Osteoarthritis (Degenerative joint disease; Bone arthritis)
Description of osteoarthritis
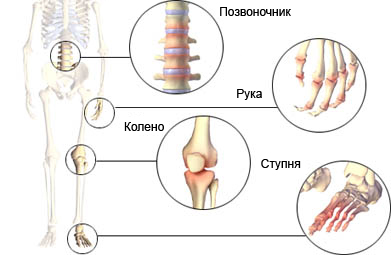
Osteoarthritis – destruction of cartilage in the joints. This is followed by chronic inflammation of the joints. Cartilage covers the connection between the bones, prevents them from friction in the joint capsule. Osteoarthritis usually affects the hands, legs, spine, hips and knees. People with osteoarthritis experience pain and limitation of motion in the affected joints.
Causes of osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is associated with aging. The exact cause of the disease is unclear. When developing osteoarthritis, a person feels “loss” Cartilage, there are bony growths around the joint, pain and muscle weakness in the extremities.
Risk factors for osteoarthritis
Factors, which increase the risk of osteoarthritis:
- Obesity;
- Genetic factors;
- Damage to the joint surface;
- Sport and proffesii, causing stress on the joints;
- Neuromuscular disorders, such as diabetes.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
Symptoms include:
- The increase in joint pain, from mild to severe, especially after overuse or long periods of inactivity, eg, the seat for a long time;
- The creaking or crackling in the joints;
- Edema, stiffness, limited movement of the joint, especially in the morning;
- Weakness in the muscles around the sore joint;
- Deformation joints.
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis
The doctor asks about the symptoms and medical history, performs a physical exam. Tests may include:
- X-ray examination – to take a picture of structures inside the body, especially bones;
- Blood tests;
- Artrotsentez – procedure, which includes the selection of joint fluid.
Treatment of osteoarthritis
There is no treatment, that stops cartilage loss or repairs cartilage, which is damaged. The goal of treatment is to reduce joint pain, reducing inflammation and improving joint function.
Medication
- Over the counter pain medications:
- Acetaminophen (paracetamol) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), Taki how ibuprofen and naproxen;
- External drugs relieve pain (eg, Creams, plasters), are applied to the skin, eg, Capsaicin, methyl salicylate, menthol, diclofenac;
- Prescription drugs against pain, such as:
- Diclofenac and misoprostol – non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, may reduce the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding;
- Opiates and opiate derivatives;
- Antidepressants, Taki how duloxetine, may be prescribed for the treatment of chronic pain in osteoarthritis;
- Hyaluronic acid, which acts as a lubricant, in the affected joint.
Nutritional supplements
Glucosamine and chondroitin – commonly used additives. But studies have shown, These additives are not useful for most people with osteoarthritis. It is necessary to ask the doctor, can you take any dietary supplements.
Alternative therapies
Some doctors report, that acupuncture has successfully reduced pain in osteoarthritis, but specific studies on this topic does not exist.
Further research is also needed on the use of balneotherapy (hot water treatment), relaxation, Yoga.
Mechanical support
Shoes with shock-absorbing soles may provide some relief during daily activities or workouts. Special shape helps to distribute the weight. The corset may relieve back pain. Besides, mattress can relieve chronic back pain. Canes, crutches, walker, and orthopedic shoes can also help patients with osteoarthritis of the lower body.
Weight reduction
Weight loss can reduce the load on the joints, affected by osteoarthritis. Losing 2 kilograms of excess weight, You can reduce stress effects at each step on 5-7 kg. The more overweight cleared, the greater the benefit to the joints.
Exercise and Physical Therapy
Strengthening muscles and arthritic joints training (especially knee, lower back and neck) can reduce pain and to develop joint. For Example, in the presence of arthritis in the knee, physical exercise, including weight training, can help improve the function of the knee.
Swimming and water aerobics are also good choices, because they do not create stress on the joints.
Another treatment option is transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. The patient is connected to the machine, which sends electrical signals through the nerves to the skin. This type of therapy can reduce pain in some people.
Supported Devices
If you experience difficulties with movement through the house, It is recommended to install handrails near the wall. Especially useful are they in the bathroom and toilet.
Heat and ice
Applying warm compresses (a hot water bottle or warmer) helps joints and muscles move more easily. This method can also reduce the pain. Using ice packs after exercise can also bring relief.
Steroids
Corticosteroid injections may be administered in the inflamed joint, if other medicines do not help. Because repeated cortisone injections can be harmful to the cartilage, they are used only for those with severe symptoms.
Surgery
The operation allows:
- Change the position of the bones and redistribute the load on the joints;
- Replace the artificial joint;
- Remove loose piece of bone or cartilage from joints.
Prevention of osteoarthritis
To reduce the risk of osteoarthritis you must:
- Maintain a healthy weight;
- Regularly perform light exercises (eg, walking, tension, swimming, yoga);
- Avoid repetitive motions and risky activities, that can cause joint injuries, particularly after 40 years;
- With age, some activities, perhaps, You have to stop or change.
