Sickle-cell anemia
Sickle-cell anemia Description
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic disorder. If any change in the shape of red blood cells (erythrocyte). This leads to a reduction in the ability to carry oxygen. Also, this type of anemia can cause acute attacks of pain. They are called sickle cell crisis. The immune system also destroys sickle cell. Loss of erythrocytes gives rise to anemia.
Changing the functionality and the number of red blood cells can reduce the supply of oxygen.
Causes of sickle-cell anemia
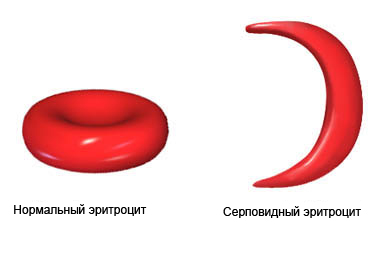
Red blood cells, usually, soft and have a circular shape. This helps them move easily through the blood vessels. The main komnonentom a hemoglobin of red blood cells.
People with sickle cell anemia have an abnormal type of hemoglobin. The red blood cells become hard and sickle. Because of their irregular shape some of the red blood cells get stuck in the small blood vessels. There they fall, and can lead to vascular blockages. The disintegration can occur in blood vessels, which lead to major organs. Reduced blood flow can cause severe pain and organ damage.
The immune system also does not perceives serovidnye cells. The body destroys them faster, than they are produced. This leads to anemia, especially under the following conditions:
- Fever;
- Infection;
- Dehydration;
- Lowering the level of oxygen in the air pressure changes (sometimes occurs during airplane flight).
Risk factors
Factors, which increases the risk of sickle-cell anemia:
- Genetic disorders: for the occurrence of the disease the defective gene must be inherited from both parents;
- Race: negros sub-Saharan Africa;
- Ethnicity: Greeks, Italians, and people from some parts of India, Central and South America, Arabian Peninsula.
Symptoms of sickle-cell anemia
This condition creates a group of symptoms, known as sickle cell crisis. It twinges, that occur with a different frequency and severity. Usually, followed by periods of remission. The risk of sickle cell crisis increases with physical activity, which increases the body's need for oxygen.
The painful crises can last from several hours to several days. They affect the bones of the back, long bones, and chest. The crises can be severe enough, require hospitalization and receiving strong painkillers.
Symptoms of impending sickle cell crisis include:
- Pain and swelling in hands and feet;
- Fever;
- Jaundice;
- Anemia;
- Chest pain, or episodic pain in joints, stomach or back;
- Breathlessness;
- Fatigue;
- Abdominal distention;
- Unusual or prolonged headache;
- Any sudden weakness or loss of sensation;
- Priapism (prolonged erection);
- Sudden changes in vision;
- Sudden, severe anemia can cause:
- Weakness;
- Odyšku;
- Heart failure;
- Shock;
- Loss of consciousness.
Complications of sickle cell anemia include:
- The collapse of the spleen;
- Severe bacterial infections:
- Pneumonia;
- Meningitis;
- Infections of the kidneys and bones;
- Damage to the joints (especially hip and shoulder);
- Damage to the eye, which leads to impaired vision;
- Stroke or other neurological disorders;
- Convulsions;
- Liver disease;
- High levels of Hepatitis C;
- Damage to the penis due to priapism (It can cause impotence);
- Ulcers on the legs;
- Heart murmurs or enlarged heart;
- Stunting;
- Delayed sexual development;
- Problems with thinking, memory and ability to work.
Diagnosis of sickle-cell anemia
The disease is diagnosed by Electrophoresis Hemoglobin. Also, the disease can be diagnosed in the fetus, while doing amniocentesis.
Treatment sickle-cell anemia
The main treatment of sickle cell crisis includes:
- Bed rest;
- Taking pain;
- Intravenous infusion;
- Kislorodnaya therapy – to reduce pain and prevent complications.
Besides, Treatment may include:
Penicillin
Newborns with sickle cell disease can be administered penicillin. It is given twice a day, since the age of two months, for at least five years.
Pneumococcal vaccine
Pneumococcal vaccine (PCV-7) It recommended to introduce children with sickle cell disease at the age of 2-5 years.
Gidroksimochevina (gidrea)
Gidroksimochevina (gidrea) It is the first drug, significantly prevent complications of sickle cell anemia. It increases the production of fetal hemoglobin. This reduces the number of deformed red blood cells. As a result,, This reduces the frequency of sickle-cell crises. Hydrea is not appropriate for all patients with sickle cell disease. It is recommended only for people over the age of 18 years, that have, at least, Three painful crisis year.
Blood transfusion
Blood transfusions can treat and prevent some complications. Transfusion therapy can help prevent recurring crises in children.
Bone marrow transplantation
The bone marrow transplant from a compatible donor can be an effective treatment. For this operation, there are medical risks. Recipients must also take drugs, that suppress the immune system for life.
Prevention sickle-cell anemia
Sickle cell anemia can not be prevented. There are a few general recommendations, to help avoid serious complications:
- It is necessary to take a daily folic acid supplements. This will contribute to the creation of new red blood cells;
- It is recommended to drink plenty of water, to prevent dehydration;
- We should avoid extreme temperatures;
- Not subject to overvoltage and stress;
- More rest;
- Regular medical examination;
- Before, how to get pregnant, We need to undergo genetic examination.
