Pancreatic cancer
Description pancreatic cancer
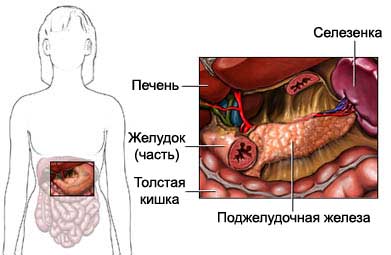
Pancreatic cancer – the appearance and development of cancer cells in the pancreas. The pancreas is a long, flattened pear-shaped organ abdominal. It produces digestive enzymes and hormones, including insulin.
Cancer occurs, when the cells of the organism (in this case cells of the pancreas) begin randomly divided. The result is a mass of tissue, called a growth or tumor. The term cancer refers to malignant tumors, that can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
Causes of pancreatic cancer
The cause of pancreatic cancer is unknown. Studies show, that there are certain risk factors, Related Disease.
Risk factors for pancreatic cancer
Factors, which increases the risk of pancreatic cancer:
- Age: 40 and older;
- Paul: male;
- Smoking and the use of smokeless tobacco (eg, chewing tobacco);
- Alcohol abuse;
- Diabetes;
- Chronic pancreatitis, hereditary pancreatitis, nonpolyposis colon cancer;
- Family or personal history of certain types of colon polyps or colon cancer;
- A family history of pancreatic cancer (especially in Ashkenazi Jews with BRCA2 gene);
- Consumption of foods high in fat;
- Being overweight or obese, which may also reduce the chances of survival of pancreatic cancer.
Symptoms of Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer does not cause symptoms in the early stages of. Cancerous cells can grow for a while, before the symptoms cause. When symptoms appear, they can be very vague. In many cases, to detect, cancer spread beyond the pancreas.
Symptoms will vary depending on location and size of the tumor. The symptoms of pancreatic cancer include:
- Nausea;
- Loss of appetite;
- Unexplained weight loss;
- Pain in the upper abdomen, which sometimes extends to the back (and outgrowth of cancer);
- Jaundice – yellowness of the skin and whites of the eyes, dark urine (if the tumor blocks the bile duct);
- Weakness, dizziness, chills, muscle spasms, diarrhea (especially, if the cancer affects the islet cells, that produce insulin and other hormones).
These symptoms may be caused by other, less serious diseases. If you experience these symptoms, should see a doctor.
Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical exam. He may appoint a blood and urine tests, as well as check for hidden blood in the stool.
Tests may include:
- Roentgen upper gastro-intestinal tract – performing radiographs upper part of the digestive system after use barium salt solution;
- Computed tomography of the abdomen – type of X-ray using a computer, to make pictures of organs inside the abdomen;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRT) – test, which uses magnetic waves, to make pictures organovvnutri abdominal;
- US – examination, which uses sound waves to find tumors;
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERKhPG) – type of X-ray inspection, in which to take pictures of the liver, gallbladder, bile duct and pancreatic;
- Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography – type of X-ray, that shows blockages in the bile ducts of the liver;
- Angiography – X-rays of blood vessels, performed after the introduction of a radiopaque dye krovotork;
- Biopsy – removal of a sample of pancreatic tissue to test for cancer cells.
Treatment of pancreatic cancer
After detecting pancreatic cancer survey is conducted, allowing to determine the extent and scope of cancer. The method of treatment depends on the degree of spread of cancer.
Operation in pancreatic cancer
It can be made removal of a cancerous tumor and nearby tissue. Nearby lymph nodes are also sometimes have to be removed. In cancer, pancreatic operation may be performed to relieve symptoms. Methods of treatment by surgery includes:
- Procedure Uippla – removing a portion of pancreas, part of the small intestine, and some tissues around it chamti;
- Complete removal of the pancreas – removing the entire pancreas, part of the small intestine, part of the stomach, biliary tract, gallbladder, spleen and most of the lymph nodes in the area of cancer spread;
- Distal pancreatectomy – removing the body and tail of the pancreas.
Radiation therapy in pancreatic cancer
Radiation therapy – Use of radiation, to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. Therapy may be the following types:
- External radiation therapy – radiation is directed at the liver from sources outside the body;
- Internal radiation therapy – the radiation source is placed as close as possible to the cancer cells. Radiation granules or compounds are delivered directly into the tumor through a special catheter, which is in the hepatic artery, blood vessel, which brings blood to the liver.
Chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer
Chemotherapy – the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. Preparations for the chemotherapy may be given in various forms: tablets, injection, the introduction of a catheter. The drugs enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body, killing mostly cancer, and also some healthy cells.
Biological therapy in pancreatic cancer
Biological therapy involves using medications or substances, produced by the body. They are used to increase or restore the natural defenses against cancer. Substances, used in this form of treatment is also called biological response modifiers (MBR).
Combination therapy in pancreatic cancer
In most cases, pancreatic cancer is detected in the late stages. In this case, the operation may be inappropriate. If the operation can not be performed, Align used chemotherapy and radiation therapy, allowing to extend the life span.
Surgery is appropriate only 25% patients with pancreatic cancer at an early stage. After the operation, treatment is continued with the use of chemotherapy and radiation therapy, allowing in some cases to extend the life span.
Prevention of pancreatic cancer
If you are at risk of pancreatic cancer, The following measures will help reduce the risk of disease:
- We need to quit smoking;
- You need to reduce or stop alcohol consumption;
- Get rid of excess weight;
- Maintain a healthy diet;
- Take action, to prevent the occurrence of diabetes (eg, diet and exercise);
- Avoid exposure to carcinogens (eg, if you work in the petroleum or chemical industries).
