Biopsy
Description biopsy
Biopsy – lifetime selected sample of tissue or cells of the body. A pathologist examines the sample under a microscope.
A biopsy can be done to any body and any part of the body.
Causes biopsy
Why biopsy performed?
Biopsy ispolyzuetsya, to detect abnormal cells in a tissue sample. Often, a biopsy is performed, to refute or confirm the presence of cancer and to determine the type and level of aggressiveness.
Biopsy vыpolnyaetsya, to determine why there was the following states:
- Infection;
- Tumor;
- Growth of cells and tissues.
The general interpretation of the results of a biopsy includes:
- Normal tissue, no abnormalities;
- Tissue irritation;
- Not normal, but difficult to interpret state;
- Not Normal, not cancerous, but a precancerous condition of the tissues;
- Cancer;
- Unclear status of the tissue.
Possible complications when performing a biopsy
Complications are rare, but no procedure does not guarantee the absence of risk. Before, how to perform a biopsy, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Bleeding
- Pain
- Infection
- Scarring
- Results, It is difficult to interpret
Factors, that may increase the risk of complications, include:
- Smoking
As biopsy?
Preparation for research
It may be necessary to stop taking some medicines:
- Aspirin or other anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Blood thinners, eg, clopidogrel (Plaviks) or warfarin.
Anesthesia
The type of anesthesia depends on the method of biopsy:
- General anesthesia – blocks pain, under its influence the patient is asleep. Administered intravenously in the arm or hand;
- Local anesthesia – Only blocks pain in performing sampling. Under her influence at the injection site occurs numbness. Are injected.
Biopsy Procedure
To perform a simple biopsy sampling place will be cleared. Local anesthesia is injected, the patient does not feel pain. You will then be selected by a piece of fabric or leather. If necessary,, if at the site of the biopsy wound formed, it will be closed.
Method of sampling, doctor who uses depends on the type of biopsy:
- Punktsionnaya biopsy – cells are removed using a thin needle;
- Aspiratsionnaya biopsy – The cells were recovered by suction cannula;
- Osnovnaya punktsionnaya biopsy – tissue sample is removed via the hollow needle, which has a special cutting edge;
- Vakuumnaya biopsy – selection fabric made using a special rotary-cutting device;
- Эndoskopicheskaya biopsy – anomaly seen with a long thin tube, Illumination of the chamber which has at one end (called an endoscope); sampling tool is inserted through the tube;
- Intsizionnaya biopsy – selected for the study of the body;
- Excision biopsy – to study organ is completely removed;
- Perforatsionnaya biopsy – a sample is taken using a special cutting tool for biopsy;
- Skin biopsy – a small piece of skin is cut off with a scalpel;
- Britvennaya biopsy – the top layer of the skin to shave a special blade;
- Bone marrow biopsy – long needle is inserted into the bone marrow cells to collect.
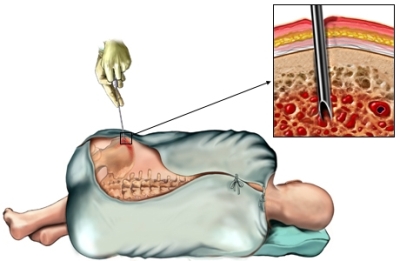
How long will the biopsy?
A simple biopsy usually takes a few minutes. Biopsy via surgery takes longer.
It will hurt?
Possible pain in the, where a sample of tissue has been removed. Your doctor may prescribe pain medication.
The average time of hospital stay
When conducting a simple biopsy of the patient can immediately return home. If the biopsy is performed using surgery, You may need to stay in the hospital 1-2 day.
Care after the procedure
Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions.
- We need to take pain medication as directed by a doctor;
- To reduce discomfort, you can make a warm compress or a heating pad to the area sampling;
- We need to ask the doctor, when you need to change bandages;
- We need to ask the doctor, when it is safe to shower, bathe or expose the surgical site to water;
- In the presence of seams is removed within a week.
It is necessary to go to the hospital in the following cases
- Redness, edema, increased pain, bleeding or discharge from the biopsy site;
- There are signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Bleeding;
- Inability to relieve pain using painkillers;
- Any warning signs.
