Carbon monoxide poisoning
Description of carbon monoxide poisoning
Carbon monoxide poisoning can be fatal. Poisoning occurs from inhaling carbon monoxide gas. Carbon monoxide is formed, when the gas is burned, wood, charcoal or other fuel. He often builds, when the combustion device, heating and cooking indoors or faulty combustion is no air circulation. The car engine can also produce carbon monoxide. Carbon monoxide is colorless,, no taste and odor. People can inhale it without knowing it.
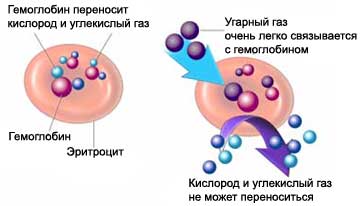
Carbon monoxide is readily absorbed into the bloodstream through the lungs. Hemoglobin carries oxygen, dissolved in blood to various organs. Carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin easily and displaces oxygen, after which the body comes a lack of oxygen. Especially dangerous is carbon monoxide poisoning to brain tissue.
Causes of carbon monoxide poisoning
Carbon monoxide poisoning is the inhalation of carbon monoxide.
People can be exposed to carbon dioxide by the combustion of fuel, equipment malfunction or no ventilation. For Example:
- If the chimney is leaky, Carbon monoxide can get into the living quarters in the house;
- Using a barbecue grill indoors can lead to the accumulation of carbon monoxide;
- Starting a vehicle with a closed garage door leads to the accumulation of carbon monoxide.
Risk factors for carbon monoxide poisoning
Factors, that increase the likelihood of carbon monoxide poisoning:
- Exposure to carbon monoxide in a poorly ventilated area, or as a result of equipment failure;
- Age:
- Fruit (cigarette smoking is the main source of pregnant exposure);
- Babies;
- Elderly people;
- Smoking (tobacco smoking in unventilated areas may increase the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning);
- Paul: mortality from poisoning is higher in men;
- Diseases of the circulatory system, heart or lungs.
Symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning
Symptoms, associated with carbon monoxide poisoning, usually, rather vague. They can be divided into acute (Immediate) and chronic symptoms.
Acute symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning
- Breathlessness;
- Scarping breathing;
- Cough;
- Hoarse voice.
Chronic symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning
- Cardiopalmus;
- Chest pain;
- Nausea or vomiting;
- Headache;
- Numbness and tingling;
- Visual impairment;
- Loss of appetite;
- Disturbed sleep;
- Dizziness;
- Fatigue;
- Memory loss;
- Decreased sex drive.
Diagnosis of poisoning by carbon monoxide
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical examination. They may be asked the following questions:
- How often symptoms?
- Who else in the family is experiencing the same symptoms?
- What equipment do you use fuel-burning?
Tests may include:
- Blood tests – for measuring the oxygen level and electrolytes;
- Test karboksigemoglobin – for determining the severity of the impact of carbon monoxide and monitoring treatment;
- Chest X-ray – test, which uses X-rays, to take a picture of structures inside the body, used, to determine whether pneumonia;
- Electrocardiogram – test, which records heart activity by measuring the electrical current in the heart muscle.
Treatment of carbon monoxide poisoning
Immediately move away from the source of the carbon monoxide and breathe fresh air (preferably on the street). This will get rid of minor poisoning.
Seek medical attention in the nearest emergency room. Tell your doctor, if you think, what, perhaps, have been exposed to carbon monoxide. Your doctor may give you oxygen to breathe, until the symptoms disappear or decrease the level of carbon dioxide in the blood.
Other methods of treatment of carbon monoxide poisoning may include:
- Ventilation – patients in a coma or with serious heart disorders, Nervous System, perhaps, required mechanical ventilation, to help them breathe;
- Giperbaricheskaya kislorodnaya therapy – the patient is placed in a special cell, in which pressurized oxygen is supplied.
Preventing carbon monoxide poisoning
Avoidance of exposure to carbon monoxide is the primary method of preventing carbon monoxide poisoning. Since the gas has no odor or color, you will not know, if it is present in the air. To reduce the risk of exposure to reduce carbon monoxide:
- It is necessary each year to check the chimney fire. The accumulated debris it can block ventilation openings, resulting in the accumulation of carbon monoxide;
- Before the start of the heating season, you need to inspect and verify, that the combustion devices are working properly;
- Check, that all the products of the combustion gas are displayed on street;
- Do not use a gas range or oven to heat your home;
- Do not use a barbecue grill, camp stove or a kerosene stove in the house or tent camp;
- Do not use generators or other liquid fuel engines indoors;
- Do not rely exclusively on a carbon monoxide detector. Use it in addition to preventive measures. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for installation and maintenance;
- Each year the need to check the exhaust system of a vehicle;
- Do not run the car in the garage, especially when it closed doors. After starting the car should immediately go to the street;
- Do not leave the door from the garage into the house, when the car engine is running.
