Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism – Alcohol addiction
Description of alcohol abuse
Alcohol abuse – excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages. The disorder may progress to chronic alcoholism.
Saint Martin's evil – chronic alcohol abuse, which ends with a physical dependence on alcohol (Withdrawal) and an inability to stop or limit its consumption.
Causes of alcohol abuse
Alcohol abuse and alcoholism can contribute to a number of factors, including:
- Genes;
- Chemical substances, contained in the brain and stimulating alcoholism (in case of deviations);
- Social pressure;
- Emotional stress;
- Pain;
- Depression and other mental problems;
- Surroundings, misuse alcohol.
Risk factors for alcohol abuse
Factors, which increase the likelihood of developing alcoholism:
- Paul: male;
- The presence of family members, who abuse alcohol (particularly males, whose fathers or brothers drink alcohol);
- Start drinking alcohol at an early age (younger 14 years);
- The use of illicit drugs or non-medical use of prescription drugs;
- Peer pressure;
- Easy access to alcoholic beverages;
- Mental disorders, such as depression or anxiety;
- Smoking.
Symptoms of alcohol abuse
Many drinkers deny problems with alcohol. Alcohol abuse can occur without physical dependence.
The symptoms of alcohol abuse comprise:
- Changing jobs, school or place of residence, in connection with the problems, associated with the consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- The risk of physical security;
- Recurring trouble with the law, often including drinking and driving;
- Continued alcohol consumption, despite alcohol-related difficulties.
Symptoms of alcoholism include:
- The desire to drink;
- Unable to stop or limit drinking;
- The need for large amounts of alcohol, to achieve the effect of intoxication;
- Refusal to work, to continue the use of alcohol;
- Drinking alcohol, even when they cause health problems;
- Inability to stop or reduce alcohol intake;
- Abstinence (Symptoms of alcohol withdrawal), It includes:
- Nausea;
- Sweating;
- Alarm, anxiety;
- Increased blood pressure;
- The attacks of delirium tremens (delirium tremens).
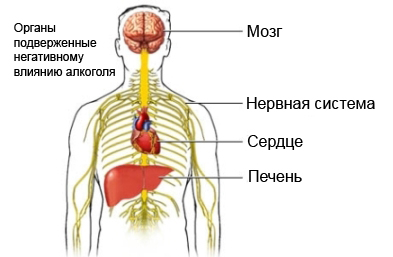
If alcoholism can be damaged brain, nervous system, heart, liver, stomach, gastrointestinal tract and pancreas.
Diagnosis of Alcohol Abuse
The doctor should ask a number of questions to the patient, to assess possible alcohol-related problems, including:
- Have you tried to stop drinking?
- You feel bad when drinking?
- Have you been annoyed by another person's criticism in the address of your drinking?
- Do you drink in the morning, to steady your nerves or cure a hangover?
- Do you have problems with work, family, or the law?
- Do you drive a car under the influence of alcohol?
It can be made a blood test , that:
- Look at the size of red blood cells and to check for deficiency transferrin;
- Check for alcohol-related liver disease and other health problems.
Treatment for alcohol abuse
Treatment for alcohol abuse or alcoholism, aimed at teaching patients manage disease. Most experts believe, it means giving up alcohol completely and permanently.
The first and most important step is to recognize, the problem exists. Successful treatment depends on the patient's desire to change. Your doctor can help to safely get out of alcohol dependence. This could require hospitalization in a detoxification center or hospital, which will be carefully monitored for side effects. You may also need treatment during detoxification.
Treatment includes:
Medication
Lekrstva can help alleviate some of the symptoms of withdrawal and help prevent relapse. Your doctor may prescribe medication, to reduce the craving for alcohol.
Medicines, used to treat alcoholism include:
- Naltrexone (Revis, Vivitrol) – blocks the desire to drink alcohol;
- Disulьfiram (Antabuse) – It causes discomfort when taking alcohol;
- Acamprosate (Campral) – It reduces the craving for alcohol.
Studies have shown, that anticonvulsant medication, Topiramate (Topamax), can reduce the dependence on alcohol.
Education and Consulting
Therapy helps to realize the danger of alcohol. Education is an understanding of the basic problems and lifestyle, that trigger the desire to drink alcoholic beverages.
Mentoring and social assistance
Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), help many people to stop drinking and stay sober. Members meet regularly and support each other. Family members may also benefit from attending meetings of AA community. Living with an alcoholic can be severe, tense situation.
Here are some general statistics on treatment outcomes individuals one year after attempting to stop drinking:
- 1/3 remained abstinent (We give up alcohol);
- 1/3 renewed use, but at a lower level;
- 1/3 I started drinking again.
When the diagnosis of alcohol abuse or alcoholism, you need to follow your doctor's instructions.
Alcohol Abuse Prevention
Understanding, that alcohol causes problems, It helps some people avoid it. Proposals to reduce the risk of alcohol abuse and dependence include:
- Communication without alcohol;
- Failure to attend cafes, bars;
- The absence of alcohol in the building;
- Avoiding situations and people, that encourage drinking;
- Finding non-drinking friends;
- Recreation and sports, are not associated with alcohol;
- Failure to drink when stressed;
- You want to limit alcohol consumption to a moderate level – 0,33 liters of beer, 150 grams of wine or 50 grams of hard liquor a day;
- A good relationship with your family and children can reduce the risk of alcohol abuse.
Most experts, who treat alcohol abuse, consider, that abstinence is the only effective form of prevention.
