Pneumonia – Pneumonia – Bronchopneumonia
Description pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs. It affects the lower respiratory tract – bronchi and air sacs (teethridge) lung.
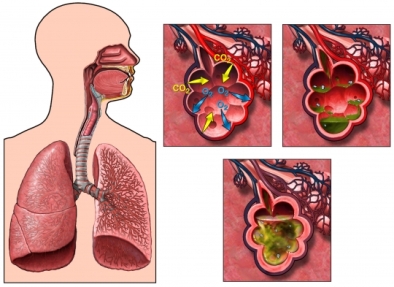
Causes of Pneumonia
There are three main reasons pneumonia:
- Bacterial pneumonia, caused by bacteria, often streptococci;
- Virus pneumonia, caused by a virus;
- Atypical bacterial pneumonia, often no visible signs, but can cause more serious and potentially fatal pneumonia.
Other causes of pneumonia include:
- Fungal infections, infections such as, which are often found in people, AIDS patients;
Pneumonia is sometimes classified in the place, where infection occurred:
- Community-acquired pneumonia – occurs when in society (eg, at school, at work, in the gym);
- Nosocomial pneumonia – It occurs during hospitalization;
- Aspiration pneumonia occurs, When foreign substances (often stomach contents) into the lungs.
Risk factors
Factors, which increase the risk of pneumonia:
- Age: 65 and older;
- Flu or other respiratory illness;
- Chronic diseases, such as heart disease or lung;
- Stroke (aspiration pneumonia due to problems with swallowing);
- Weakened immune system due to AIDS or chemotherapy;
- Chronic bronchitis;
- Malnutrition;
- Pregnancy;
- Infancy and Childhood;
- Substance abuse;
- Smoking;
- Chronic exposure to certain chemicals (eg, work in construction or agriculture).
Symptoms of pneumonia
| Bacterial pneumonia | Virus pneumonia | Atypical bacterial pneumonia |
| Fever | Fever | Fever, often insignificant |
| Chills | Chills | Chills |
| Coughing green, yellow or red slime | Dry cough | Cough, growing from time to time; Provided white mucus |
| Chest Pain | Headache | Nausea or vomiting |
| Profuse sweating | Muscle weakness | Pain |
| Bluish lips and nails due to the decrease of oxygen in the blood | Bluish lips and nails due to the decrease of oxygen in the blood | |
| Confusion | Weakness |
Diagnosis of pneumonia
The doctor asks about the symptoms and medical history. Produced physical examination. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and listening to the chest. Additional tests may include:
- Chest X-ray – test, which uses X-rays, to take pictures of structures inside the body, in this case the chest;
- CT scan – type of X-ray examination, wherein the computer is used, to make pictures of structures inside the chest;
- Blood tests;
- Bronchoscopy – Direct examination of the upper respiratory tract;
- Testing sputum and mucus from the lungs;
- Pulse oximetry – It measures the amount of oxygen in the blood;
- Arterial blood gas analysis – measurement of oxygen, carbon dioxide and blood acidity.
Treatment of pneumonia
Treatment of pneumonia depends on the:
- Type of pneumonia;
- The severity of symptoms;
- Other factors.
Common treatment approaches include:
- For bacterial pneumonia – antibiotics;
- For viral pneumonia – It may be prescribed antiviral drugs for small children and people with weakened immune systems;
- Note: Antibiotics are ineffective for treating viral pneumonia;
- SARS – antibiotics.
It is important to take prescribed medication. Stopping treatment early can lead to relapse ilisozdat strain with resistance to drugs.
Treatment also includes:
- Recreation and drinking large amounts of fluids;
- Healthy eating (consuming large amounts of fruit and vegetables) – if the diet is not enough vitamin C., you need to ask your doctor about taking additional drugs (to 1000 mg). This can be helpful for some people, Patients with pneumonia;
- You can take medication, without a prescription written out to reduce the temperature, pain and cough;
- Hospitalization (in severe cases).
Prevention of pneumonia
Some vaccines may prevent pneumonia:
- The flu shot for people at high risk of its occurrence, especially in the elderly (Pneumonia may be a complication of the flu);
- Pneumococcal vaccine – Common recommendations include:
- Introduction of pneumococcal vaccine for children;
- PCI for adults aged 65 and older and for young people, who are at high risk of infection.
Other preventative measures include:
- We need to quit smoking. Smoke weakens the resistance to lung infections;
- We need to avoid close contact with people, who are sick with cold or flu;
- It is necessary to wash hands frequently. It is very important, If you had contact with infected people;
- You need to eat healthy foods. If the diet is not enough vitamin C or zinc, you need to take supplements to make up for these substances;
- It should be a lot of rest;
- Regular exercise is to be performed.
