Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome – Cut wrist muscles when carpal tunnel syndrome
Description of operations for carpal tunnel syndrome
Cm. also The injection at the wrist tunnel syndrome
Cut Muscle carpal tunnel – operation, at which ligament, which covers the wrist cut.
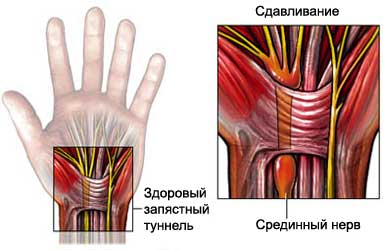
Causes surgery on carpal tunnel
The median nerve runs from the forearm to the wrist. Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs, When this nerve is compressed at the wrist, it passes through the carpal tunnel - a narrow tunnel on the palm side of the wrist. This leads to the pain, weakness, tingling or numbness in the hand and wrist. It may also feel pain in the arm.
The cut in the area of the carpal tunnel is an operation, can reduce pressure on the median nerve. Pressure is reduced by cutting the transverse carpal ligament.
The operation for the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome is usually recommended in the following cases:
- Other therapies have failed, including cooling, imposition of tires or braces, anti-inflammatory drugs, steroid injections, physiotherapy and ultrasound;
- There is muscle weakness and atrophy of control of the fingers;
- Studies show, that the median nerve is not functioning properly.
Possible complications during an operation on the carpal tunnel
Complications are rare, but no procedure does not guarantee the absence of risk. Before, how to perform the operation, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Infection;
- Bleeding;
- Swelling;
- Nerve Damage;
- Stiffness in the fingers;
- Further numbness, pricking, weakness or pain.
Factors, that may increase the risk of complications include:
- Smoking and alcohol abuse;
- Diabetes;
- Receiving steroid medications for other conditions.
How is the surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome of the hand?
Preparation for the procedure
Before the operation can be assigned to the following tests:
- Medical checkup – the doctor will focus on finding problems and unpleasant sensations in the hands of;
- Blood tests;
- Nerve conduction studies - measuring the ability of nerves to send impulses to the muscles of the thumb;
- Electromyogram – recording electrical activity in muscles;
- MRT – test, which uses magnetic waves, to make pictures of structures inside the body.
In the run-up procedure:
- The patient may be asked to stop taking certain medicines a week before the procedure,:
- Aspirin or other anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Blood-thinning drugs, such as clopidogrel or warfarin;
- We need to organize a trip to the hospital and back after surgery, as well as help at home after the procedure;
- In the evening before surgery you can eat a light meal. You can not eat or drink anything after midnight on the day of the procedure;
- In the morning before the procedure may be requested to take a shower.
Anesthesia
Used general anesthesia or local anesthesia in conjunction with sedatives. When using general anesthesia the patient will sleep during the procedure.
With local anesthesia will numb the surgical site, and the patient may receive a sedative, which will help you relax.
Description of the procedure
They can be used in classic technique of open incision or endoscopic surgery:
Technique open incision carpal tunnel
At the bottom of the palm and wrist will make a short incision. Carpal ligament will be open. This will allow the doctor to release the median nerve. The incision is then sewn stitches. In place of surgery bandage.
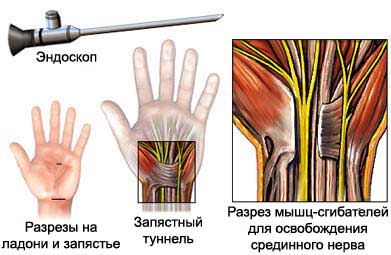
Endoscopic surgery to release the median nerve
On hand will be made two small incisions – one on the palm, another on the inner side of the wrist. A small device with a camera is inserted through the incision. This camera will allow the doctor to see the inside of the wrist. After another incision will be introduced other surgical instruments. The doctor will use these tools, to cut the carpal ligament. After, the camera and instruments are removed, They will be needed several stitches to close cuts. On the site of incision bandage.
How long will the surgery?
The duration of the operation 15 minutes before 1 o'clock.
Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome – Will it hurt?
Anesthesia will prevent pain during the procedure. After anesthesia at the site of surgery may feel some pain. In this case, the doctor prescribes taking pain medications.
Care of the patient after surgery
Care in a hospital
The doctor will monitor the recovery process, until the patient is ready to go home. On the hand and wrist bandage. The wrist is elevated, to reduce swelling. Periodically may be applied ice packs.
Home Care
Upon returning home, you need to perform the following actions, to ensure the normal recovery:
- It is necessary to keep a hand as high as possible within a few days. This will help reduce swelling and pain;
- Applying ice to the wrist and hand during 20 minutes at a time, every 3-4 o'clock, during the first few days after the procedure will reduce the pain and swelling;
- If the bandage becomes soiled, the doctor may recommend replacing it;
- We need to ask your doctor about, when it is safe to shower, bathe, or to expose the surgical site to water;
- Do not lift heavy things or strain the hand and arm, as long as it does not allow a doctor;
- We must come to the doctor for 7-10 days, to remove the sutures;
- Once the cuts have started to heal, you need to perform the exercise on the program, recommended by your doctor. You may also need help of a physiotherapist;
- It is necessary to organize a home help, particularly if an operation has been performed on both arms;
- Many cases of carpal tunnel syndrome, believed, occur due to repetitive actions (often associated with the work). It is necessary to consult with your doctor about, how to prevent these actions;
- Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions.
Communication with the doctor after the surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome
After discharge from the hospital need to see a doctor, If the following symptoms:
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Redness, edema, increased pain, bleeding, or any discharge from the incision;
- Nausea and / or vomiting, which do not disappear after taking the prescribed medicines, and persist for more than two days after discharge from the hospital;
- Pain, which does not pass after taking pain medication appointed;
- Increased tingling or weakness in the arms;
- Fingers become extremely bloated, cool, or discolored;
- Cough, shortness of breath or chest pain.
