General anesthesia – General anesthesia
Description of general anesthesia
General anesthesia puts the body into sleep, after taking special medications. It is often used during emergency surgery. It is also widely used anesthesia, if the operation can cause inconvenience.
Anesthetist administered anesthesia, carefully controlling the vital functions of the organism. Anesthetics are used for:
- Preventing pain;
- Relaxation of muscles;
- Adjustments body functions.
Reasons for the implementation of general anesthesia
Anesthesia is used in the following cases:
- To remove the sensation of pain during surgery;
- Do not cause inconvenience to the patient.
Possible complications of general anesthesia
Anesthesia should be performed with caution, to prevent complications. Often some medications are prescribed in advance, to avoid certain problems during anesthesia, such as nausea and vomiting. But even in this case, complications may occur and include:
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Allergic reaction to anesthetic;
- Damage to nerves;
- Disease or damage to the throat, teeth, or vocal cords;
- There is a small risk of the following complications, especially among the elderly or those, who are experiencing health problems:
- Lung infection;
- Stroke;
- Heart attack;
- Immune to anesthesia – a rare complication, in which the patient is resistant to an anesthetic.
Factors, that may increase the risk of complications, include:
- Disease – heart, Airways, kidney disease, diabetes;
- Certain medications – especially those, which increase the risk of bleeding (eg, aspirin);
- Smoking;
- Alcohol abuse – may increase the susceptibility of the liver to anesthesia;
- Eating before operation – food from the stomach can enter the lungs;
- Adverse reaction to the anesthesia last;
- Allergies to certain foods or drugs.
How is the general anesthesia?
Preparation for the procedure
Before the surgery, the anesthesiologist must provide the following information:
- If the patient has previously been subjected to anesthesia, you must tell the doctor about the reaction to it. Also, perhaps, must be reported, what action anesthesia had on family members, which operations were anesthetized;
- You must provide information about the, what medications the patient is taking lately.
Before the procedure:
- They will be measured height and weight;
- On the night before surgery do not eat;
- In the morning before surgery, perhaps, You will need to take certain medications.
Procedure anesthesia
General anesthesia is divided into three phases:
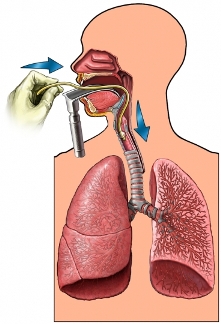
- The induction phase – administered drugs, giving the effect of loss of consciousness. They are administered intravenously or through the gas into the lungs. The breathing tube is placed into the trachea, and is attached to the apparatus, that helps maintain breathing.
- The middle phase, or maintenance phase – entered mainstream medicine, that can sustain a dream or regulate body functions;
- The recovery phase – performed the procedure for the gradual removal of the patient from anesthesia. When the patient begins to wake up and be able to breathe on their own, breathing tube will be removed.
After the procedure
After the expiry of anesthesia checked organizma.Po important indicators necessary, provided the necessary drugs.
The duration of anesthesia procedures
The duration of anesthesia depends on the duration of the operation. Usually this time is not shorter than the duration of the operation.
Will it hurt?
Anesthesia no pain is felt, because the brain does not perceive pain signals.
The time spent in hospital
Time, that the patient is in the hospital will depend on:
- The type of surgery;
- Reaction to the surgery and anesthesia.
Postoperative care
After the expiry of anesthesia, the patient is sent to the ward or discharged home. For the first 24 hours to avoid actions, that need attention, such as driving. It is necessary to adhere to doctors' instructions.
It is necessary to go to the hospital in the following cases
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Nausea and / or vomiting, which lasts more than two days after leaving the hospital, and does not stop after taking the appropriate medications;
- Cough, shortness of breath or chest pain;
- Dizziness, weakness.
