Amiloidoz
Description amyloidosis
Amyloidosis is a group of rare diseases. It involves deposition of amyloid protein. This protein accumulates in the tissues and organs. There are three basic forms:
- Primary amiloidoz, deposits are located in the heart, light, skin, language, thyroid, intestine, liver, kidney and blood vessels;
- Secondary amyloidosis – protein is in the spleen, liver, kidney, adrenal glands, and lymph nodes;
- Hereditary amyloidosis deposits – in nerves, heart, kidney and blood vessels.
The accumulation of amyloid may hinder the functioning of organs or tissues.
Prichinы amyloidosis
Causes of amyloidosis vary in its different forms.
- Primary amyloidosis – caused by the accumulation of antibody fragments, often it occurs as a result of diseases of the bone marrow (mnozhestvennaya myeloma);
- Secondary amyloidosis – develops in response to chronic infection or inflammatory disease;
- Hereditary amyloidosis, caused by mutations of amyloid in the blood.
Faktorы risk amyloidosis
Factors, which may increase the likelihood of amyloidosis include:
- Primary amyloidosis:
- Paul – Men are at greater risk;
- Age – senior 40 years;
- Mnozhestvennaya myeloma;
- Secondary amyloidosis:
- Paul – Men are at greater risk;
- Age – senior 40 years;
- Chronic inflammatory and infectious diseases, such as: tuberculosis, rheumatoid arthritis, osteomyelitis;
- Mediterranean fever;
- Hemodialysis – selection of blood from the arteries, purification, adding nutrients, and returning it into the vein;
- Anamnesis;
- Hereditary amyloidosis:
- Nationality: Portuguese, Swedes, Japanese;
- The presence of the family Mediterranean fever patients.
Simptomы amyloidosis
When these symptoms should see a doctor:
Symptoms for all forms of amyloidosis:
- Fatigue;
- Weight loss;
- Enlarged liver;
- Irritability;
- Signs of heart failure.
The extent of the disease and the type of the affected organ will also help identify additional symptoms, if any. Their level can vary from mild to severe. Below is a list of additional symptoms, which relate to specific systems of the body:
- Urinary tract – renal failure;
- Skin – light wrinkles, purple color (reddish skin around the eyes, caused by leakage of blood from the capillaries);
- Lymphatic System – hyperadenosis;
- Endocrine system – enlargement of the thyroid gland;
- Digestive system:
- Difficulty swallowing;
- Swollen tongue;
- Enlarged liver;
- Diarrhea;
- Ileus:
- Malabsorption (inadequate absorption of nutrients from the intestinal tract);
- Light brown chair;
- Neurological System:
- Imbecility – may develop Alzheimer's disease;
- Insensitivity, pricking, weakness in the arms and legs;
- Swelling in the wrist;
- Weakness in hands;
- Cardiovascular system:
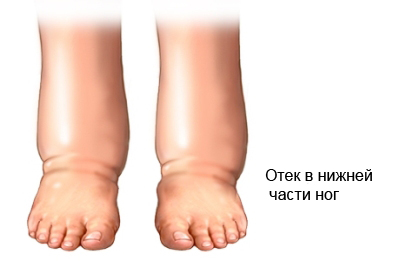
- Accumulation of fluid, causing swelling in the tissues;
- Abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia);
- Enlarged heart;
- Cardiac arrest;
- Sudden death;
- Respiratory system;
- Labored breathing;
- Breathlessness.
Diagnosis amyloidosis
This disease can cause difficulty in diagnosis. In the absence of initial symptoms, disease can lead to death. The doctor does a physical exam and sends the patient to specialists for further analysis. Tests may include the following:
- Biopsy – selecting a small sample of tissue or organ, needle or cut-off;
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) – measurement of the electrical activity of the heart to diagnose heart disease;
- Echocardiogram – detailed examination of the movements of the heart monitor, using high-frequency sound waves;
- Assessment of renal function – determines, whether there is excess protein in the urine;
- Analysis of urine – chemical and microscopic examination of urine for the presence of disease;
- Research serum creatinine – test for the study of kidney function and muscle mass;
- Analysis of levels of blood urea nitrogen (AMK) – blood tests to assess kidney function;
- Abdominal ultrasound – test, which uses sound waves to study abnormalities of internal organs and blood vessels;
- Nerve conduction velocity – evaluates the condition of the nerves.
Treatment amyloidosis
At the moment, there are no treatments for amyloidosis. The main goal is to treat the underlying disease. Treatment to decrease or control symptoms and complications bring only modest success. Treatment includes:
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy may be in the form of tablets, injection, or through a catheter. It is used, to help improve symptoms and slow the progression of the disease in:
- Primary amyloidosis;
- Secondary amyloidosis – aggressive treatment of the underlying inflammatory disease process or;
- Hereditary amyloidosis.
Stem cell transplantation
Stem cells are immature cells in the body. They are transplanted to replace damaged or diseased cells. This process is used for:
- Primary amyloidosis – They used their own immature blood cells for transfusion. This process is called autologous stem cell transplant. In this method of treatment can additionally be used as medicaments, and chemotherapies;
- Hereditary amyloidosis – cells transplanted from a donor organ.
Organ transplantation
Transplant – removal of the patient's body and transplanting healthy from donor to recipient. Usually performed a liver transplant, or kidneys. It may be performed for all major forms of amyloidosis.
Splenectomy
Operation can reduce the production of amyloid. It may be done for primary and secondary amyloidosis.
Prevention amyloidosis
Currently known methods of prevention of amyloidosis.
