Endoscopy of the upper gastrointestinal tract – Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Description of upper gastrointestinal endoscopy
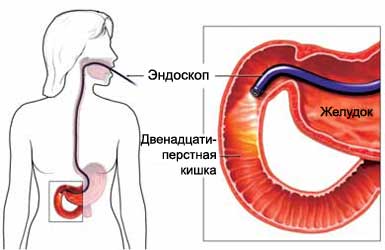
Endoscopy of the upper gastrointestinal tract – test, which uses a fiber-optic instrument for the study of the esophagus (throat), stomach and upper small intestine.
Causes reduction of upper gastrointestinal endoscopy
Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy may be imposed in the case of the following disorders:
- Abdominal pain;
- Severe heartburn;
- Constant nausea and vomiting;
- Difficulty swallowing;
- Blood in the stool or vomit;
- Detecting anomalies in the X-rays or other examination of the gastrointestinal tract.
Disease, which can be diagnosed using endoscopy, upper GI:
- Ulcers;
- Tumors;
- Polyps;
- Abnormal narrowing;
- Inflammation.
Possible complications of upper gastrointestinal endoscopy
Complications are rare, but the procedure does not guarantee the absence of risk. If you plan to upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Bleeding;
- Damage to the esophagus, stomach or intestines;
- Infection;
- Respiratory depression (reduction of frequency and / or depth of respiration);
- Reaction to sedatives or anesthesia.
Some factors, that may increase the risk of complications:
- Age: 60 and older;
- Pregnancy;
- Obesity;
- Smoking, alcoholism or drug use;
- Malnutrition;
- Recent illness;
- Diabetes;
- Heart or lung disease;
- Blood clotting;
- The use of some drugs.
We need to discuss these risks with your doctor before the test.
How is esophagogastroduodenoscopy?
Preparation for the procedure
In anticipation of the upper gastrointestinal endoscopy:
- Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics;
- We need to organize a trip home after the test. Besides, We need to organize care at home after endoscopy;
- On the eve of the procedure in the evening you can eat a light meal. Do not eat or drink for 6-10 hours before the test;
- Tell your doctor about taking any medications. A week before surgery, perhaps, you need to stop taking certain drugs:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (eg, aspirin);
- Blood thinners, such as clopidogrel (Plaviks) or warfarin.
Procedure upper gastrointestinal endoscopy
To numb the throat, It can be assigned to gargling solution anesthetic. It may also be used as a spray anesthetic. After the catheter may be introduced sedative. This will help you relax during the test.
You may be asked to lie on your left side. Connected sensors to monitor breathing, heart rate and blood oxygen levels. If a sedative, It is fed through the nose for breathing supplemental oxygen.
In the mouth it is inserted into a special mouthpiece, to help keep it open. During the test, a small suction tube will be used for the removal of liquids and saliva from the mouth. The endoscope will be lubricated and put into the mouth. He will be cautious and move slowly through the esophagus to the throat, in the stomach and intestine.
With the introduction of the endoscope, the doctor will see on the screen an image of the internal organs. Through the endoscope into the gastrointestinal tract of air may be introduced, smoothing wrinkles in fabric. This allows the physician to examine in more detail the area of interest to him. Also through the endoscope can be introduced miniature tools, to spend Biopsie or other tests.
After upper GI endoscopy
After testing you for an hour under the supervision of. You will then be allowed to return home.
After returning home, follow these steps:, to ensure the normal recovery:
- Relax, when you are at home;
- Ask your doctor, whether it is possible to resume a normal diet;
- Sedatives can slow the response time. Do not drive or operate machinery with the remainder of the day;
- Avoid alcohol the rest of the day;
- Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions.
How long will the upper gastrointestinal endoscopy?
About 10-15 minutes.
Endoscopy of the upper gastrointestinal tract – Will it hurt?
During the test will feel discomfort, after endoscopy is sore throat. Besides, you may feel bloated after the test.
The results of upper gastrointestinal endoscopy
The survey gives the physician information about the state of the digestive system. The results may help to explain the existing symptoms. According to the results of endoscopy doctor can prescribe treatment or further evaluation.
Contact your doctor after upper GI endoscopy
After the test, you need to see a doctor, if there was any of the following symptoms of:
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Severe abdominal pain;
- Constipation;
- Difficulty swallowing and breathing;
- Any change or worsening of initial symptoms;
- Bloody or black stools;
- Nausea and / or vomiting;
- Cough, shortness of breath or chest pain;
- Bleeding.
