Cephalotrypesis, craniotomy: what is this operation, causes, Contraindications, how they do it, what after
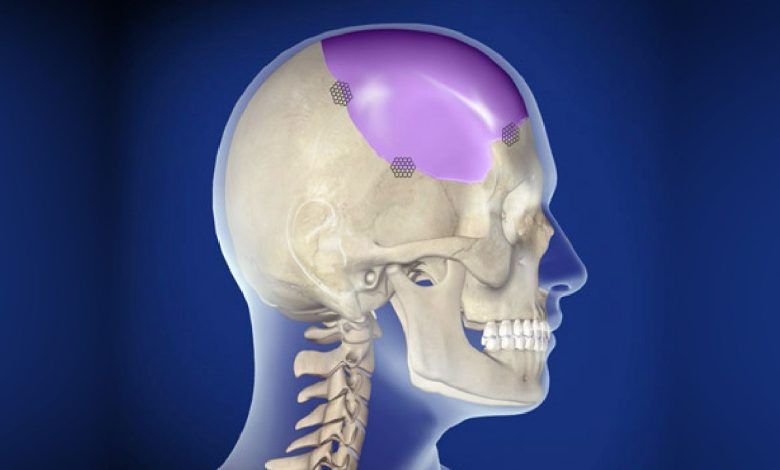
Description craniotomy
A craniotomy is a head operation.. The surgeon cuts through the skull, to reach the brain. There are various types of craniotomy, including:
- Burr hole – a small hole is made in the skull;
- Traditional craniotomy – the skull is cut, and then, postoperatively placed back;
- Stereotaxy – used computer, to see the structure of the brain, which is necessary to operate;
- Kraniotomiâ in the minds of – the patient is awake during part of the operation.
Reasons for craniotomy
The success of the operation depends on its cause. The most common reasons for a craniotomy include:
- Biopsy – to get a sample of brain tissue;
- Brain Cancer;
- Head injury;
- The blood clot in the brain;
- Problems of blood vessels in the brain;
- Nervous disorders;
- Cephaledema;
- Infections of the brain.
Factors, that may increase the risk of complications:
- Smoking.
Possible complications of craniotomy
Before, how to perform a craniotomy, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Bleeding;
- Infection;
- Cephaledema;
- Brain damage, then it may be:
- Changes in memory, behavior, thinking, speeches;
- Vision problems;
- Problems with balance;
- Problems bowel and bladder;
- Convulsions;
- Paralysis or weakness;
- Reaction to anesteziyu (eg, dizziness, lowering blood pressure, breathlessness);
- Heart attack;
- Blood clots.
How is the craniotomy?
Preparation for the procedure
If surgery is planned, your doctor may prescribe the following tests:
- Physical examination, check the nerves and brain work;
- MRT, CT scan, PET scans of the brain (Positron Emission Tomography);
- It should answer the following questions:
- What will help at home after surgery?
- What symptoms on brain?
Be sure to ask your doctor, If you have questions, eg:
- How will pass recovery?
- Do I need to undergo rehabilitation after surgery?
- When can I return to work?
It is necessary to remember the following:
- You may be asked to stop taking certain medicines a week before the procedure,:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (eg, aspirin);
- Blood thinners, such as clopidogrel, warfarin, or ticlopidine;
- We need to organize a trip home from the hospital;
- Organize home assistance during recovery;
- We need to stop taking food and liquids during 8-12 hours before surgery. In this connection, ask your doctor, whether you can drink water prescribed medications before surgery.
Anesthesia
General anesthesia applicable for most types of craniotomy. General anesthesia will block any pain and maintain the patient in a state of sleep during surgery. It is administered intravenously through a needle in the arm or hand.
If you are in the minds of craniotomy, the patient will be given a general anesthetic for the operation of the.
Stereotaxy can be performed under local anesthesia. Anesthesia numb only the area of the operation.
Procedure craniotomy
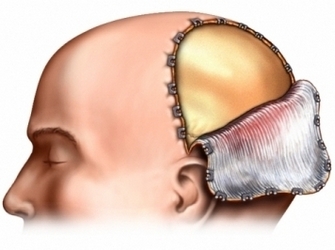
After, as you fall asleep and do not feel pain, breathing tube will be introduced in the throat. Your head will be shaved, Skin treated with antiseptic. The surgeon cuts through the scalp. Further, part of the skull is removed, cortex will be open to further intervention.
Depending on the reason for the operation, It can be done as follows:
- A removal of the tumor;
- Selected part of brain tissue for research (biopsy);
- Maybe an operation on the brain vessels.
After the operation the brain is closed, extracted bone is put in place. To close the skin incision will be used staples and sutures. To remove blood and fluid within the first few days after surgery, the surgical site can be placed drainage tube. Around the head bandage.
Immediately after craniotomy
After surgery, you will be taken to the recovery room for monitoring vital parameters. The breathing tube will be removed. Mental status and vital signs (temperature, heart rate, blood pressure and respiration) will be checked regularly. After some time, the patient is sent to the intensive care unit, and then – in the hospital ward.
How long will the craniotomy?
Several hours (depending on the type of operation and causes).
Will it hurt?
During the operation, you will not feel any pain. After surgery, it will be given pain medication, to reduce pain.
The average hospital stay
3-7 days (The doctor can extend the stay, If there are complications).
Caring for the patient after craniotomy
Care in a hospital
- To reduce the risk of increased pressure in the brain:
- Can be administered steroids and other drugs, to maintain a reduced level of fluid in the body;
- The head should be raised;
- It may be restricted fluid intake;
- Administer, to prevent vomiting;
- Mental condition will be checked;
- They can be assigned to medication, to prevent convulsions;
- They can be treated with antibiotics, to prevent infection;
- The bandage will be removed from the head through 24-48 hours after surgery;
- After the operation, may be used drainage, to prevent excessive accumulation of fluid. In most cases it will be removed prior to discharge;
- You may be asked to get out of bed and walk, to prevent the occurrence of complications – blood clots or pneumonia.
Home Care
When you return home, Follow these steps:, to ensure the normal recovery:
- Keep the area clean and dry operation. Regularly check it for redness, edema, exudation, or separation of the edges;
- Engage in physical therapy, occupational therapy and / or speech therapy, if ordered by a doctor;
- We need plenty of rest and eat a healthy diet, to help the body recover;
- If you are feeling depressed, Talk with a therapist, psychologist or other counselor on these issues;
- Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions.
Contact your doctor after craniotomy
After discharge from the hospital need to see a doctor, If the following symptoms:
- Any changes to the physical sensations (balance, force, or movement);
- Any changes in mental status (level of consciousness, memory, thinking, or reaction);
- Redness, edema, increased pain, bleeding, or any discharge from the incision;
- Persistent headache;
- Kryvosheya;
- Changes in vision (eg, bifurcation, disturbance or loss of vision);
- Fainting and seizures;
- Numbness, tingling or weakness in the face, hands or feet;
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Nausea and / or vomiting, which do not disappear after taking the prescribed medicines, and persist for more than two days after discharge from the hospital;
- Pain, which does not pass after taking pain medication appointed;
- Labored breathing;
- Cough, shortness of breath or chest pain;
- Problems control bladder and / or bowel;
- Swelling, soreness, fever, redness in the legs.
