Cerebellar stroke
Description cerebellar stroke
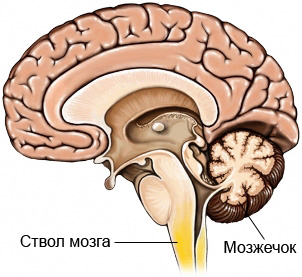
The cerebellum is located in the lower part of the brain, closer to the back. It plays an important role in the control of body movements, eye, and maintaining the balance.
Cerebellar stroke occurs, where cerebral blood flow to this area of the brain is interrupted. Without oxygen and nutrients, coming from the blood, brain tissue dies quickly. This leads to a loss of some functions of the organism. Stroke It is a life-threatening condition and requires emergency medical care.
Causes of cerebellar stroke
There are two main types of stroke:
- Ischemic;
- Hemorrhagic.
Ischemic stroke (the most common form) caused by a sharp decrease in blood flow to areas of the brain, which can cause:
- Clot, which is formed in the other body part (eg, or near the neck) and blocks blood flow in a blood vessel, supplying the brain (embolism);
- Clot, which is formed in the artery, which carries blood to the brain (thrombus);
- Angiorrhexis, supplies blood to the brain (arterial dissection).
The reason for hemorrhagic stroke is the rupture of a blood vessel, which leads to hemorrhage into the brain.
Risk Factors cerebellar stroke
Risk factors, that can be influenced:
- Certain disorders, such as:
- High blood pressure;
- High cholesterol;
- Atherosclerosis (narrowing of the arteries due to the build-up of plaque on their inner walls);
- Atrial fibrillation (heart rhythm disturbance);
- Obesity;
- Metabolic syndrome;
- Diabetes Type 2;
- Substance abuse;
- Problems with blood circulation;
- Drugs (eg, long-term use of birth control pills);
- Lifestyle factors:
- Smoking;
- Lack of physical activity;
- A diet high in sodium and processed foods.
Risk factors, that can not affect:
- Previous stroke or cardiovascular disease, such as heart attack;
- Previous transient ischemic attack (TIA) – some people experience “predinsult” or TIA. This is a temporary cessation of the blood supply to the brain (mini-stroke). These stroke symptoms completely resolve within a few minutes. They may indicate a very high risk of a full stroke in the near future;
- Age: 60 and older;
- The presence of family members, who have had a stroke;
- Paul: male;
- Blood diseases, which increases its coagulation.
Symptoms of cerebellar stroke
Symptoms of cerebellar stroke come on suddenly and can include:
- The lack of coordination of limbs or trunk (ataxia);
- Difficulty walking, including problems with balance;
- Abnormal reflexes;
- Tremor;
- Dizziness (a feeling of rotation or whirling, when you are not moving);
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Intense headache;
- Speech problems (eg, gibberish) and difficulty swallowing;
- Problems with pain and temperature sensation;
- Hearing problems;
- Vision problems (eg, the eyes move rapidly, and is difficult to control their movement);
- Eye problems (eg, chuzhenie zrachkom, fallen eyelid);
- Loss of consciousness.
If you notice any of the symptoms, immediately seek medical advice, because brain tissue dies quickly.
Diagnosis cerebellar stroke
Because cerebellar stroke is an emergency, doctor makes a diagnosis as quickly as possible. Tests may include:
- CT scan – X-ray views, which uses computer, to make pictures of the brain;
- CT angiography – Type CT, wherein studied the condition of blood vessels in the brain and / or neck;
- MRT – test, which uses magnetic waves, to make pictures of the brain;
- MRA – type MRT, wherein studied the condition of blood vessels in the brain and / or neck;
- Heart function tests (eg, ECG);
- Doppler ultrasound – test, which uses sound waves to study the blood vessels;
- Blood tests;
- Kidney function tests;
- Tests to verify the ability of swallowing.
Treatment of cerebellar stroke
Emergency treatment is necessary, that:
- Rastvoritь clot, that causes an ischemic stroke;
- Stop the bleeding during a hemorrhagic stroke.
Medications for the treatment of cerebellar stroke
For the treatment of ischemic stroke, It may be needed the following medications:
- Solvents clots and medication to prevent their formation;
- Blood thinners;
- Drugs to control blood pressure;
- Preparations, allows to treat irregular heart rhythm.
For the treatment of hemorrhagic stroke, your doctor may prescribe these medications:
- Drugs for blood clots;
- Medications to reduce the impact of stroke on the brain;
- Drugs to control blood pressure.
The operation for the treatment of cerebellar stroke
For the treatment of ischemic stroke, your doctor may do the surgery, that:
- Redirect blood flow around a blocked artery;
- Remove the clot or deliver clot medication for dissolving;
- Remove fatty deposits from the carotid artery (carotid endarterectomy);
- To expand and maintain an open carotid artery. (Angioplasty and stenting).
For the treatment of hemorrhagic stroke, your doctor may:
- Remove part of the skull, to relieve pressure on the brain (cephalotrypesis);
- Put a clip or a small plug in the aneurysm, to stop the bleeding.
Rehabilitation after cerebellar stroke
Therapy program focused on restoring as much of the lost abilities:
- Physiotherapy – to recover maximum mobility;
- Occupational therapy – to assist in everyday tasks and self-service;
- Rechevaya therapy – to improve swallowing and speech;
- Psychological Therapy – to provide support in adapting to life after stroke.
Prevention cerebellar stroke
To reduce the likelihood of cerebellar stroke, Follow these steps::
- Exercise regularly;
- Eat more fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Limit your intake of salt and fat;
- Maintain a healthy weight;
- Drink alcohol only in moderation (50-100 grams per day);
- Quit smoking;
- Control chronic diseases – high cholesterol and diabetes;
- Ask your doctor about the possibility of the use of statins. These medications can help prevent certain kinds of strokes;
Seek medical advice, If you experience symptoms of a stroke, even if they subsequently disappeared.
