plaques grow, it can slow and even stop blood flow. It means, the fabric, which supplies blood to the affected artery is cut off from the blood supply to grow, which often leads to pain or impair the functioning of organs. Atherosclerosis can cause a number of serious health problems. Depending on the location of, may:
- Coronary artery disease – reduced blood flow to the heart area;
- Stroke – umenshnie blood supply to the brain;
- Peripheral vascular disease – characterized by pain in the legs while walking.
Besides, it may damage the blood vessels, in the form of damage to the inner walls of the arteries, of blood clots. They can lead to a further reduction of blood flow. In some cases, a thrombus may become so large, that completely covers the artery. Also, the blood may be collected in clumps, called an embolus. These clumps travel through the bloodstream and entering the small arteries, block them. In these cases, the tissue does not receive oxygen and quickly dies. When this occurs in the heart, it is called a heart attack, brain – stroke.
Long atherosclerosis can also cause weakening of arteries. In response to the pressure, they may bulge, vыzыvaя aneurysm. If untreated, the aneurysm may rupture and bleed. In some cases it can lead to death.
The causes of atherosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis is caused by the accumulation of plaque on the inside of the container – plaques. Plaques occur due to high levels of cholesterol and blood fat. Scar tissue and calcium in the damaged vessel may also cause an increase in plaques.
Process, This leads to, It can begin in childhood. It may take decades before, as this will cause serious health problems.
Risk factors for atherosclerosis
There are two types of factors, that increase the likelihood of atherosclerosis:
- Risk factors, uncontrollable:
- Father or brother, atherosclerosis which originated aged 55 years, or mother, sister, atherosclerosis which originated aged 65 years;
- Age: 45 and older men; 55 years and older women;
- Paul: Men have a higher risk of the disease;
- Risk factors, that can be controlled:
- High cholesterol, especially “bad”, and low “good” cholesterol;
- High blood pressure;
- Cigarette smoking;
- Diabetes – type 1 and type 2;
- Overweight and obesity;
- Lack of physical activity;
- Metabolic syndrome – a combination of three of the five factors:
- Low levels of good cholesterol;
- High levels of triglycerides;
- High blood sugar;
- Elevated blood pressure;
- Increased waist circumference (more 110 cm in men and 90 cm in women).
Symptoms of Atherosclerosis
At the beginning of the appearance of symptoms of atherosclerosis invisible. As the arteries become harder and narrowed, symptoms may begin to appear. If a clot blocks the blood vessel, or off a large embolus, symptoms may occur suddenly.
Symptoms depend on the affected arteries:
- Koronarnыe (heart) artery – can cause symptoms of heart disease, such as chest pain;
- The arteries in the brain – may cause symptoms of a stroke, such as weakness or dizziness;
- Arteries in the lower extremities – can cause pain in the legs or feet problems with walking.
Diagnosis of atherosclerosis
Most people go after diagnosis, they have symptoms. Nonetheless, It can also be examined and treated at the emergence of risk factors.
In the presence of symptoms, the doctor asks questions, to determine, which arteries may be affected. Doctors also need to know the complete history. Conducted a physical inspection. Tests depend on, which arteries may be affected by atherosclerosis. The decision on the need for an analysis is made based on symptoms, medical examination and / or risk factors. Many of the tests are designed to identify problems with the tissues of the body, who do not get enough blood. Two common tests, that directly evaluate the atherosclerotic arteries:
- Angiography (Angiography) – a thin tube is inserted into an artery. After it is introduced into the vessel radiopaque dye, and x-rays are performed. This allows you to assess the degree of blood flow. When the procedure is performed in the heart, This test is called cardiac catheterization.
- Ultrasonography – test, that uses sound waves to the study of internal body parts. In this case, check the size and shape of arteries.
Treatment of Atherosclerosis
An important part of treatment is reducing risk factors. Besides, Treatment depends on the most affected areas of the body.
Treatment may include:
Medication
These include:
- Medicines, impeding the formation of blood clots, such as aspirin or clopidogrel (Plaviks);
- Medications to control high blood pressure;
- Drugs to lower high cholesterol;
- Medicines, which improves blood flow through the narrowed artery, such as cilostazol or pentoxifylline (Trental).
Procedures using a catheter
These procedures include the use of a thin tube (catheter), which is inserted into an artery (most often done for arteries of the heart). The catheter may be used for the treatment of atherosclerosis and other parts of the body. Treatments include:
- Ballonnaя angioplasty – an inflatable balloon at the tip of the catheter is used to apply pressure on the artery wall. This allows you to expand the lumen of the artery and increases the amount of space for blood flow;
- Stenting – usually done after angioplasty. The tubular mesh is placed in a damaged artery. It supports the artery wall and prevents it narrowed again;
- Atherectomy – Special instruments are inserted through the catheter. They are used, to cut away and remove plaque, and increase blood flow. This procedure is now performed fairly rare.
Operation
Surgical options include:
- Endartyerektomiya – removing the inner part of the artery with a large number of plaques. This is often done in carotid arteries of the neck, supplying blood to the brain;
- Arterioplasty – operation anevrizme. The procedure is usually done with synthetic tissue;
- Şunt – the creation of an alternate route for blood flow.
Prevention of atherosclerosis
There are many ways to prevent, as well as to get rid of atherosclerosis. They include:
- Healthy eating. The diet should contain low amounts of saturated fat and cholesterol. The diet should be a lot of whole grains (croup), fruits and vegetables;
- It is necessary to exercise;
- It is necessary to maintain a healthy weight;
- You must quit smoking;
- It is necessary to treat diabetes;.
- If the doctor recommends, you need to take medication, to reduce the risk factors. This may include medications to reduce high blood pressure or high cholesterol;
- It is advisable to carry out tests for the detection of latent forms of atherosclerotic heart disease (coronary artery disease), If you have risk factors.
