Jaundice – Yellowing of the skin
Description jaundice
Jaundice – yellowing of the skin, mucosas (including tissue lines the mouth) and the whites of the eyes. This is a sign of disorders of the liver and gall bladder. It can also occur when certain violations blood supply and metabolism.
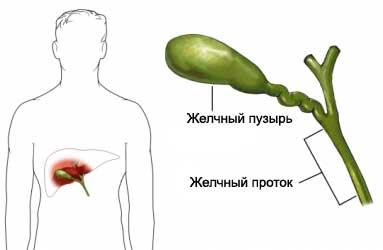
Causes of jaundice
Jaundice occurs due to excessive accumulation of bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin – substance tan bile, which is produced during the normal process of destruction of red blood cells in the body. Bile is a liquid, which are wastes (including bilirubin) liver. It also helps break down fats in the small intestine.
There are several causes of excessive accumulation of bilirubin. These include:
- Excessive disintegration of red blood cells, reasons which may be:
- Some forms of anemia;
- Some infectious diseases, such as malaria;
- Lock in the area of the liver, which prevents the flow of bile:
- Stones or pancreatitis;
- The tumor in the canal liver, or gallbladder;
- Pancreatic cancer;
- Birth defects, including biliary atresia;
- Pregnancy.
- Liver damage, which cause a variety of reasons:
- Viral hepatitis;
- Cirrhosis of the liver;
- Alcoholic liver disease;
- Side effects of certain drugs or environmental toxins;
- Children insufficient amount of certain liver enzymes during the first two weeks of life, perhaps, aggravated by breastfeeding;
- Hereditary metabolic disorders, syndromes including Gilbert, Crigler-Najjar and Dubin-Johnson.
Risk factors for jaundice
The risk factors for jaundice are reasons, which increase the risk of diseases of the liver and gall bladder. These include:
- Excessive alcohol consumption;
- Use of narcotics;
- Medication, which can damage the liver;
- Infection with hepatitis A (through contaminated food or water), hepatitis B or hepatitis C (through contaminated needles or unsafe sex);
- Exposure to certain industrial chemicals.
Symptoms of jaundice
Jaundice appears as a yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes and / or eyes.
Depending on the specific cause, which causes jaundice, there may be other symptoms, such as fatigue, fever, chills, and unexplained weight loss.
Diagnosis of jaundice
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical examination. He will ask you questions about:
- Alcohol and drugs;
- The presence of abdominal operations;
- Infected HIV;
- Family history of liver diseases.
Tests may include:
- Blood tests – test to detect elevated levels of bilirubin and liver enzymes, or other disorders, relating to the alleged cause of jaundice;
- Ultrasonography – test, which uses sound waves to study the internal organs, in this case, liver, gallbladder and bile ducts;
- CT – such as X-rays, which uses computer, to take pictures inside the body, in this case, liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and surrounding tissues;
- Kholangiografiya – invasive test, which uses X-rays and the introduction of a large needle into the liver to explore the gallbladder and bile ducts, sometimes performed during abdominal surgery;
- ERKhPG – It combines x-rays and examination using an endoscope. The procedure is done, to examine the duodenum (the initial part of the small intestine), bile duct and pancreatic duct. An alternative to ERCP test is magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography;
- Laparoscopy – introducing tube and other instruments through small incisions in the abdominal wall for the direct study of the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and other structures;
- Biopsy roasted – removing a sample of liver tissue for testing. This is usually done with a long needle.
Treatment of jaundice
Mild jaundice in newborns is normal and usually goes away without treatment. If the bilirubin rises above a certain level, the child can be assigned phototherapy – treatment with a special ultraviolet light. When Gilbert's syndrome, jaundice, usually, It occurs during stressful periods and goes away without treatment.
Most other types of jaundice, the specific cause of the disease. There are many ways to treat problems of the liver and gall bladder, depending on the specific disease. These include:
- Avoiding substances (alcohol or drugs), that cause jaundice;
- Eliminating the cause of anemia;
- Medication for the treatment of infectious diseases;
- The release of bile duct obstruction:
- Cutting tumors;
- Extraction of stones from the gallbladder;
- Removal of the gallbladder;
- Treatment of inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis).
If diagnosed with jaundice, you need to follow your doctor's instructions.
Prevention of jaundice
Prevention depends on the disorder, which causes jaundice. Sometimes it is impossible to prevent some violations. Nonetheless, You can take steps, that reduce the likelihood of developing liver disease:
- Limit your alcohol intake – no more than 100 grams per day for men and 50 grams per day for women;
- Be careful when mixing drugs, especially alcohol and prescription drugs;
- Avoid exposure to industrial chemicals;
- Do not use drugs;
- Practice Safe Sex;
- To reduce the risk of infection with hepatitis A, Get vaccinated hepatitis A vaccine;
- To reduce the risk of hepatitis B, make hepatitis B vaccine.
