Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (brain hypoxia, GIE): what is this, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
Description of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (GIE) – state, in which the brain does not get enough oxygen.
HIE can be fatal. Brain cells begin to die just five minutes after their oxygen supply is cut off.. The disease can also cause long-term complications., including mental development problems, seizures and cerebral palsy.
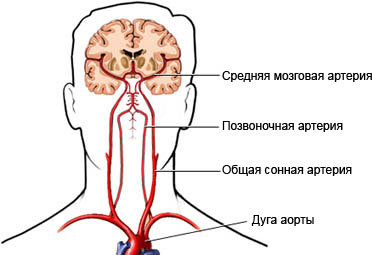
Causes of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
There are many causes of HIE. Any injury and many different diseases can lead to insufficient oxygen supply to the brain.. Some Common Causes of Hypoxia:
- Respiratory failure;
- Blockage or rupture of blood vessels;
- Exposure to carbon monoxide or cyanide poisoning;
- Drug Overdose;
- Drowning;
- Lack of oxygen due to smoke inhalation;
- Extremely low blood pressure;
- suffocation;
- Cardiac arrest;
- Carbon monoxide poisoning;
- Being at high altitudes;
- Suffocation;
- Compression or damage to the trachea;
- Complications general anesthesia;
- Disease, causing paralysis of the respiratory organs and muscles, such as myasthenia gravis and Guillain Barre syndrome.
Risk factors for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
Any injury, complications or diseases, which reduce blood flow and oxygen supply to the brain are a risk factor for HIE.
Symptoms of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
Symptoms include:
- Mild cases of hypoxia:
- Difficulty concentrating;
- Vision problems;
- Poor coordination;
- intense emotions;
- Severe drowsiness.
- Severe cases of hypoxia:
- Convulsions;
- Loss of consciousness;
- Blue skin or lips;
- Labored breathing.
Diagnosis of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
The doctor will perform a medical examination. Usually, medical history is the most important factor in making a diagnosis.
Tests may include the following:
- Blood tests;
- Pictures of internal organs and structures of the body. For these purposes, it can be used:
- CT scan;
- MRT;
- Echocardiogram;
- US;
- The activity of the heart and brain is checked. For this purpose,:
- Electrocardiogram;
- Electroencephalogram;
- evoked potential method.
Treatment of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
Treatment depends on the cause of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy., as well as the severity of brain damage. Treatment includes:
- If brain function has stopped, but the damage is not yet extensive, life-sustaining treatments are applied;
- Mechanical ventilation – can be used, if the victim is unable to breathe without assistance;
- Treatment of the cardiovascular system – appropriate medications are provided to maintain heart function and blood pressure;
- To control seizures, anticonvulsants may be prescribed or general anesthesia;
- Cooling – hypoxic brain injury is often caused by high fever. Cooling agents can be used to lower body temperature.;
- Hyperbaric oxygen treatment – method of treatment used in cases of carbon monoxide poisoning.
Prevention of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
In most cases, HIE appears suddenly and cannot be prevented. To prevent significant or long-term damage to the brain after oxygen supply to the brain is cut off, to the victim as soon as possible SLR.
