Transurethral resection of the prostate, TURP: what is this operation, how they do it, Contraindications, what after
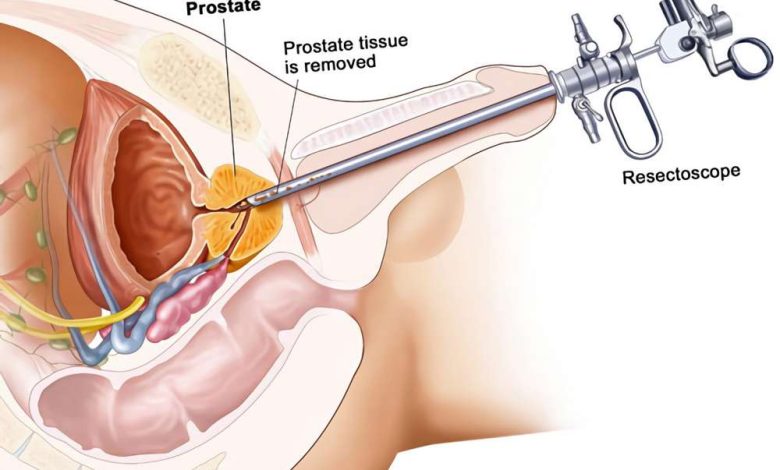
Description TURP
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) It is an operation to remove part of the prostate gland.
Prostate – part of the male reproductive system. It produces and stores seminal fluid (milky liquid, which is part of semen). Iron is a little below the bladder, front of the rectum. After prostate urethra passes (muscular tube, through which the urine flows).
Reasons for TURP
TURP is done in benign prostate enlargement, called benign prostatic hyperplasia (DGPŽ) or BPH. When BPH prostate gland enlarges and puts pressure on the urethra and bladder. The pressure can cause problems with the normal flow of urine.
TURP may also be carried out in the presence of prostate cancer, If the doctor finds, that the complete removal of the prostate gland is too risky. In this case, the removal of part TURP prostate, which reduces blocking urine and reduces symptoms.
Possible complications of transurethral resection of the prostate
TURP syndrome may occur (It occurs in approximately 2% patients, usually, during the first 24 hours). Symptoms may include:
- Increase or decrease in blood pressure;
- Abnormal heart rhythm;
- Increased respiratory rate;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Blurred vision;
- Confusion;
- Excitation.
Other complications may include:
- Urinary tract infections (often);
- Bleeding, which may require Blood Transfusion (the second most common problem);
- Urinary incontinence (inability to control urination);
- Retrograde ejaculation – semen into the bladder, and goes out of the end of the penis (not dangerous);
- If you plan to have children in the future, ask your doctor about the side effects of this operation;
- Reaction to anesthesia.
Some factors, that may increase the risk of complications include:
- Obesity;
- Smoking and alcohol abuse;
- The use of some drugs;
- Malnutrition;
- Recent or chronic illness;
- Diabetes.
How is transurethral resection of the prostate?
Preparation for the procedure
Your doctor may be made or assign the following:
- Medical checkup;
- Revision of the list of accepted medicines and dietary supplements;
- Blood tests, urine and urine culture;
- Ultrasonography – test, which uses sound waves to visualize the kidney, bladder and / or prostate;
- Urinoscopy;
- Roentgen.
In the run-up procedure:
- Tell your doctor about taking any medications. A week before the surgery may need to stop taking certain drugs:
- Aspirin or other anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Blood thinners, such as clopidogrel (Plaviks) or warfarin;
- On the eve of the operation in the evening you can eat a light meal. Do not eat or drink for the night.
Anesthesia
When applied TURP general anesthesia, which blocks the pain and the patient support in a sleep state during operation. Also used spinal anesthesia, anaesthetises that the lower part of the body.
Description of the procedure of transurethral resection of the prostate
The doctor will use a special device (resectoscope), which looks like a thin tube with a light source at the end. It is inserted into the hole at the tip of the penis, where urine comes out. The bladder is filled with a special solution, allowing the doctor a better view of its contents. The prostate gland is carefully studied. Through resectoscope will be inserted into the small surgical instruments, used, to remove part of the enlarged prostate. The bladder catheter, to provide drainage of urine after surgery. It can also be used for purification of the bladder and removal of blood clots.
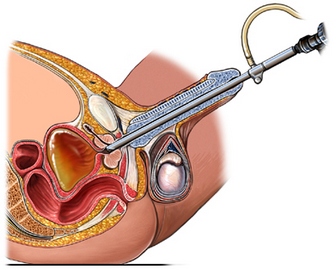
Immediately after transurethral resection of the prostate
Removed tissue will be sent to the laboratory for testing.
How long will TURP?
About 60-90 minutes.
TURP – Will it hurt?
Within a few days after surgery, you may feel some pain. The catheter can cause some discomfort. Doctor will prescribe pain medication, to prevent bolevye sensation.
The average hospital stay after a transurethral resection of the prostate
After TURP, usually, I need to stay in hospital overnight. In some cases, it may take up to stay 2-3 days.
Care after transurethral resection of the prostate
Care in a hospital
- The bladder catheter to drain urine. The catheter is left for the night. The urine may be blood, but it is normal. Through a catheter in the bladder may be introduced water, to clean up the blood and blood clots;
- Always keep the container for collecting the urine below the bladder;
- Perform regular exercise, prescribed by a doctor;
- You stay in bed until the next morning after surgery. The nurse can help you the first time to climb out of bed.
Home Care
After returning home, follow these steps:, to ensure the normal recovery:
- Clean the area of the catheter into the urethra several times a day. Use soap, water and soft towel;
- Drink plenty of fluids, especially during the day. This will help to clear your bladder;
- Avoid heavy or strenuous work during the 3-4 weeks;
- Avoid sexual activity for 4-6 weeks after surgery;
- Avoid alcohol, caffeine and spicy foods;
- Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions.
Recovery after surgery takes about three weeks. Some time these symptoms can last, as frequent or painful urination. They should disappear within the first six weeks. If there is blood in the urine, I need to lie down and drink a glass or two of fluid. Next, when you urinate, bleeding should stop. If this does not happen, consult a doctor.
The operation should not affect sexual desire or ability to have sex. Sometimes it can happen retrograde ejaculation – semen into the bladder instead of penis. This should not affect the ability of conceiving children.
Contact your doctor after transurethral resection of the prostate
After discharge from the hospital need to see a doctor, If the following symptoms:
- Difficulty or inability to urinate;
- Pain, burning, frequent urination or persistent blood in the urine. This may be normally within the first few days after surgery. If symptoms persist or worsen, consult a doctor;
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Pain, which does not pass after taking pain medication appointed;
- Nausea and / or vomiting, that do not pass after taking the prescribed medicines, and persist for more than two days after discharge from the hospital;
- Impotence for more than three months after surgery.
