Tracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation
Description intubation and mechanical ventilation
Intubation and mechanical ventilation are carried out using tubes and apparatus, which supplies and sucks air from the lungs. Often, the procedure is performed Emergency, but it can also be carried out during a scheduled operation.
Reasons for intubation and mechanical ventilation
Light help the exchange of gases in the body. Oxygen is removed from the air in the lungs and into the blood, and carbon dioxide from blood passes through the lungs into the air. This movement of gases is necessary for life. If it is impossible to inhale and exhale air and gas exchange is not possible. Intubation and mechanical ventilation is carried out, to assist breathing in the event, When a person does not breathe on his own impossibility.
Possible complications of intubation and mechanical ventilation
Complications are rare, but no procedure does not guarantee the absence of risk. If you plan to intubation and mechanical ventilation, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Damage to the teeth, lips, or tongue;
- Damage to the trachea, which leads to the pain, hoarseness, and sometimes difficulty breathing after removing the tube;
- Intubation of the esophagus (when the tube is accidentally inserted into the esophagus and the stomach, rather than into the trachea);
- Low blood pressure;
- Pneumonia;
- Lung Injury;
- Infection.
Some factors, that may increase the risk of complications:
- Smoking;
- Injury of neck and cervical spine;
- Pre-existing lung disease (eg, эmfizema);
- Poor dental health;
- A recent meal;
- Dehydration.
How is endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation?
Preparation for the procedure
If intubation and mechanical ventilation is performed in conjunction with an operation or planned in advance:
- The night before, you can have a light meal. Do not eat or drink anything after midnight;
- Ask your doctor, what else needs to be done before the procedure.
Anesthesia
In most cases, a potent sedative or general anesthesia. It can be used local anesthesia, to numb the throat. It may also be administered muscle relaxant. This is done to prevent nausea during and after insertion of a tube.
Procedure tracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation
If the procedure is scheduled, you have to breathe through an oxygen mask during 2-3 minutes. This is to ensure, to enrich the body with oxygen during the procedure.
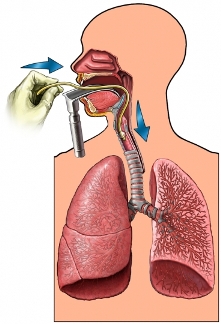
Doctor reject your head back slightly. Then it will use an instrument called a laryngoscope, which has a handle, lamp and a smooth dull blade. This tool is used to lift the tongue from the posterior pharyngeal wall, so the doctor can see your vocal cords. When the doctor sees your vocal cords, it will begin to enter one end of the breathing tube down, trachea.
When the tube is in the desired position, the doctor will remove the laryngoscope. The tube is fixed in the corner of the mouth. Then the doctor connects the tube to a ventilator, that will deliver air to the lungs. In some cases, the tube will be inserted through the nose, and not through the mouth.
Immediately after the start of intubation and mechanical ventilation
The physician must:
- Do chest X-ray, To make sure, that the tube is in the trachea;
- Ubeda, air that enters the lungs;
- Measure Blood gas level, To make sure, that the ventilation works fine.
How long will the intubation and the beginning of mechanical ventilation?
Less than five minutes.
Tracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation – Will it hurt?
Anesthesia prevents pain during the procedure. The tube will cause discomfort and can cause coughing. It can also irritate your vocal cords and trachea.
The average hospital stay
This procedure is performed in a hospital. Typically, the residence time depends on the underlying disease.
Care after tracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation
After intubation, you get extra help from nurses and other hospital staff.
You can not have, drink and talk, until the endotracheal tube is removed. Before the doctor will remove the tube:
- We need to start to breathe on their own through the tube, without ventilator;
- Before removing the tube measured the following parameters:
- Respiration rate;
- Oxygen levels in the blood;
- The volume of air inhaled;
- If ventilation is needed in a few weeks, It can be made tracheotomy. In this case the tube is inserted into the airways through an opening, made in the neck, and not through the mouth or nose.
Contact your doctor after tracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation
After discharge from the hospital need to see a doctor, If the following symptoms:
- Labored breathing;
- Frequent coughing;
- Signs of infection, such as fever or chills;
- The tendency to inhale food or drinks;
- Whistling and noise during breathing (the so-called stridor).
