Cardiomyopathy
Description cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy refers to heart muscle disease, in which the damaged heart pumps blood inefficiently. The disease usually progresses to the point, when patients ill with life-threatening heart failure. Besides, people with cardiomyopathy is a high probability of occurrence or irregular heartbeat Arrhythmia.
There are two main types of cardiomyopathy: ishemicheskaya and neishemicheskaya cardiomyopathy.
Ishemicheskaya cardiomyopathy found, when the heart muscle is damaged from heart attack of coronary artery disease.
Neishemicheskaya cardiomyopathy It includes types of cardiomyopathy, are not associated with coronary artery disease.
There are three main types of non-ischemic cardiomyopathy:
- Dilatatsionnaya cardiomyopathy – damage to the heart muscle leads to a decrease in operating in conjunction with an increase in cardiomyocyte cells and increased elasticity of the heart;
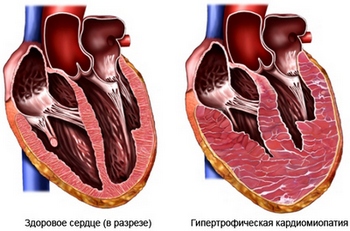
- Gipertroficheskaya cardiomyopathy – abnormal growth of the heart muscle fibers. The heart wall thickens, reducing the space in the chambers of the heart. Since the heart between beats almost relaxes, pumped by a very small amount of blood;
- Restriktivnaya cardiomyopathy – some areas of the heart wall become rigid and lose their elasticity. Hardness often occurs due to abnormal tissue, invading the heart muscle.
Causes of cardiomyopathy
In many cases, the exact cause is not known. Possible causes:
Dilatatsionnaya cardiomyopathy
The reasons for the initial damage is often not found, but may include:
- Ischemic heart disease with reduced blood flow to the heart;
- Infection, usually, Viral;
- Chronic exposure to toxins, including alcohol and certain chemotherapy drugs;
- A rare complication of pregnancy and childbirth (perhaps, immune related);
- Rarely – other diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes or thyroid disease.
Gipertroficheskaya cardiomyopathy
The reasons may be:
- Heredity (sometimes present at birth, but it often develops in adolescents);
- Aging, associated with hypertension.
Restriktivnaya cardiomyopathy
The reason is usually associated with the presence of other diseases, such as:
- Amiloidoz – protein accumulation in cardiac muscle fibers;
- Sarkoidoz – the emergence of a small inflammatory masses (granulomas) in many organs;
- Gemoxromatoz – accumulation of large amounts of iron in the body.
Risk factors for cardiomyopathy
Factors, which increase the risk of cardiomyopathy:
- The presence of family members with cardiomyopathy;
- Alcoholism;
- Obesity;
- diabetes;
- Hypertension;
- Coronary artery disease;
- Taking certain medications.
Symptoms of cardiomyopathy
Symptoms vary, depending on the type of cardiomyopathy and its severity.
Patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy often do not notice any symptoms. Sudden cardiac death may be the first sign of disease.
With the development of dilated cardiomyopathy symptoms may last for years. Because of the abnormal accumulation of blood in the heart can be formed thrombi. If the clot travels to another part of the body (embolism), symptoms, associated with that body (eg, brain) may be the first sign of heart disease.
Cardiomyopathy ultimately leads to heart failure and the following symptoms:
- Fatigue;
- Weakness;
- Breathlessness, often deteriorated while in a lying position or excessive physical activity;
- Cough;
- Swelling of the legs or feet;
- Chest pain;
- Cardiac arrhythmias.
Diagnosis of cardiomyopathy
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. Examine physically. The doctor listens to the heart with a stethoscope. Cardiomyopathies often produce noise and other unusual sounds in the heart.
Tests may include:
- Chest X-ray – test, which uses X-rays, to photograph the structures inside the thorax. Used to find expansion of the heart.
- ECG – test, which detects heart activity by measurement of electrical current through the heart muscle;
- Echocardiogram – test, which uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound), to examine the size, shape and motion of the heart;
- Blood tests, to ensure damage to the heart and other organs, and, perhaps, reason (s) kardiomiopatii
- Heart catheterization – special tool inserted into the heart through a vein or artery (usually in the arm or leg), to detect problems with the heart and its blood supply;
- Biopsy Serdtse – removal of a sample of heart tissue for testing.
Treatment of Cardiomyopathy
In heart failure due to blockages in the coronary arteries, treatment, aimed at their removal by angioplastiki, stenting or coronary artery bypass grafting can lead to an improvement in cardiac function and reduce the symptoms of the disease. If cardiomyopathy is caused by genetic causes, to improve heart function can lead other treatments. For many patients, However, treatment is aimed at relieving symptoms and preventing further damage.
Lifestyle changes
The changes are aimed at removing all, that contributes to disease or deterioration of symptoms:
- Avoid alcohol;
- If you are overweight, Try to lose weight;
- Go to high fat diet, to minimize the risk of coronary heart disease;
- Need to limit salt intake to reduce fluid retention;
- Follow the advice of your doctor. Maybe, you have to restrict physical activity.
Medication
Medications may include:
- Diuretics, to remove excess fluid;
- ACE inhibitors, to help relax the blood vessels, lower blood pressure and reduce the load on the heart;
- Hydralazine and Isosorbide dinitrate, that can be used in addition to the IAPF;
- Angiotensin receptor blockers – action similar to ACE inhibitors;
- Preparations Foxglove, to slow and regulate the heart rate, and slightly increase the force reductions;
- Beta Blockers, to slow the disease progression;
- Spironolactone – improves the condition of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy and initial symptoms.
Operation with cardiomyopathy
Surgical options include:
- Kardiostimuljator – can be implanted, to stabilize the heart rate;
- For people with hypertrophic disease form – the doctor may remove part of the thickened wall, separating the Chambers of the heart. Surgery may be needed to heart valve replacement. Another option is called alcoholic septal′naâ ablation. This procedure helps to reduce symptoms and improve the functioning of the heart;
- For those patients who have irregular heart rhythm threatens life, perhaps, need to implant cardioverter defibrillator-;
- Heart transplant may be a possible option for healthy patients, If other methods have proven ineffective. Candidates often have to wait long for a new donor heart. The waiting period may be temporarily installed andskusstvennyj ventricle – mechanical pump, that assumes some or most of the pumping heart function.
Prevention of cardiomyopathy
Aggressive treatment of hypertension, Ischemic disease of the arteries and their risk factors is the best way to prevent most cases of cardiomyopathy.
Other, less common causes, cure is often impossible. People with a family history of the disease should consult a doctor to undergo screening tests, especially before the beginning of the intensive physical loads.
