Angiography – Arteriography – Angiogramma
Description angiography
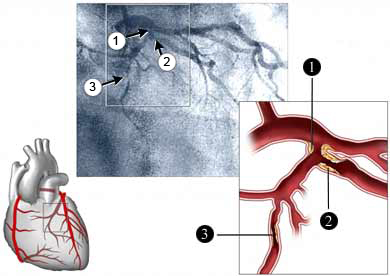
Angiography – X-ray of blood vessels. The study used a chemical, is injected into the blood vessels, to make them more visible for X-ray.
Reasons angiography
This procedure can be done with the aim of:
- To help identify narrowed, increased, and blocked blood vessels;
- Determine, whether there is leakage of blood vessels in other parts of the body.
In some cases, during angiography can cure the blocked blood vessel. This avoids the need for another procedure.
Possible complications of angiography
Complications are rare, However, if you plan to do angiography, You need to know, that may occur:
- An allergic reaction to the chemicals;
- Abnormal heart function (arrhythmia);
- Bleeding at the catheter insertion site;
- Damage to blood vessels, that may cause damage to organs and tissues;
- Renal contrast agent;
- Infection.
Factors, that may increase the risk of complications include:
- Allergies, especially to an X-ray dye, Iodine, drugs, or certain foods, including shellfish;
- Kidney problems;
- Diabetes;
- Coagulation failure.
How is angiography?
Preparation for the procedure
Before the procedure, the doctor will make:
- Blood tests;
- Zadast NA:
- In the history of past illnesses;
- About the medication;
- About allergy;
- Do you currently pregnant;
- You must also complete a medical examination.
A few days before the procedure, necessary:
- Follow the instructions of your doctor. Maybe, You have to make changes to the list of accepted medicines or diet.
Anesthesia
The catheter insertion site will be used local anesthesia. An hour before the procedure, or when it may be intravenously administered sedative. This will help the body to relax.
Angiography Procedure
A catheter is inserted into an artery in the groin or arm (usually in the crook of the elbow, or less, in the wrist). Area introduction shave, sterilized, then injected anesthesia. On the skin, a small incision is made, through which a catheter is inserted into an artery (a long, thin tube). The catheter is fed to the field, to be examined. Through the catheter is inserted radiopaque substance. The doctor watches the procedure on a monitor, take pictures of the blood vessels of interest. After, as the necessary pictures will be made, the catheter is removed from the artery. Province administration clamped on 10 minutes.
Duration of treatment
The procedure takes from several tens of minutes to several hours, depending on the required number of analyzes.
Will it hurt?
Although the procedure, usually, not painful, it may cause some discomfort, including:
- Burning sensation (at the site of catheter insertion);
- Pressure, when the catheter is inserted;
- Nausea, when injected radiopaque substance.
Postoperative care
In the hospital
Immediately after treatment:
- It is necessary to soak a period of time. The duration will depend on the general condition and health reasons, which was performed angiography;
- Maybe, will have to press the catheter insertion site, avoid bleeding;
- If you notice swelling, bleeding, black and blue spots, pain is felt along, where the catheter was inserted, you must inform your doctor or nurse;
- It is necessary to drink plenty of fluids, It came to the contrast agent from the body;
- Hospital allowed to leave after a recovery period, but the term may depend on other medical problems.
Home Care
It is necessary to follow the recommendations of doctors.
Houses need to do the following, to ensure the normal recovery:
- Drink plenty of fluids, in accordance with the instructions of the doctor. This will help to cleanse the body of a contrast agent;
- Do not lift heavy objects, or exercise of physical or sexual activity for 24 hours or more after the procedure, in accordance with the instructions of the doctor.
- Change the dressing around the incision area as instructed;
- Take the medication as instructed;
- You must check with your doctor, when it is safe to shower, bath, or expose the catheter site to water.
The results of angiography
The radiologist will examine the x-ray photos and provide their findings to the doctor. The doctor prescribe the necessary treatment.
It is necessary to go to the hospital in the following cases
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Redness, edema, increasing pain, bleeding, or any discharge from the injection site;
- Strong sweating, nausea or vomiting;
- Severe pain, including chest pain;
- The leg or arm feels cold, the skin becomes white or bluish, numb or tingling;
- Shortness of breath;
- Any problems with speech or vision;
- Weakness of the facial muscles.
