Complex regional pain syndrome
Description of the complex regional pain syndrome
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) It refers to chronic diseases, that affect the nerves and blood vessels of one or more limbs. The disorder involves unpleasant burning sensation, puffiness, Sweating, color changes and other symptoms.
There are two types of CRPS:
- CRPS 1 (also called reflex sympathetic dystrophy or RSD) – siptomy diseases occur in intact nerves;
- CRPS 2 (also called causalgia) – Symptoms occur when nerves intact.
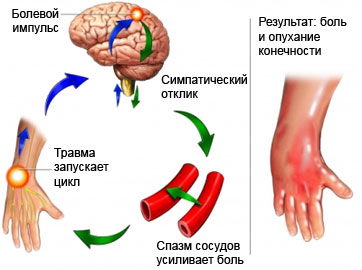
The causes of complex regional pain syndrome
The cause of CRPS is not known. Disease, probably, It is the result of coincidence of several factors, for example may include hyperactivity of the sympathetic nervous system. Also, in the event of disturbances can act as an inflammation of the nerve fibers.
Risk factors for complex regional pain syndrome
Factors, which can cause complex regional pain syndrome, They include:
- Trauma;
- Fractures;
- Cuts;
- Burns;
- Chilblain;
- Operation;
- Penetrating injuries;
- Crush injury;
- An injection into the muscle;
- Hemorrhage;
- Diabetic neuropathy;
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Stroke;
- Carpal tunnel syndrome.
The symptoms of complex regional pain syndrome
These symptoms, in addition to the complex regional pain syndrome, They may be caused by other diseases.
Most often suffer from upper limb, especially hands. Symptoms may progress and change in the course of the disease. The pain may spread from one part of the body to another. Many doctors describe symptoms in terms of stages of.
Within a few hours or days after injury
Symptoms may include:
- Severe pain or burning, usually, heavier, than expected;
- Sensitivity to touch or even a light breeze;
- Swelling of the hands or feet;
- Strong sweating;
- Too warm or cold skin;
- Changes in the appearance of hair and nails.
Symptoms can be aggravated by the presence of stress and worsen over time.
3-6 months after injury
Symptoms may include:
- Burning pain above and below the primary areas of trauma;
- Hard swelling of the hands or feet.
- Muscle cramps or weakness;
- Limbs become cold;
- Slow hair growth;
- Brittle nails.
Six months or later after injury
Symptoms may include:
- Pale, blue, and / or shiny skin;
- Restricted joint mobility;
- Loss of muscle mass.
Diagnosis of complex regional pain syndrome
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical examination. To diagnose CRPS doctor uses four criteria:
- Injury or onset of pain in the limbs, and save it for some period of time;
- Continuing pain in the limb, reaction to any stimulus, even light touch;
- History of edema, changes in skin blood flow, or temperature of the affected limb;
- The absence of other causes for the symptoms.
They can be assigned to additional tests, to rule out other diseases:
- You must meet snapshots problem limbs. For this purpose, the following methods:
- Roentgen;
- Bone scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRT);
- Maybe, must be tested electrical activity of nerves and muscles,. For this purpose:
- Nerve conduction study;
- Rheotachygraphy;
- Sometimes it is necessary to measure the temperature of various parts of the body. This can be done by using thermography;
- You may need to estimate the autonomic nervous system via quantitative test sudomotornogo axon reflex (KTSAR).
Treatment of complex regional pain syndrome
Treatment is directed at reducing pain and improving the function of the affected organ. In some cases, the disease is in itself (more common in children).
Treatment includes:
- Biofeedback;
- Acupuncture;
- Physiotherapy – active and passive exercises help maintain the functioning. Classes in the warm pool will improve health;
- Mirror Therapy (with mirrored cabinet) – to a patient in the sagittal plane mirror located so, that it reflects a healthy limb. This visual inspection is carried out only for the healthy limb and its reflection, which creates the patient visual illusions, if both halves of the body are functioning properly. Mirror therapy can reduce pain and improve motor function in people with CRPS, arisen as a result of stroke;
- Stimulation nervrv through a variety of devices:
- Transcutaneous nerve stimulation – the device is worn on the skin surface, which creates a tingling sensation, and in some cases can alleviate the pain;
- Implantable Spinal Cord Stimulators – It may be useful for some patients;
- Drugs, such as:
- Antitrevozhnыe drugs, Lower doses of antidepressants and drugs, used for the treatment of epilepsy;
- Painkillers;
- Bisfosfonatы – preparations, used to treat osteoporosis;
- Steroids;
- Drugs, are applied to the skin, eg, capsaicin and dimetilsulyfoksid;
- The blockade of the sympathetic nerves – injection drugs, that delay signals, passing through the sympathetic nerves. In some cases, can temporarily relieve the pain;
- Sympathectomy – if the nerve block is successful, a surgeon can permanently destroy sympathetic nerves. But, In some cases, surgical intervention can worsen symptoms;
- Psychological support – Long-term pain often leads to depression or alarm. Advice needed, to help patients deal with chronic pain and loss of function of a limb.
Prevention of complex regional pain syndrome
Quick mobilization after surgery or injury can minimize the risk of CRPS in the affected extremity. Other steps, that may be useful:
- The use of painkillers immediately after the injury;
- Using the blockade of the sympathetic nerves after injury;
- Application of desensitization, if necessary;
- The use of vitamin C may reduce the risk of CRPS after a wrist fracture.
