Knee Replacement – Total Knee Arthroplasty
Description knee replacement
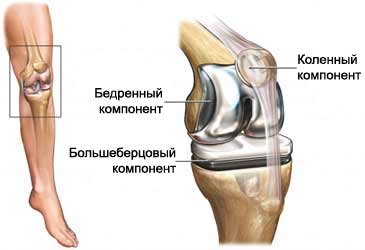
The operation is the removal of sick or injured knee joint and replacing it with an artificial.
Causes of knee replacement
The operation is performed the presence of pain and stiffness in the knee joint, which limits normal activities. Before the operation, using other therapies, such as:
- Recreation;
- Medicines;
- Physical exercise.
Knee replacement is most often done for the following reasons:
- To reduce the pain in the knee and treat disabilities, arisen due Arthritis, osteoarthritis or knee injury;
- To correct deformities of the knee.
Possible complications of total knee replacement
Complications are rare, but no procedure does not guarantee the absence of risk. If you plan to Knee Replacement, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Infection;
- Blood clots;
- Severe swelling or bleeding;
- Damage to the close of the nerves and blood vessels;
- Problems, associated with anesthesia.
Some factors, that may increase the risk of complications:
- Smoking;
- Obesity;
- Pre-existing diseases;
- Current infection;
- Diabetes;
- Steroids.
How is Knee Replacement?
Preparation for the procedure
The doctor prescribed, or does the following:
- Medical checkup;
- Blood tests;
- Roentgen – test, which uses X-rays, to take pictures of structures inside the body, especially bones;
- MRT – test, which uses magnetic waves, to make pictures of structures inside the body.
In the run-up procedure:
- If you are overweight, You need to lose weight. This will help reduce the stress on the joint;
- It is necessary to prepare the house, to make recovery easier:
- Set the required safety equipment:
- Hands on the wall for support;
- Raised toilet seat with arms;
- Bench in the shower;
- Handrails on stairs and steps;
- It is necessary to clear things up, which may cause a drop, such as rugs and extension cords;
- Buy an armchair with footrest;
- Try in the recovery period does not climb stairs;
- Set the required safety equipment:
- Consult your doctor about the drugs taken. A week before surgery you may be asked to stop taking some medicines:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (eg, aspirin);
- Blood thinners, such as clopidogrel (Plaviks) or warfarin;
- As a physician you need to take antibiotics;
- We need to organize a trip for the operation of the hospital and back. Besides, We need to organize care at home;
- The night before, you can have a light meal. Do not eat or drink the night before surgery.
Anesthesia
They can be used the following types of anesthesia:
- General anesthesia – blocks any pain and the patient support in a sleep state during operation. Administered intravenously in the arm or hand.
- Spinalynaya or эpiduralynaya anesthesia – blocks pain in the lower body, from the chest down, the patient is awake. Was injected in the back.
Procedure knee replacement
The doctor makes an incision in the skin. The damaged cartilage and bone will be removed. The remaining bone will be prepared for the installation of new plastic and metal compounds.
The physician has an artificial joint in the correct position, after which secures it in the bone. The doctor closes the incision with staples. Set drainage, drain accumulated fluid.
Immediately after knee replacement procedures
- You will be directed to the recovery room for monitoring vital parameters;
- They are installed tires or knee braces to maintain in the correct position.
How long will the knee replacement?
About 2 hours.
Total Knee Arthroplasty – Will it hurt?
The pain will be felt during the recovery process. The doctor will give pain medicine.
The average hospital stay after knee replacement
This procedure is performed in a hospital. Usually the duration of stay of 3-4 day. The doctor can extend the period of stay, If there are complications.
Care after knee replacement
Care in a hospital
During the restoration of the hospital:
- You may need to use a special apparatus of continuous passive motion, which is designed to:
- Slow motion knee;
- Recovery knee operation;
- Reduce swelling;
- Improve the circulation of fluids;
- Move your foot and ankle, to increase blood flow;
- Wear compression stockings. This may help prevent the formation of blood clots in the legs;
- Work with a physical therapist. You can start the next day after surgery. You will learn safe ways to move the knee and support the balance;
- Wear a brace or splint. The hospital staff will teach, how to use a walker, crutches or other devices to support;
- Take blood-thinning medication.
Home Care
When you return home, Follow these steps:, to ensure the normal recovery:
- Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions;
- Keep the incision site clean and dry. Bandaging it clean bandage;
- Ask the doctor, when it is safe to shower, bathe, or to expose the surgical site to water;
- Gradually begin to walk, and then up the stairs. Avoid jogging and other sports with high load;
- Clamps are removed within a few weeks;
- Maintain a healthy weight after surgery;
- Talk to your doctor, before taking new drugs;
- Take antibiotics before other operations or dental procedures. Antibiotics reduce the risk of infection.
Within six weeks after surgery you will be able to return to daily activities. You may feel light clicks in the joint when walking or bending the knee. Continue to work with a physiotherapist. Vocabulary water can reduce joint pain, swelling around the knee, and expand the range of motion.
Contact your doctor after knee replacement
After discharge from the hospital need to see a doctor, If the following symptoms:
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Redness, edema, increased pain, bleeding or discharge from the incision;
- Pain, which does not pass after taking pain medication appointed;
- Nausea and / or vomiting, which do not disappear after taking the prescribed medicines, and persist for more than two days after discharge from the hospital;
- Cough, shortness of breath or chest pain;
- Legs, Feet, fingers are chalky white, blue or black;
- Numbness or tingling in your leg, foot, arm or hand;
- Pain, burning, frequent urination or persistent blood in the urine;
- Swelling, redness or pain in the legs, caviar, or feet.
