Heart catheterization – Angiokardiografija – Coronary arteriography – Coronary angiogram
Description catheterization
Heart catheterization – research, wherein the catheter is used (tube) and x-ray machine to assess the condition of the heart and its blood supply.
The reasons for catheterization hearts
The procedure is used, to find the cause of symptoms, such as chest pain, which may indicate problems with heart.
Cardiac catheterization helps doctors:
- Determine the narrowing or blockage of the arteries of the heart;
- To measure blood pressure in the heart;
- Estimate, how well the heart valves and chambers;
- Check heart defects;
- Assess the degree of increase in the size of the heart;
- Make a decision about the choice of method of treatment.
Possible complications of cardiac catheterization
If you plan to undergo cardiac catheterization, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Bleeding at the catheter insertion site;
- Damage to the arteries;
- Heart attack or arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat);
- Allergic reaction to x-ray dye;
- The formation of a blood clot (thrombus);
- Infection.
Some factors, that may increase the risk of complications include:
- Allergies to medications or x-ray dye;
- Obesity;
- Smoking;
- Coagulation failure;
- Age: 60 and older;
- Pneumonia;
- Recent heart attack;
- Diabetes;
- Kidney disease.
How is heart catheterization?
Preparation for the procedure
Before the procedure, you must:
- Make blood and urine tests;
- Go electrocardiogram (ECG) – test, that records heart activity by measuring the strength of an electric current, passing through the heart muscle;
- Perform a chest radiograph;
- Take the test stress.
It may be necessary to stop taking certain medicines a week before surgery:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (eg, aspirin);
- Blood thinners, such as clopidogrel (Plaviks) or warfarin;
- Metformin (Glyukofazh) or glibenclamide and metformin (Hlyukovans).
Before the procedure:
- You can not eat or drink anything after midnight on the day of the procedure.
Anesthesia
The catheter insertion site will be used local anesthesia. An hour before the procedure, or when it may be intravenously administered sedative. This will help the body to relax.
Description catheterization
Immediately before the needed procedure intravenously administered fluids and medications. Electrocardiogram will monitor the activity of the heart.
The patient is awake, but sedatives remove stress. The doctor checks the basic functions, such as cough, exhalation and retention of breath. If you feel pain in the chest, dizziness, nausea, tingling, or other discomfort, you must report it.
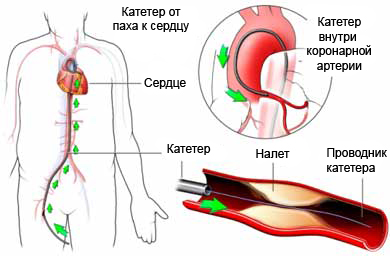
A catheter is inserted into an artery in the groin or arm (usually in the crook of the elbow, or less, in the wrist). Area introduction shave, sterilized, then injected anesthesia. The needle is inserted into a blood vessel. Special wire (guide catheter) inserted through the needle into the blood vessel until, until it reaches the heart. Soft, a flexible catheter tube is put over the wire, and also brought to the hearts.
The doctor controls the location of the wire and catheter pictures X-ray machine. For this purpose, a special blood injected radiopaque dye, and arteries and the heart can be seen on radiographs.
Once in place, catheter used, to take measurements. It can be measured by the pressure in the various chambers of the heart. They may also be taken blood samples. At this time it can be made aortogramma. This procedure gives the image of the aorta (large artery, leaving the heart). Once all the tests are done and the pictures, the catheter is removed.
Sometimes, Doctor makes balloon angioplasty and stenting, if the site is in the arteries narrow or clogged okazhetsja. These procedures help to open narrowed arteries.
At the end, in the groin or arm bandage applied.
Duration of treatment
The procedure takes 1-2 o'clock. Preparation prior to introduction of the catheter takes 1-2 o'clock.
Will it hurt?
Although the procedure, usually, not painful, it may cause some discomfort, including:
- Burning sensation (at the site of catheter insertion);
- Pressure, when the catheter is inserted or replaced with other catheters;
- Nausea, When the dye is injected;
- Feeling headache;
- Cardiopalmus.
If necessary, enter the appropriate medication.
The time spent in hospital
Usually ranges 0-1 day.
Postoperative care
In the hospital
- They can be made an electrocardiogram and blood tests;
- If the catheter has been inserted in the groin, must lie in bed on the back of some period of time. If the catheter was inserted in the arm, you can get out of bed earlier;
- The insertion site is bandaging boats, avoid bleeding.
Home Care
Houses need to do the following, to ensure the normal recovery:
- Do not get behind the wheel, until after the effects of drugs;
- We need to limit physical activity for 5-7 days;
- Timely change bandage around the catheter site;
- Consult with your doctor about, what medicines to take home;
- Ice can help reduce the discomfort at the site of catheter insertion. May be used for ice 15-20 minutes every hour, during the first few days. You can not apply ice directly to the skin. First you need to wrap it in a towel and put on the skin;
- To reduce the risk of further complications of the heart, it is desirable to make changes in lifestyle. We need to stick to a healthier diet, give up smoking, seeking treatment for stress;
- You must check with your doctor, when it is safe to shower, bath, or to expose the surgical site to water.
It is necessary to go to the hospital in the following cases
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Excessive sweating, nausea or vomiting;
- Changes in sensation in the leg or arm, in which a catheter is inserted, including numbness, rhigosis, or discoloration;
- Redness, edema, pain, excessive bleeding at the site, where the catheter insertion;
- Cough, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing;
- Severe pain;
- Chest pain;
- Sagging facial muscles;
- Changes in vision or speech;
- Difficulty walking or moving limbs.
