Carpal tunnel syndrome – Carpal tunnel syndrome
Description of carpal tunnel syndrome
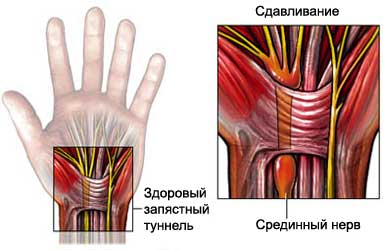
Carpal tunnel disease – nerve disorder hands, caused by compression of the median nerve. The median nerve passes through the narrow channel in the wrist and provides sensitivity great, index, middle finger, and half of the ring finger.
The causes of carpal tunnel syndrome
If carpal tunnel syndrome is pressure on the median nerve. This pressure is caused by narrowing of the wrist, which can be caused by many factors, including:
Swelling of tissues in the wrist due to injury or change in the balance of fluid in the body;
Heredity (narrow wrist);
Tumors (rarely).
Risk factors for carpal tunnel syndrome
Factors, which increase the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome:
- Paul: female;
- Advanced age;
- Obesity;
- Excessive alcohol consumption;
- Smoking;
- Actions with repetitive hand movements:
- Some sports;
- Sewing;
- Playing musical instruments;
- Print;
- Work on assembling the parts and mechanisms;
- Fluid retention for the following reasons:
- Heart failure;
- Kidney problems;
- Injuries to the wrist:
- Arthritis;
- Diabetes;
- Raynaud's disease and conditions, which impair the blood flow in the hands;
- Hormonal changes:
- Pregnancy;
- Breast-feeding;
- Menopause;
- Gipotireoz;
- Cushing's disease;
- Elevated levels of growth hormone;
- Medicines:
- Birth control pills;
- Kortizon (tablets or injections);
- Some medications to reduce high blood pressure.
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome causes symptoms in one or both hands or wrists. Symptoms may include:
- Pricking, burning or numbness, especially in the thumb and index or middle fingers;
- Pain or numbness, are limited in the following:
- The movement of the wrist, hand or finger;
- Bad dream (symptoms may lead to frequent awakenings);
- Stiff hands or cramps, which are after:
- Shaking hands;
- Waking up in the morning;
- Weakness or clumsiness of the hand:
- Loss of grip strength;
- Difficulties compressive hand into a fist;
- Often things fall out of the hands;
- Pain, that moves up the arm.
Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, perform a physical examination, wrists and hands. Inspection will include a test of strength, sensitivity and signs of irritation or damage to the nerve.
Other tests may include:
- Electrodiagnostic Tests – measured and recorded the speed of the electrical conductivity of the median nerve (To make sure, that the nervous impulse passes normally or delayed in the wrist);
- MRT – test, which uses magnetic waves, to make pictures of structures inside the body, In this case, the neck (whiplash);
- Roentgen – test, which uses radiation emissions, to take a picture of inside the body. More often take pictures of bones;
- US – examination, that uses sound waves, to measure the width of the median nerve (It can be used as a screening test, or to guide the implementation of injections).
Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
It is important to treat the cause, causing carpal tunnel syndrome. Sometimes simple changes in the workplace or at home may relieve symptoms.
Treatment may also include:
Recreation, ice, lifting limbs and exercise
- Do not load the wrist, Do not perform movements that worsen pain;
- Apply ice packs to the area of pain;
- Raise your hands above the level of the heart, to reduce swelling;
- At the direction of a physician perform the exercises.
Overlay tires
The bus will reduce the range of motion of the wrist. It is most effective at night. Application of tires will avoid spillages from severe pain.
Medication
For the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome are applied:
- Painkillers, eg, aspirin and ibuprofen;
- Cortisone injections in the wrist.
The operation for the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
Surgery may be needed, if there are severe symptoms of the disease, or after, both tried other treatments. The most common procedure is incision carpal tunnel.
If you are diagnosed with carpal tunnel syndrome, Follow your doctor's instructions.
Prevention of carpal tunnel syndrome
Actions, which reduce the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome:
- When possible, should avoid repetitive hand movements;
- Switch between activities or reduce the load on the arm and hand;
- Try to keep your wrist straight, so that the load is evenly passed on the arms and shoulders;
- Lift weights with both hands;
- If you work in an office, set the table, chair, keyboard and so, that:
- The back remains straight;
- Feet on the floor or on a footrest;
- His knees were at or slightly below the hips;
- Shoulders in the middle position, without deviating forward or backward;
- The elbows are bent at an angle 90 degrees;
- Forearms should be parallel to the floor;
- Take breaks at least, every hour:
- Relax and let the rest hands;
- Massage your hands and wrists;
- Exercise regularly (jogging or swimming);
- Reduce your intake of caffeine and limit smoking (can reduce blood flow to the hands).
