Bone scintigraphy – X-ray examination of isotope bone
Description bone scintigraphy
X-ray examination of bones (ctsintigrafiya bones) – analysis, which detects the field increased or decreased activity of the bone. They may indicate damage or bone disease. Radioactive isotopes and radioactive tracers used for, to see the problem areas.
Causes of bone scintigraphy
The test is conducted to detect abnormal processes in the bones of the subject, including the following:
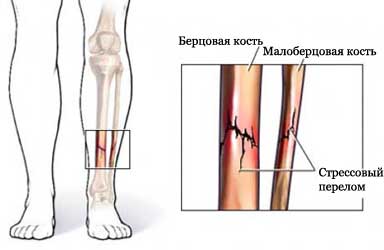
- Stress injury (eg, stress fracture of the tibia);
- Infection (osteomyelitis);
- Arthritis;
- Bone tumors;
- Cancer;
- Trauma;
- Metabolic disorders (eg, Paget's disease);
- Eating Disorders, that can affect the bones, Low levels of vitamin D (eg, rickets);
- The withering away of bone tissue due to a blocked metabolic (aseptic necrosis).
Possible complications during bone scintigraphy
Complications are rare, but that does not mean the absolute absence of risk. If you plan to perform a bone scintigraphy, the doctor will review the possible complications, which may include:
- An allergic reaction to the material;
- Infection.
Some people are worried about the use of the radioactive material in bone scan. However, the amount of radioactive dose received very little, a little more, than when the X-rays (chest X-ray, dental X-rays). Radioactive material is excreted within 2-3 days.
How is bone scintigraphy?
Preparing for scintigraphy
It is necessary to inform the doctor of a pregnancy or breast-feeding. Maybe, I have to give up breast-feeding for a few days after, as a bone scan will be carried out.
It is necessary to inform your doctor about recent reception preparations containing barium (eg, contrast agent) bismuth (contained in some medications).
Three hours before the scan examinee is injected with radioactive chemical indicators. It is necessary to drink plenty of fluids between injection and scanning. You also need to empty the bladder before scanning.
Procedure scintigraphy
The subject will lie on your back on a special table. Chambers above and below the section, moving slowly, will scan the body.
The subject can be asked to take a different position during the scan. It is important to lie still during the movement of the camera.
The camera is able to detect a small amount of radioactive material is injected. This will allow the doctor to see areas, where there may be bone injury or disease.
After scintigraphy
The injection site is checked for redness and swelling.
How long will the bone scintigraphy?
The subject will be in for a scanner 20-60 minutes. Sometimes re-scan through 24 o'clock.
Will it hurt during Bone scintigraphy?
No, painless examination, except for a slight discomfort at the injection site.
The results of bone scintigraphy
If the bone is healthy, Scan shows, that the chemical is distributed evenly across all the bones. If there is an area of disease, scanning will be seen on dark or light areas.
Depending on the results of bone scintigraphy, may require additional survey, such as:
- The X-ray test, which uses radiation, to take pictures of structures inside the body, especially bones;
- CT scan – such as X-rays, which uses computer, to make pictures of structures inside the body;
- MRI scan – test, which uses magnetic waves, to make pictures of structures inside the body;
- Test on bone density;
- Biopsy.
Contact your doctor after bone scintigraphy
It is necessary to call the doctor, to see the test results, or if you have any questions about the survey.