Auricular flutter; fibrillation; atrial fibrillation: What's it, symptoms, treatment, diagnostics, prevention
Synonyms: atrial fibrillation; auricular flutter; Atrial fibrillation; FP.
Atrial fibrillation or flutter; Auricular fibrillation; A-fib; Afib
Atrial fibrillation description
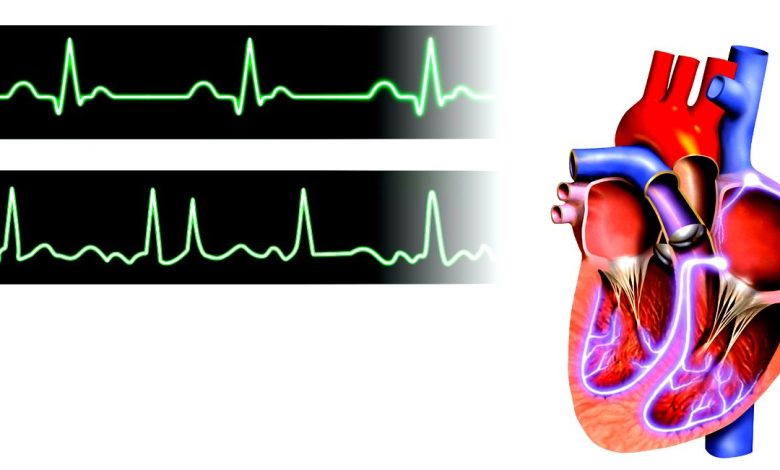
Atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter is a common type of abnormal heartbeat. Heart rate is fast and often irregular. The electrical system of the heart usually produces regular, predictable signals, which cause the heart muscles to contract.
The heart consists of two upper Chambers, which are called Atria, and the two lower chambers, which are called ventricles. Every signal on reduction begins in Atria and transmitted to the rest of the heart. When atrial fibrillation electrical signals from the atria are transmitted quickly and irregularly. Some signals do not reach the ventricles and the ventricles are reduced, usually, irregular, sometimes faster. This inconsistency may decrease the effectiveness of the rhythm of the heart when pumping blood. The blood remains in the Chambers of the heart, and when this can form blood clots. Sometimes blood clots break away, and moving to the brain can cause a stroke.
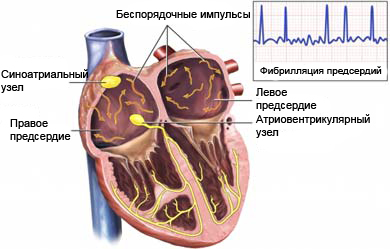
Causes of atrial fibrillation
In most cases, atrial fibrillation occurs because of an existing heart disease. But atrial fibrillation can occur in people without any heart problems. Thyroid disorders or other disorders can also lead to abnormal rhythms. In some cases, the cause of atrial fibrillation is unknown.
Risk factors for atrial fibrillation
Risk factors include:
- Cardiovascular diseases:
- High blood pressure;
- Coronary artery disease;
- Congestive heart failure;
- Heart attack;
- Diseases of the heart valves;
- Endokardit (inflammation of the heart valves);
- Cardiomyopathy (disease of the heart muscle);
- Congenital heart disease;
- Atrial fibrillation in the past;
- Lung disease:
- Эmfizema;
- Asthma;
- Blood clots in the lungs;
- Age: 55 and older;
- Smoking;
- Chronic diseases:
- Overactive thyroid;
- Diabetes;
- Excessive alcohol consumption;
- The use of habit-forming drugs, including caffeine;
- Paul: male;
- The operation under general anesthesia;
- Stress, emotional or physical;
- Family history of atrial fibrillation.
Symptoms of atrial fibrillation
Symptoms can range from mild to severe, Depending on the function of the heart and general health. Some people may not notice any symptoms.
Symptoms of atrial fibrillation include:
- Irregular or rapid pulse or rapid heartbeat;
- Heartbeat, or feeling of booming beats in the chest;
- Dizziness or loss of consciousness;
- Sweating;
- Pain or pressure in the chest;
- Breathlessness;
- Fatigue or weakness;
- Deterioration of the general condition during physical exercise.
Diagnosis of atrial fibrillation
Doctor:
- Asked about symptoms and medical history;
- Performs medical examination;
- Listening to the heart with a stethoscope.
Tests for determining atrial fibrillation may include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) – test, that records heart activity by measuring electrical current, passing through the heart muscle;
- 24-hour Holter monitoring – wearing a portable heart monitor, which records heart rhythms within 24-hours;
- Echocardiogram – test, which uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound), to examine the size, shape and motion of the heart;
- Coronary angiography – execution of x-ray images of the heart after the introduction of paints in coronary artery;
- Chest X-ray, to look for the root causes;
- Blood tests, to look for the root causes.
Treatment of atrial fibrillation
The goal of treatment is:
- Restore regular rhythm, if possible;
- Maintain heart rate close to normal;
- Generally, in the absence of loads of heart rate should be within 60-80 bpm, and 90-115 beats per minute during moderate physical exertion.
- Preventing blood clots.
If the primary cause of atrial fibrillation found, may consider its treatment. Some patients in the rhythm returned to normal without treatment.
Treatment of atrial fibrillation includes:
Taking medication for atrial fibrillation
- Medications to slow the heart rate:
- Foxglove;
- Verapamil;
- Diltiazem;
- Metoprolol;
- Atenolol;
- Medications to maintain regular heart rhythm:
- Sotalol;
- Propafenone;
- Amiodarone.
- Medicines, to prevent blood clots, such as warfarin.
Cardioversion for atrial fibrillation
Cardioversion is the process, which uses an electric current or medication, to help in normalizing heart rhythm. If the atrial fibrillation lasts 48 hours and more, the patient may be prescribed blood thinners before this procedure.
Ablation for atrial fibrillation
In some cases, the flutter, deemed responsible for mercatel'nuju arrhythmia can be surgically removed or changed remotely using different methods, including using krioabljacii or radiofrequency ablation.
Lifestyle changes in atrial fibrillation
You should avoid caffeine and other stimulants, that could provoke the emergence of atrial fibrillation. Alcohol can also act as a trigger in some people.
Prevention of atrial fibrillation
If there are risk factors for atrial fibrillation to avoid known triggers, such as alcohol and caffeine. You should follow the doctor's advice, treat heart disease, reduce high blood pressure.
Sources
- Calkins H, Tomaselli GF, Morady F. Atrial fibrillation: clinical features, mechanisms, and management. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald’s Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 66.
- Heidenreich PA, Estes NAM 3rd, Fonarow GC, et al. 2020 Update to the 2016 ACC/AHA Clinical Performance and Quality Measures for adults with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Performance Measures. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77(3):326-341. PMID: 33303319 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33303319/.
- January CT, Wann LS, Calkins H, et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society in collaboration with the Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Circulation. 2019;140(6)e285. PMID: 30686041 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30686041.
- Lip GYH, Banerjee A, Boriani G, et al. Antithrombotic therapy for atrial fibrillation: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest. 2018;154(5):1121-1201. PMID: 30144419 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30144419/.
- Meschia JF, Bushnell C, Boden-Albala B, et al. Guidelines for the primary prevention of stroke: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2014;45(12):3754-3832. PMID: 25355838 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25355838.
- Zimetbaum P. Supraventricular cardiac arrhythmias. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 58.
