Burns
Burns – description
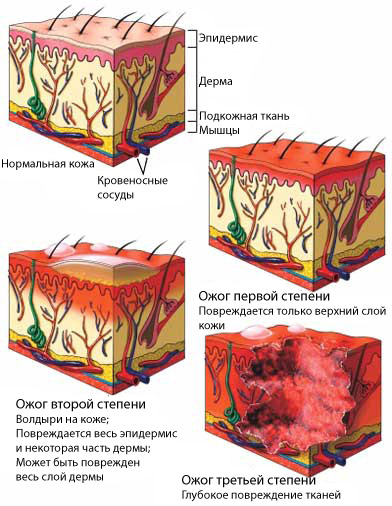
Burn – skin damage, and sometimes under her fabrics under heat or certain chemicals. Burns are classified according to the depth and the degree of skin damage:
- Singe (also called first-degree burn):
- Easy burn type;
- Often it is exposed to ultraviolet light, or very short (flash) open flames;
- It affects only the outer layer of skin (epidermis);
- Usually does not cause scarring;
- Healing takes about 3-6 days;
- Superficial partial thickness burns (also called second-degree burn):
- Often caused by a burn with boiling water (spill or splash), or very short (flash) open flames;
- The outer layer of the skin is affected more profoundly, usually causing blistering;
- Sometimes it can lead to scarring, but basically it causes long term changes in skin color;
- Healing takes about 1-3 weeks;
- Deep partial thickness burns (also called second-degree burn):
- Often caused by a burn with boiling water (flood), , hot oil or fat;
- Affects the outer and underlying layers of the skin (dermis), causing the formation of bubbles;
- Usually causes scarring;
- Healing takes more than three weeks;
- Burn full thickness skin (also called third-degree burns):
- Very serious injury;
- Often caused by a burn with boiling water (immersion), It may result from exposure to the flame, couple, burning oil, grease, chemicals or high voltage;
- It causes damage to all layers of the skin, and can damage the deep tissues (muscle and bone);
- Cicatrizant;
- Heals only at the edges of the wound, rubtsuyas, If not done skin grafting.
Causes burns
Burns can cause:
- Exposure to heat or flame (thermal burns):
- Hot foods or beverages, such as boiling water, tea, or coffee;
- Hot oil or fat;
- Hot water;
- Exposure to sources of heat – oven, Heaters, or hair curlers;
- Open fire;
- Flammable liquids, such as gasoline;
- Fireworks;
- Chemical substances (corrosive burn) – strong acids or strong bases, such as:
- Cleaning products;
- Battery electrolyte;
- Chemicals for swimming pools;
- Aggressive cleaners;
- Sunlight (sunburn) or solarium;
- Electricity (flash-burn):
- Damage to the electrical wires;
- Electrical outlets;
- High voltage wires;
- Lightning;
- Radiation (radiation burn):
- Nuclear radiation;
- X-rays;
- Radiation therapy for cancer treatment.
Risk factors for burns
Factors, increases the risk of burns include:
- Age: less than four years;
- Paul: male;
- Low socio-economic status;
- Smoking;
- Alcohol consumption;
- Drug use;
- Missing or broken smoke detectors and fire alarm;
- Faulty and old housing;
- The lack of control and supervision of children;
- Using tap water hotter, than 50 °C.
Symptoms of burns
Symptoms and signs of burning varies depending on the type of.
Singe
Symptoms include:
- Burned area turns red and it felt soreness;
- Region pales (whitens) when you press;
- The area can swell without blistering.
Superficial partial thickness burns
Symptoms include:
- Bubbles on the site of the burn;
- Area burn wet, redness of the skin;
- Region pales (whitens) when you press;
- Painful place burn when exposed to elevated temperatures.
Deep partial thickness burns
Symptoms include:
- Watery bubbles, usually easily pierced, in secretions no traces of blood;
- Field burning can be wet or waxy dry;
- Skin color can vary from white to inhomogeneous or red;
- The area is not pales when pressed;
- When you can feel pain.
Burn full thickness skin
Symptoms include:
- The skin may look waxy white, gray, or charred and blackened;
- If the nerves are damaged, Pain may be felt only when strong pressure on the affected area.
Diagnosis burn
The doctor will ask, What is the cause of the burn, obsleduet obozhzhennuyu region.
Treatment will depend on the cause of the burn, its depth and the affected area. Doctors have methods and charts to estimate the body surface area, hit by injuries. This estimate depends on the age, eg, the baby's head has a greater percentage of the body surface area, than the head of an adult.
Treatment of burns
Treatment of burns depends on their causes. Rapid initiation of treatment reduces tissue damage. First aid for minor burns may include:
- Cooling the burn with running water or a cold damp cloth. Do not use ice, this may lead to further damage to the skin;
- Do not use oil, fats or ointment for the treatment of burns;
- Cover the burn sterile gauze or a clean cloth;
- Do not use cloth nappies, such as a towel or blanket;
- Take a pain reliever, eg, paracetamol;
- Do not pierce the blisters formed. This may lead to infection;
- If you see signs of infection, consult a doctor. Signs of infection include:
- Increased pain;
- Redness;
- Fever;
- Swelling;
- Pyorrhea.
After minor burns, After cooling the affected area of skin can be treated with lotion or moisturizer, to prevent drying.
For more severe burns, consult a doctor or call an ambulance. Prior to the arrival of emergency:
- Do not remove clothing, which is stuck to the burn;
- Check, that the victim is no longer exposed to smoke or heat;
- Do not spray water burns, you can cover the affected area with cool, moist sterile bandage or clean cloth;
- In severe lesions, make sure, that the person is breathing and, if you want to start to perform CPR.
If the burn is small, Follow your doctor's instructions.
Hospitalization at a burn
The need for hospitalization depends on many factors. They include age, the cause, and the extent and depth of burns. The reasons for hospitalization in the human burn may include:
- Age: younger than five years old or older 55 years;
- Small, but deep burns on his hands, face, eyes, feet, or perineum (groin / genital area);
- The extensive area of the burn;
- Burns, which may require complex dressings or continuous medical observation;
- Injury or heavy electrical burn;
- Circular burn;
- Other medical problems, that predispose a person to infection:
- Diabetes;
- Immunosuppression;
- Serpovidnokletochnaya anemia.
Treatment of major burns
If the burn is serious, They can be assigned the following treatments:
- Oxygen, to maintain breathing;
- Intubation;
- Intravenous fluids;
- Skin graft;
- Bus – imposed on the joints, to help maintain mobility;
- Physiotherapy – in the case of large burns.
Preventing burns
Most burns occur in accidents. To prevent burns:
- We need to teach children the rules of fire safety and keep dangerous materials out of their reach;
- Be careful when cooking over an open fire;
- Do not wear flammable clothing children;
- Do not hold the baby in your arms or lap while cooking or consumption of hot food or liquid;
- Do not leave matches, Lighters, Candles, burning cigarettes unattended;
- Wear protective gloves and clothing when working with corrosive chemicals;
- Install the protective covers on electrical outlets;
- Do not wear tight-fitting clothes hands while cooking;
- Keep children and pets away from the stove while cooking;
- Store chemicals and cleaners in a locked cabinet;
- Children under the age of one year can get burns from hot seat belt buckle. Check, that the car seat is not hot, before putting the child in the seat. If you park in the sun, Seat cover cloth.
