Bradycardia
Description bradycardia
Bradycardia – an abnormally slow heart rate. In adults, bradycardia is defined as a heart rate less than 60 bpm. There are several types of bradycardia (collectively “ʙradiaritmii”):
- Sinusovaya bradycardia – slow heartbeat due to heart disease, reaction to the drug or for any other reason;
- Sick sinus syndrome – an unusually slow heartbeat due to problems of the natural pacemaker of the heart (atrionector);
- Heart block (atrioventrikulyarnaya blockade) – an unusually slow heartbeat due to slowing or blocking of electrical impulses in the conducting system of the heart.
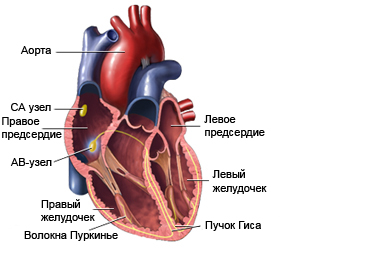
Causes of bradycardia
Bradycardia may cause:
- The normal reaction to:
- Deep relaxation;
- Being in excellent physical shape;
- The natural pacemaker of the heart is not working properly, with the result that appears abnormal rhythm;
- Problems with the electrical conductivity of normal cardiac nerves;
- The function of the natural pacemaker of the heart intercepts another.
Risk factors for bradycardia
Factors, which increases the risk of bradycardia:
- Advanced age;
- Gipotireoz;
- Medicines, frequently used to treat certain diseases:
- Clonidine and other alpha2 agonists central action (high blood pressure);
- Cholinesterase inhibitors (Alzheimer's disease);
- Calcium antagonists (high blood pressure, Heart Disease);
- Digitalis and other cardiac glycosides (heart failure, and arrhythmia);
- Preparations lithium;
- Beta Blockers (high blood pressure, heart disease), and the use of some eye drops;
- Exposure to certain toxins;
- Heart disease, such as:
- Heart attack;
- Degeneration, calcification;
- Congestive heart failure;
- Valvular insufficiency;
- Heart disease, which are inherited or present at birth (congenital heart disease);
- Electrolyte imbalance (high or low potassium);
- Sleep apnea;
- Rarely – lupus or other collagen vascular diseases;
- Head Injury;
- Gipotermiя;
- Gipoglikemiâ;
- Infectious diseases, such as:
- Diphtheria;
- Rheumatic fever;
- Viral myocarditis;
- Lyme Disease;
- Chagas disease.
The symptoms of bradycardia
Some types of bradycardia are asymptomatic. Others may cause noticeable symptoms, such as:
- Fainting or loss of consciousness;
- Dizziness, feeling dizzy;
- Weakness;
- Light fatigue;
- Cardiopalmus;
- Breathlessness;
- Chest pain;
- Low blood pressure (hypotension).
Severe bradycardia, such, as the complete heart block, require immediate medical attention. They can lead to loss of consciousness or sudden cardiac arrest.
Diagnosis of bradycardia
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical exam. In particular, doctor listens to the heart with a stethoscope.
Tests may include:
- Blood tests – to look for certain abnormalities, that may explain the bradycardia (eg, electrolytes, Glucose, thyroid dysfunction and the level of certain chemicals);
- Electrocardiogram – test, that records heart activity by measuring electrical current through the heart muscle;
- Echocardiogram – test, which uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound), to examine the size, shape and motion of the heart;
- Holter Monitor – portable device for the continuous recording of heart rate during normal daily activities;
- Stress test – test, which records the electrical activity of the heart during increased physical activity;
- Nuclear scanning – injected into a vein and observed radioactive material, he spreads the heart muscle. It allows you to determine the presence of coronary heart disease;
- Coronary angiography – after the introduction of a radiopaque dye into the artery to take pictures of blood vessels, that allows the doctor to find abnormalities in the coronary arteries of the heart.
Treating bradycardia
If heart disease is not found, and there are no signs of abnormal heart functionality, Treatment may not be required. Your doctor may periodically monitor the heart rhythm. Patients with symptoms of heart disease usually requires treatment.
Treatment of symptomatic bradycardia, and may include:
- Stopping medications, that slow the heart rate;
- Diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the heart;
- Intravenous administration of atropine – It can be used to temporarily increase heart rate;
- Artificial pacemaker (pacemaker) – the device may be temporarily or permanently implanted under the skin of the chest wall. Every time, when the heart rate falls, pacemaker generates electrical pulses, needed to create and maintain a normal heart rhythm.
Prevention of bradycardia
To prevent bradycardia:
- It is necessary to treat the disorder, which can lead to bradycardia;
- Carefully follow your doctor's instructions when using drugs (especially those, that can potentially cause bradycardia);
- Check with your doctor or pharmacist before using medication or supplements, To make sure, they do not interact with other drugs;
- Follow the general recommendations for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases:
- Maintain a healthy weight;
- Talk to your doctor about safe methods of exercise performance;
- Quit smoking;
- Eat a healthy diet, Low in saturated fat and more cereals, fruits and vegetables;
- Take the treatment of high blood pressure and / or diabetes mellitus;
- Take your medicines, lowering high cholesterol or triglycerides.
