Cellulitis (inflammation)
Description of cellulite
Infection called cellulitis skin and subcutaneous tissue. Infection may occur anywhere on the body, but it is most common on the lower legs.
Causes of Cellulite
Cellulitis often caused by a bacterial infection. Its cause may be bacteria, which normally live on the skin or bacteria from other sources. The emergence of bacterial infection can cause:
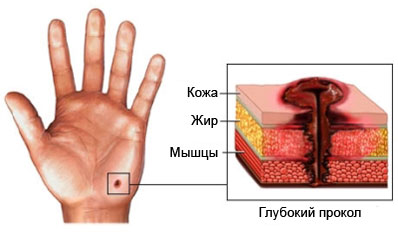
- Minor damage to the skin (eg, tax, scratch, blister, burn, puncture or bite), which infected and the infection spreads into the surrounding skin;
- Injuries while swimming in natural waters, leading to infection by microbes, living in water;
- A cut or abrasion in the processing of fish, birds, eggs or meat, through which the microbes in the wound fall;
- Bacteria, that enter the body through a surgical wound or venous catheter;
- Bacteria, getting under the skin of the upper respiratory tract and ear.
Risk factors for cellulitis
Factors, that may increase the risk of the appearance of cellulite include:
- Insect bite, animal or human;
- The presence of certain diseases (eg, diabetes, HIV, kidney or liver disease, poor circulation);
- Alcohol abuse or drugs;
- Regular intake of steroids;
- Recent surgery;
- Fluid retention;
- Exposure to certain products, such as raw fish, meat, seafood, bird, eggs.
The symptoms of cellulitis
Symptoms may begin within a few hours or days, and may include:
- Dermatitis, which starts at a small area, but then spreads and causes:
- Redness;
- Pain or soreness;
- Swelling;
- Feeling the heat;
- Red stripes (sometimes);
- Hyperadenosis;
- Fever or chills;
- Fatigue;
- Confusion.
Cellulitis near the eyes may cause pain when moving them and require immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis Cellulite
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical examination. He may also ask about exposure to the natural water bodies or contact with animals. There will be an inspection of skin inflammation. The doctor may mark the border of cellulite on the skin. This will help to monitor its progress.
Tests may include:
- Bakteryalnaya culture – to determine the type of bacterial infection;
- Blood tests – to check, It does not spread the infection into the bloodstream.
In severe cases, the infection can lead to tissue death (gangrene) or spread to the bone. If you suspect that complication physician may prescribe additional tests:
Cellulite Treatment
The goal of treatment of cellulite is, to eliminate infection and to reduce the discomfort. In most cases, recovery occurs within a week or two after the initiation of treatment.
Inpatient care may be needed, if you:
- A severe case of cellulite;
- Diabetes or a weakened immune system;
- The infection spread to the face.
Cellulite treatment includes:
Medication for the treatment of cellulite
Antibiotics, which can be taken orally or injected into a muscle or a vein. The method of treatment will depend on the severity of the infection.
Supportive therapy for the treatment of cellulite
Treatment may include:
- The rise of the infected area above heart level;
- Replacement bandages, as prescribed by your doctor;
- Protect your skin from additional injury;
- Avoid scratching or rubbing the affected area.
If you are diagnosed with cellulitis, Follow your doctor's instructions.
Other treatments for cellulite
An infected wound should be cleaned, it is removed from dead tissue. In certain situations, the wound may accumulate pus (developing abscess), to be drained (merge).
Prevention of cellulitis
To reduce the risk of cellulite:
- Keep the skin clean;
- Moisturize dry skin with lotion;
- Avoid skin damage:
- Wear protective clothing when playing sports;
- Wear long pants and long-sleeved shirts in the tourist trips;
- On the beach, wear sandals, Do not go barefoot;
- Be careful with animals, treat them well, to avoid bites;
- Do not swim in natural waters, if you have cuts or sores;
- Try not to cut yourself during fishing or water sports;
- If you have a small cut, bite or other skin damage, you need to carefully care for the wound:
- Clean cuts or scrapes with soap and water;
- Apply antibiotic ointment wound;
- Close the wound with a bandage or dressing;
- Do not scratch, do not rub the wound;
- Consult your doctor, If the wound becomes red or inflamed;
- If your feet often swell and swell, We need to raise them several times a day above the level of the heart and wear support stockings.
