Peptic ulcer disease – Stomach ulcer or duodenal ulcer
Description of peptic ulcer
Peptic ulcer disease – pain in the gastric mucosa or the initial part of the small intestine, duodenum. Peptic ulcer disease is characterized by its location:
- Ulcer stomach – stomach;
- Duodenal ulcer – into the duodenum.
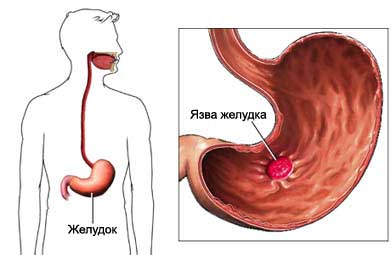
Causes of peptic ulcer
Disturbances in the balance of gastric acid and digestive juices can lead to ulcers. It can cause:
- Helicobacter pylori bacterium (H.pylori);
- The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – block the body's ability to protect the gastric mucosa;
- Disease, which cause an increase in the amount of acid, such as Zollinger-Ellison.
Not all people, who take NSAIDs or infected with Helicobacter Pylori risk of occurrence of ulcer.
Rare causes of ulcers include:
- Radiation therapy;
- Bacterial or viral infections;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Trauma;
- Severe stress (eg, operation, trauma, traumatic brain injury, shock, or burns).
Risk factors for peptic ulcer
Risk factors for ulcer from H. pylori infection:
- Age: 60 and older;
- Paul: male;
- The lower socio-economic groups;
- Unsanitary living conditions;
- Cigarette smoking;
- Family history of peptic ulcer disease;
- First blood.
Risk factors for ulcer from taking anti-inflammatory drugs:
- Age: 60 and older;
- Paul: male;
- History of stomach disorders from NSAIDs;
- Previous peptic ulcer;
- Cigarette smoking;
- Alcohol abuse.
The symptoms of ulcer disease
Peptic ulcer disease does not always cause symptoms. Symptoms may come and go. Stomach pain after eating, in ulcer, may increase. Also, the food often relieves the pain in the duodenum.
Symptoms include:
- Gnawing pain:
- Sometimes the pain is impossible to sleep;
- May change during the meal;
- It may last from a few minutes to a few hours;
- Feeling unusually strong hunger;
- Nausea;
- Vomiting;
- Loss of appetite;
- Swelling;
- Belching.
Ulcers can cause serious problems and severe pain in the abdomen. Problems include:
- Bleeding – symptoms may include:
- Black, tarry stools;
- Vomiting, that looks like coffee grounds;
- Weakness;
- Dizziness;
- Anemia;
- Perforated ulcer – break the wall of the stomach or duodenum, and then may receive:
- Sudden and severe pain;
- Scar tissue, which restricts and eventually closes the exit from the stomach into the intestine and can cause:
- Vomiting;
- Weight Loss;
- Severe pain.
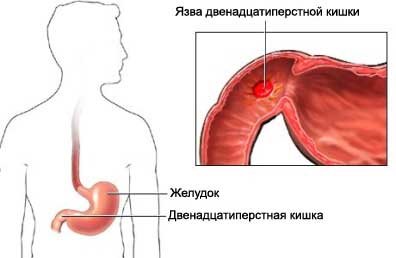
Diagnosis of gastric ulcer or duodenal ulcer
The doctor asks about the symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical examination. Tell your doctor about all the medicines, that you take.
Tests may include:
- Rectal examination and test to detect hidden blood;
- A blood test or breath test – to verify the presence of Helicobacter Pylori infection;
- A blood test may also show the presence of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome;
- Roentgen upper gastro-intestinal tract – performed after drinking a barium sulfate solution;
- Endoscopy– in a thin tube is inserted down his throat, allowing to examine the gastrointestinal tract. The procedure used for the next:
- Preparation of tissue samples, to test them for infection of Helicobacter Pylori or cancer;
- To rule out other causes of gastrointestinal symptoms.
The treatment of ulcers of the stomach or duodenum
The goal is, to eliminate the source of the problem and heal the ulcer. The healing of gastric ulcers can take a long time.
Treatment includes:
Medication
Some medications block or reduce acid production. Some create a skin ulcer on, to close it. If ulcers caused by h. pylori, you need to take a combination of drugs to kill bacteria. It usually consists of antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors. It is important to take these drugs on prescription. Your doctor may order additional tests through 6-12 months after treatment. This is done, To make sure, bacteria that disappeared.
Medications may include:
- Antacids – may provide some relief from heartburn, not heal ulcers;
- Antibiotics (eg, amoksiцillin, tetracycline and clarithromycin);
- Bismuth-containing drugs;
- Proton pump inhibitors – decrease the production of stomach acid (eg, omeprazole, lansoprazole);
- N2-blockers – to reduce stomach acid formulation (eg, famotidin, ranitidine, cimetidine, nizatidin);
- Medications to cover the ulcer (eg, sucralfate);
- Medications to protect stomach against NSAID damage (eg, Misoprostol).
Lifestyle changes
- If you smoke, you need to quit smoking. Smoking interferes with ulcer healing;
- Do not drink alcoholic beverages;
- NSAIDs should be avoided, Taki how aspirin and ibuprofen;
- Spicy or fatty foods may worsen symptoms of ulcers. Keep in mind, that these products do not cause ulcers, and do not affect its healing.
- If stress increases ulcer pain, to learn and practice stress management techniques.
Surgery and Endoscopy
If there is bleeding, perforation or neprohodimosty, perhaps, need surgery. Surgical options include:
- Selektivnaя (Election) vagotomy – It is the technique of the cut-off of the vagus nerve. This operation does not require additional drainage;
- Vagotomy combined with antrumectomy (antrektomiey) – operation involves cutting off the vagus nerve in combination with removing the bottom part of the stomach (pylorus). Gatekeeper generates chemical, which promotes the development of acid. Without this chemical acid level falls.
Endoscopy
It can be used, krovotechenie.Tonkuyu to stop tube is inserted through the throat into the stomach or intestines. Then, using heat, electricity, adrenaline, or a substance, called “fibrin glue” early, causing bleeding closes.
Vagotomy and drainage
Vagotomy – cut off part of the vagus nerve. This procedure can greatly reduce acid production. Stripping all the nerve can lead to problems with stomach. In this case it should be created drainage. Drainage can be done one of two ways:
- Pyloroplasty – an increase in the gap between the stomach and duodenum, allowing stomach contents easy to get into the intestine;
- Gastroduodenostomiya – creating a new compound (anastomosis) between the stomach and duodenum;
- Gastrojejunostomy – create a new connection between the stomach and the scrawny gut (part of the small intestine).
Two other forms of vagotomy include:
- Selective vagotomy – It cuts off only part of the vagus nerve; It requires no additional drainage;
- Vagotomy with antrektomiey – the vagus nerve is cut and removed the lower part of the stomach (privratnik). Gatekeeper generates chemical, which stimulates the production of acid.
Prevention of ulcers of the stomach or duodenum
To reduce the risk of ulcers from H.pylori infection:
- Wash your hands after using the toilet, before eating or preparing food;
- Drink clean water;
- Do not smoke. Cigarette smoking increases the likelihood of ulcers.
To reduce the risk of ulcers from NSAIDs:
- Use other medications, where possible;
- Take the lowest possible dose of medication;
- Do not take the drug longer, than necessary;
- Do not drink alcohol while taking medicines;
- Ask your doctor about switching to a new NSAIDs. Ask your doctor about taking other drugs to protect the stomach and intestines;
- Do not smoke. Smoking increases the likelihood of ulcers.
