Laryngoscopy
Description laryngoscopy
Laryngoscopy – visual inspection of the larynx and vocal cords. There are two main types of laryngoscopy:
- Indirect laryngoscopy – for the study of the larynx and hypopharynx (part passage to the lungs and stomach) used mirror;
- Direct laryngoscopy – for inspection using a special tool – laryngoscope – tube with a light source at the end.
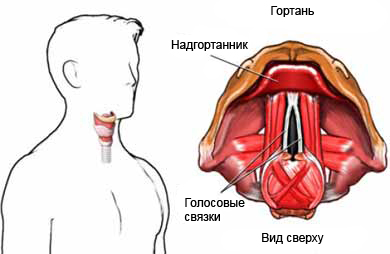
Reasons for laryngoscopy
Laryngoscopy is used to examine and diagnose problems in the throat. It is most often done:
- To diagnose the cause of cough, bloody cough, hoarseness, sore throat or halitosis;
- To find the causes difficulty swallowing;
- To evaluate possible causes constant pain in the ear;
- To remove a foreign body;
- To find a throat tumor.
Possible complications of laryngoscopy
If you plan to laryngoscopy, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Pain;
- Vomiting and nausea;
- Excessive swelling or bleeding in the throat;
- Lesions of teeth on the underside of the tongue;
- Bleeding from the nose, If the laryngoscope is inserted through the nose;
- The negative reaction to anesthesia.
How is laryngoscopy?
Preparation for the procedure
Before the operation can be carried out:
- Medical checkup;
- Chest X-ray;
- Radiopaque barium study – X-rays of the larynx and esophagus, which occurs after ingestion of barium solution containing liquid;
- CT scan – type of X-ray, which uses a computer to take pictures of structures inside the body.
In the run-up to the procedure:
- When using general anesthesia or sedation is necessary to organize a trip to the hospital and back home after the procedure;
- If during the operation will be applied general anesthesia, You can not eat or drink for eight hours before the examination. In carrying out the procedure under local anesthesia, there is no need to comply with this requirement.
Consult your doctor about the drugs taken. A week before surgery you may be asked to stop taking some medicines:
- Aspirin or other anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Blood thinners, such as clopidogrel (Plaviks) or warfarin.
Anesthesia
When laryngoscopy can be used topically or general anesthesia. Local anesthesia numb the throat. When using general anesthesia, you will sleep during the inspection.
Procedure laryngoscopy
In carrying out any type of laryngoscope may be made photos.
Indirect laryngoscopy
You will sit up straight in a chair with a high back. The jaw and the head will be fixed in a special holder. Anesthetic spray is sprayed into the throat. You will need to rinse the throat and spit anesthetic solution. Language will be closed with gauze. You will then need to breathe through the mouth in such a way, as if you are choking. The mirror is introduced into the back of the throat. The doctor will ask you to pronounce the sound “eeee”. At this time, the doctor will monitor the larynx. If the larynx has a foreign object, eg, bone stuck, it can be removed.
Direct laryngoscopy Fibreoptic
The direct method is most often carried out after the application of the indirect method. The direct method allows the doctor to better examine the throat. The direct method may also be used, If the gag reflex does not allow for a thorough examination using the indirect method. Through the nose or mouth and into the throat is inserted laryngoscope. Through the eyepiece of his doctor can examine the larynx. The doctor may then collect samples for analysis, conduct the removal of tumors, or remove the foreign body, stick in one's throat. This method is often performed in the operating room under general anesthesia.
How long will laryngoscopy?
An indirect laryngoscopy only takes a few minutes. Direct laryngoscopy takes about 5-45 minutes, depending on the complexity of the problem.
It will hurt during laryngoscopy?
Anesthesia will prevent pain during the procedure. Under the direct method, throat pain can be felt within a few days, especially if there was made biopsy.
Care after laryngoscopy
If the tissue sample has been removed, he will be sent to a lab for testing.
Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions, which may include:
- Do not smoke for 24 hours after treatment. Smoke irritates the throat;
- Do not try to swallow, has not yet resumed the gag reflex. Spit saliva and release. Gag reflex should reappear after about two hours after laryngoscopy. At that time, candy or a liquid gargle will help decrease hoarseness and throat irritation;
- If a biopsy was performed, Avoid coughing or coughing.
The doctor may discuss with you the results of examination and treatment options or refer you to a specialist. The biopsy results will be ready in 3-5 days.
Contact your doctor after laryngoscopy
After discharge from the hospital need to see a doctor, If the following symptoms:
- Increased pain;
- Cough, isolation or vomiting blood;
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing;
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Hoarse voice;
- Cough, breathlessness, chest pain, or severe nausea or vomiting.
