Aterэktomiя or angioplasty nekoronarnыh utensils – Conservative revascularization non-coronary vessels
Description atherectomy, non-coronary vascular angioplasty
Aterэktomiя and angioplasty – methods, which can be used to open narrowed arteries without surgery.
There are some Devices, that can be delivered through the blood vessels to the site of narrowing or occlusion. When the device is removed the obstacle, the blood flow is restored.
Reasons for atherectomy, non-coronary vascular angioplasty
Most often, these procedures are carried out, when an artery is narrowed by atherosclerosis. If the artery is too narrow, blood is not able to pass through it. Parts of the body experiencing ischemia (lack of oxygen). This can cause a variety of symptoms, depending on the parts of the body, who do not get enough oxygen.
Possible complications during atherectomy, non-coronary vascular angioplasty
Before, how to perform the operation, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- The artery may close again after the procedure;
- Damage to the artery;
- Bleeding;
- Infection.
Factors, that may increase the risk of complications:
- Smoking;
- The poor state of health or disease;
- The presence of arterial disease;
- Problems of blood coagulation.
Be sure to inform your doctor about allergy to shellfish, iodine, or a radiopaque substance.
How is atherectomy, Angioplasty nekoronarnыh utensils?
Before surgery
The patient is carefully examined to decide on the method of treatment. The survey may include x-rays, Ultrasound or computerized test (Mahnytorezonansnuyu or computed angiography) to identify problem areas. The patient will be asked not to eat or drink anything for several hours before the procedure.
- It may be necessary to stop taking some medicines:
- Aspirin or other anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Blood thinners, eg, clopidogrel (Plaviks) or warfarin.
Anesthesia
Patients prescribed sedatives, without the use of sleeping pills (operable not put to sleep). The local anesthetic used for pain relief in place of catheter insertion.
Procedure atherectomy, non-coronary vascular angioplasty
The patient is lying down. The X-ray machine is operating, as well as the necessary surgical equipment. Depending on the affected artery to be opened blood vessel in the groin or arm. The doctor pierces the skin, introducing the catheter into a blood vessel, and brings it to the site of obstruction. Through a catheter can be introduced contrast material, to see obstacles in the X-ray monitor. The vessel may be more than one piece, require that opening. Type of procedure, used to expand the vessel will depend on the type and location of obstruction. Possible options for the operation:
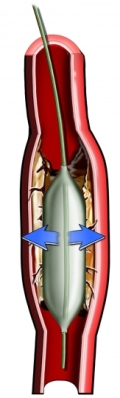
- Angioplasty – inflated balloon, which opens the vessel;
- Angioplasty and stenting – after use of the ball in the vessel is a stent to support its walls;
- Atherectomy – plaque is removed using a rotary razor or using a laser.
Immediately after treatment
Recovery time minimum. The patient was transferred to the House before the end of anesthesia and sedatives.
How long does the procedure?
From 30 minutes to two hours
Will it hurt?
The procedure may be accompanied by some minor inconveniences.
The average time of hospital stay
This procedure is performed in a hospital. Maybe, the patient will have to stay for the night under observation. The doctor can extend your stay, If there are complications.
Care after the procedure
- You will need to lie down for a while, if the catheter is inserted through the groin;
- Maybe, you need to put a bandage on the catheter insertion site to stop the bleeding;
- When edema, bleeding, black and blue dots, pain at the site of catheter insertion, I must say the nurse;
- It is necessary to drink plenty of fluids, to bring the contrast agent from the organism;
- They may be prescribed blood thinners, such as aspirin. Activities, related stress will be limited. It is necessary to carry out exercises and consume plenty of fluids;
- Your doctor may prescribe a survey in a few days or weeks after surgery.
It is necessary to go to the hospital in the following cases
- Redness, edema, increased pain, bleeding, or discharge at the site of catheter insertion;
- Signs of infection, including fever and / or chills;
- Strong sweating, nausea or vomiting;
- The leg or arm feels cold, the color is white or blue, or there is leaking or tingling;
- Severe pain, including chest pain;
- Shortness of breath.
