Laparoscopy – Operation via the "keyhole"
Description laparoscopic surgery
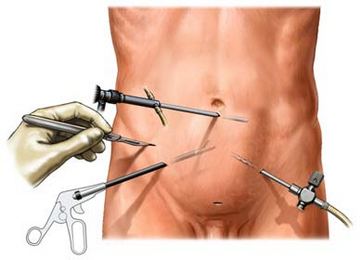
Laparoscopy – type of surgery, performed through a few small incisions in the abdomen. Through small incisions are introduced surgical instruments and a laparoscope (tiny camera with a light source), which allows the surgeon to see the target organs and perform surgical tasks necessary. This type of surgery is very popular, because it significantly reduces the recovery time. Also, in most cases, after the surgery are very small scars.
The reasons for laparoscopic surgery
Many types of operations can now be done with a laparoscope. In most cases, laparoscopy is used to perform the following operations:
- Treatment of hernia;
- Biopsy abdominal organs;
- Appendectomy;
- Colectomy;
- Removal of the gallbladder or gallstones;
- Tubal ligation;
- Surgery for an ectopic pregnancy;
- Hysterectomy;
- Removal of fibroids;
- Removal of the adrenal glands;
- Splenectomy;
- Lysis spaek abdominal.
Laparoscopy can also be made, to help establish an accurate diagnosis.
Possible complications of laparoscopy
Complications are rare, but no procedure does not guarantee the absence of risk. If you plan to laparoscopic surgery, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Infection;
- Bleeding;
- Damage to the blood vessels and organs;
- Problems, associated with anesthesia;
- The need to move with laparoscopic to open operation.
Factors, that may increase the risk of complications:
- Smoking;
- Obesity;
- Diseases of the heart and lungs;
- Previous abdominal surgery;
- Diabetes.
How is laparoscopic surgery?
Preparation for the procedure
Depending on the cause of the operation, your doctor may carry out and assign the following:
- Medical examination and revision of the medication;
- Blood tests (eg, pregnancy test, liver function, electrolyte status);
- Urinalysis to detect urinary tract infection and diabetes;
- US – test, which uses sound waves for medical imaging inside of the body;
- CT of the abdomen – such as X-rays, which uses computer, to make pictures of internal body parts;
- MRT – test, which uses magnetic waves, to make pictures of structures inside the body.
A few days before laparoscopy:
- Depending on the type of operation, perhaps, You need to take a laxative or use an enema;
- It is necessary to arrange a ride home after surgery;
- The night before, you can have a light meal. Unless otherwise stated by your doctor, Do not eat or drink for the night.
Consult your doctor about the drugs taken. A week before the surgery may need to stop taking some medicines:
- Aspirin or other anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Blood thinners, such as clopidogrel (Plaviks) or warfarin.
Anesthesia
The most commonly used general anesthesia, that supports the patient in sleep.
Procedure laparoscopy
After, as you fall asleep and no longer feel the pain, into the abdominal cavity of the needle will be inserted for introducing carbon dioxide. Gas will expand the stomach, which will allow the internal organs to see more detail. The laparoscope is inserted through a small incision in the skin. The laparoscope lights, increases, and transmits the image to the screen. Inspect the field operations.
If necessary, the abdomen will be made other cuts. Through these tiny instruments are inserted, to do a biopsy or surgery. After laparoscopic incisions are closed stitches or surgical staples are attached.
How long will a laparoscopy?
Time varies greatly, depending of the procedure.
Laparoscopy – Will it hurt?
You will experience pain and discomfort during recovery. The doctor will give pain medicine.
You may also feel some “inflation” or pain in the shoulders of the gas, used during the procedure. The discomfort may last up to three days.
Care after laparoscopy
Returning home, Follow your doctor's instructions, which may include:
- Remove the dressing the morning after surgery;
- Avoid heavy work;
- Do not drink carbonated beverages for two days after a laparoscopy.
Ask the doctor, when it is safe to shower, bathe, or to expose the surgical site to water. You can return to normal activities within one week.
If the procedure was carried out to diagnose diseases, the doctor will suggest options for further treatment. Biopsy results will be known in about a week.
Contact your doctor after laparoscopy
After returning home, you need to see a doctor, If the following symptoms:
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Redness, edema, increased pain, bleeding or discharge from the incision;
- Nausea and / or vomiting, that do not pass after taking the prescribed medicines, and persist for more than two days after discharge from the hospital;
- Pain, which does not pass after taking pain medication appointed;
- Headache, myalgia, a feeling of weakness or dizziness;
- Pain, burning, frequent urination or persistent blood in the urine;
- Difficulty urinating or defecating;
- Cough, shortness of breath or chest pain.
