EEG brain – EEG brain
Description EEG brain
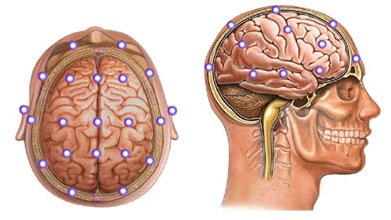
Electroencephalogram (EEG) – test, wherein by means of special sensors measured electrical activity of the brain.
Reasons for electroencephalogram
EEG It may be performed for the following reasons:
- To help diagnose seizures;
- To assess the function of the brain, affected by certain conditions and diseases, such as:
- Trauma;
- Coma;
- Brain infection (encephalitis).
How is the EEG brain?
Preparation for the procedure
Depending on the cause of the EEG, You can get some of the instructions:
- Ask your doctor, should I stop taking medication, such as stimulants, prior EEG;
- Avoid caffeine for eight hours before the test;
- Wash your hair the day of the analysis. Do not use this day hairspray or gel;
- If EEG is performed to determine the cause of insomnia, you may need to stay awake the night before the test. You should also arrange a trip to the procedure and back home;
- If you are prone to seizures, you need to organize a trip to the procedure and back home.
Procedure EEG brain
You will sit in a chair or lying on the couch. To the scalp with a special gel or paste will be attached the electrodes, which will record the electrical activity of the brain. You will be asked to close your eyes and do not move during the most entries. Sometimes you may be asked to breathe deeply and often. For some of the tests may also be used flashes of light. In some cases, the doctor will make a video of EEG brain.
After EEG brain
The technician will remove the electrodes, and you can go home.
Ask your doctor to resume medication, that, perhaps, abolished before the electroencephalogram.
How long will the EEG brain?
About an hour. In some cases, the EEG is performed all night, at home or in the hospital.
EEG brain – Will it hurt?
No, Removing the EEG is painless.
Deciphering the EEG
The results of this test will be interpreted by a neurologist. The attending physician will receive a report within 1-2 weeks after the test.
Communication with the doctor after the EEG brain
After returning home, you need to see a doctor in the following cases:
- If you have a epilepsy, or there were changes in the activity of the electrocardiogram, once you have resumed medication.
