Femoropopliteal bypass – Bypass leg arteries
Description bypass leg arteries
In this operation, use of the artificial tube or a vein to create a main artery bypass a blocked leg. Blocking of the arteries in the legs, usually, caused by the accumulation of plaque (plaques) on their inner walls. This buildup is called peripheral arterial disease (PAD).
Causes of leg artery bypass grafting
- To restore proper blood supply to the lower leg;
- To ease the pain in the legs, caused by a blocked artery;
- To avoid amputation.
Possible complications of femoral-popliteal bypass surgery
If surgery is planned, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Bleeding;
- Blood clots (eg, blood clots, causing the lock bypass place);
- Infection;
- Adverse reaction to anesthesia;
- Damage to organs;
- Need for amputation;
- Heart attack or death.
How is the femoropopliteal bypass?
Preparation for the procedure
They may be assigned or conducted the following procedures:
- Blood tests;
- Electrocardiogram – test, which detects heart activity by measurement of electrical current through the heart muscle;
- Chest X-ray – test, which uses X-rays, to make pictures of structures inside the body;
- Ultrasonography – test, which uses sound waves, to see images of organs inside the body.
On the eve of the operation:
- Consult your doctor about the drugs taken. A week before surgery you may be asked to stop taking some medicines:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (eg, aspirin)
- Blood thinners, such as clopidogrel (Plaviks) or warfarin;
- As directed by the doctor need to take antibiotics, to prevent infection;
- Organize home care after surgery;
- In the evening before surgery you can eat a light dinner. Do not eat or drink anything after midnight.
Anesthesia
It can be used:
- General anesthesia (almost always) – blocks pain and puts the patient to sleep at the time of surgery;
- Spinalynaya anesthesia – the area from the chest down anesthetized. Provided in the form of injections in the back.
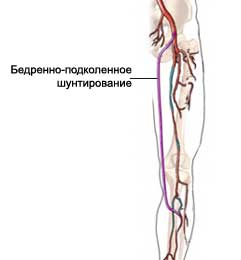
Procedure leg artery bypass grafting
The doctor makes an incision in the skin on the leg. Through this incision the doctor takes a vein, which will be used to circumvent. If Vienna can not be used, the use of artificial veins.
Further, It will make an incision in the groin, to reach the femoral artery. The doctor will make another incision in the back of the knee to reach the other, popliteal artery.
The doctor will use clamps, to block the flow of blood through these two arteries. One end of a bypass vein is sewn into the femoral artery, and the other end will be sewn into the popliteal artery. After the procedure the blood will again be submitted through graft, to test a new vessel for leaks. If a leak is detected, the doctor removes clips. This allows blood to flow through the graft. The doctor closes the incision using sutures.
In some cases, Vienna on hip will be used as a graft without removing it. In this procedure, the vein part is separated from the main vein by using a cutting tool. Vienna will then be sewn to the arteries, to form a graft.
Immediately after treatment
- First 24-48 hours may be administered through the IV fluid and painkillers;
- Maybe, you will have to wear an oxygen mask 10-12 hours after surgery;
- Needle for epidural anesthesia may be left in place during the first 3-5 days, to reduce pain. Once it is removed, the doctor will give you pain medicine.
How long will the femoral-popliteal bypass?
1-3 o'clock.
Femoropopliteal bypass – Will it hurt?
The pain may be felt for weeks or even months. Ask your doctor about pain medications, to reduce pain. Keep in mind, that the foot may be swollen for 2-3 months.
The average hospital stay
7-10 days.
Care after femoropopliteal bypass
Care in a hospital
During recovery, the hospital may be granted:
- First 1-2 Day use cold compresses, to reduce pain and swelling. The nurse will put a cold compress on the area of surgery 15-20 minutes;
- You can wear boots or special socks to help prevent blood clots;
- You may be asked to use an incentive spirometer, to breathe deeply and cough frequently. This will improve lung function;
- The incisions will be inspected, to timely detect signs of infection.
Home Care
When you return home, Follow these steps:, to ensure the normal recovery:
- Do not drive for 4-6 weeks, or held until the pain and swelling;
- If your doctor advises, you need to go every day. Walking will make legs more. Gradually increase the distance traveled;
- Work with a physical therapist;
- Gradually return to daily activities;
- When sitting, Keep your feet in the raised position;
- Puts a pillow under your legs during sleep;
- Ask the doctor, when it is safe to shower, bathe, or to expose the surgical site to water;
- Keep the wound dry. Avoid using talc or powder;
- Avoid fatty foods;
- Do not smoke. Smoking can interfere with healing;
- Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions.
Contact your doctor after femoropopliteal bypass
After discharge from the hospital need to see a doctor, If the following symptoms:
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Severe pain in the leg;
- The feet become cold, pale, blue, It felt tingling or numbness;
- Redness, edema, increased pain, bleeding or discharge from the incision;
- Nausea, vomiting or constipation;
- Pain, which does not pass after taking pain medication appointed;
- Cough, shortness of breath or chest pain;
- Dizziness and weakness;
- Pain and / or swelling of the legs, calves and feet;
- Pain, burning, frequent urination or persistent bleeding in the urine;
- New disease symptoms.
