Heart attack – Acute myocardial infarction – Myocardial infarction
Description myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction occurs, When blood flow to the heart muscle is reduced or interrupted. Oxygen does not flow to the heart muscle, and this causes the damage and necrosis of tissue (ischemic myocardial necrosis).
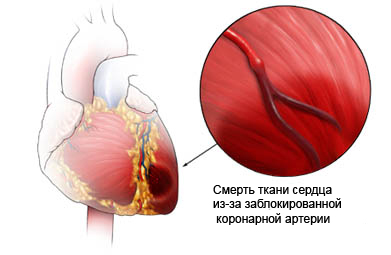
The causes of myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction can be induced:
- Thickening of the artery walls, supplying the heart muscle (coronary artery);
- Accumulation of fatty plaques in the coronary arteries;
- Narrowing of the coronary arteries;
- Coronary artery spasm;
- The development of a blood clot in the coronary arteries;
- Blockader (circulatory disturbance), which affects the coronary arteries.
Risk factors
Factors, which increase the risk of myocardial infarction:
- Paul: male
- Advanced age;
- Obesity;
- Smoking
- High blood pressure
- Passive lifestyle
- High blood cholesterol (in particular, High LDL cholesterol, and low levels of HDL cholesterol)
- High levels of blood triglycerides;
- Diabetes;
- Stress;
- The presence of family members with heart disease.
Symptoms of myocardial infarction
Symptoms include:
- Compression, severe chest pain, especially after or during:
- Exercise, or high physical exertion
- Emotional stress;
- In cold weather;
- Acceptance of a heavy meal;
- Pain in the left shoulder, the left hand, jaw;
- Breathlessness;
- Sweating, lipkaya skin;
- Nausea;
- Weakness;
- Loss of consciousness;
- Alarm, especially the sense of doom or panic without apparent reason;
Unusual symptoms of heart attack (may occur more often in women):
- Stomach ache;
- Sore shoulders;
- Loss of coordination;
- Swoon.
Diagnosis of myocardial infarction
If you suspect a heart attack is an urgent need to go to hospital.
Tests may include:
- Blood tests, search for certain enzymes in the blood over several hours or days after a heart attack;
- Urine, to find specific substances, in urine within a few hours or days after a heart attack;
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) – records heart activity by measuring electrical current through the heart muscle, changes can show, whether there is a deviation;
- Echocardiogram – It uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound), to examine the size, form, function and motion of the heart;
- Stress test – recording of the electrical activity of the heart during increased physical activity, usually, done in a few days or weeks after the heart attack;
- Nuclear (Radiation) scan uses a radioactive material (label), to show areas of the heart muscle, where blood flow is reduced;
- Electron-beam computed tomography (EBCT) – such as X-ray examination, which uses a computer to create detailed images of the heart, coronary artery, and surrounding structures, It may be useful, there is an immediate risk of coronary heart disease;
- Coronary angiography – It uses radiopaque substances and X-rays, to look for narrowing or blood clot in the coronary arteries.
Treatment of myocardial infarction
Therapeutic treatment includes receiving these drugs and substances:
- Breathing pure oxygen;
- Medications for pain relief (such as morphine);
- Medications based on nitroglycerin;
- Aspirin and other antiplatelet drugs;
- Uspokaivayushtie drugs;
- Solvents clots (Thromboltics) – during the first six hours after a heart attack, the patient can be given drugs, to break up blood clots in the coronary arteries;
- Other medications, that block the function of platelets (so-called receptor blockers platelet IIb / IIIa);
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs (eg, statin drugs).
Surgical intervention
Surgery includes:
- Coronary artery bypass (AKS);
- Atherectomy;
- Ballonnaя angioplasty with or without stenting.
According to observations, Patients, which was done coronary artery bypass surgery is also less risk of angina, compared with those, who received percutaneous coronary intervention (CHKV). PCI involves the use of balloon angioplasty or coronary stenting.
A physical or rehabilitation therapy
During recovery, perhaps, You need physical or rehabilitative therapy, to recuperate.
Treating Depression
After a heart attack patient may feel depressed. Therapy and medication may help relieve it. To accelerate vyzdoroleniya should follow the doctor's instructions.
Prevention of myocardial infarction
Prevention or treatment of coronary heart disease, can help prevent a heart attack. For the prevention of myocardial infarction necessary:
- Maintain a healthy weight;
- You must quit smoking;
- Eat a healthy diet. Foods should be low in saturated fat and rich in whole grains, fruits and vegetables;
- Treatment of high blood pressure, diabetes and high cholesterol;
- Consult with your doctor about taking a daily low-dose aspirin. While most people are able to take low-dose aspirin regularly, sometimes it can lead to serious bleeding, especially from the gastrointestinal tract (GI). Aspirin in combination with other analgesics may not work.
