Appendectomy – Appendectomy – Laparoscopic Surgery
Description of laparoscopic removal of the appendix
Appendectomy surgery to remove the appendix. The appendix is a small appendix, which is attached to the colon.
Causes Appendectomy
Appendectomy is most often done as an emergency operation to treat appendicitis. Appendicitis – inflammation of the appendix, which may be caused by infection or obstruction.
Complications of Appendectomy
Complications are rare, but no operation ensures no risk. Before, how to perform the appendectomy, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Bleeding;
- Infection;
- Damage to other organs;
- Reaction to anesthesia.
Factors, that may increase the risk of complications:
- Smoking;
- A ruptured appendix;
- Age: 65 and older;
- Obesity;
- Diabetes;
- Chronic lung disease or heart disease;
- Pregnancy.
How is laparoscopic appendectomy?
Preparing for Surgery
The doctor performs the following tests:
- Physical examination;
- Blood and urine tests;
- Roentgen – to take pictures of structures inside the body;
- Ultrasonography – test, which uses sound waves, to find the appendix and other organs;
- CT scan – X-ray examination, which uses computer, to take pictures inside the body.
Since appendicitis can occur unexpectedly, appendectomy – Emergency surgery, and the delay in its conduct can cause complications.
Anesthesia
During the operation using general anesthesia. During the operation, the patient is asleep. To facilitate the breathing tube is inserted into the throat for ventilation.
Description of the procedure
The abdomen will be made three small incisions. In one of the sections of the laparoscope is inserted (special tool with a camera on the end). The abdominal cavity is injected carbon dioxide, the better to see the internal organs. Other instruments are entered in the remaining sections. The camera will send images of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity on the screen. The doctor will use it to find and remove the appendix.
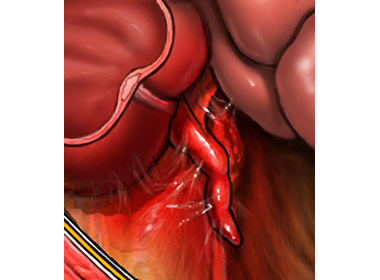
The appendix is separated from the surrounding tissue. The doctor stops the bleeding from blood vessels. The appendix is then cut. Opening, where the appendix was connected to the intestine, cramp. Laparoscopic instruments are removed, incisions are closed with stitches or staples seams.
After appendectomy
Removal of the appendix is investigated in the laboratory.
How long does the surgery?
Operation takes one to two hours.
Will it hurt?
Anesthesia will prevent pain during surgery. To facilitate postoperative pain painkillers are administered to the patient.
The time spent in hospital
After surgery, the patient is discharged from the hospital on the same day, if there were no complications.
Postoperative care after appendectomy
In the hospital
- You can get out of bed at six hours after surgery.
Nursing homes
Recovery takes 1-2 of the week. When you return home, you need to perform the following actions, to ensure the normal recovery:
- You can resume normal preoperative diet;
- The patient may be given antibiotics to fight infection. It is necessary to go through the entire course of the reception, even if the condition has improved;
- It is necessary to keep the incision clean and dry;
- We need to ask the doctor about, when it is safe to shower, bathe, or to expose the surgical site to water;
- It is necessary to wash your hands before changing the dressing;
- You must rest for 1-2 weeks;
- You can not play sports or do heavy labor from one to several weeks, as prescribed by your doctor;
- Gradually the need to increase the activity, in accordance with the instructions of the doctor;
- Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions.
It is necessary to go to the hospital in the following cases
- There are signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Redness, edema, increased pain, bleeding or rupture of the seam on the cut;
- Cough, breathlessness, chest pain, severe nausea or vomiting;
- Increased abdominal pain;
- Fainting and dizziness;
- Blood in the stool.
