Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty
Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty Description
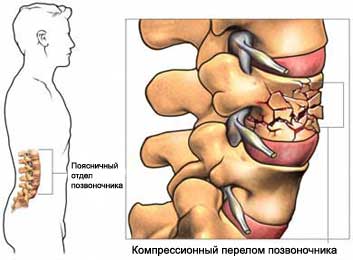
Vertebrae – several bones, components of the spine. When a fracture of a vertebra, it can put pressure on surrounding nerves and cause severe pain and disability. With vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty bone can be restored.
When vertebroplasty in the fractured vertebra acrylic cement is injected. The cement strengthens the bone and decreases pain from the fracture.
During the balloon kyphoplasty is used to create a cavity for the introduction of cement. This procedure is designed to relieve pain. It can also reduce the deformation of the spine fractures.
Reasons for vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty
Both procedures are used, to reduce the pain of vertebral fractures. Kyphoplasty also restores the shape of the bones. Treatments can reduce the deformation of the spine, cause destruction of the vertebrae.
Other methods of treating fractures of the spine may include nonsurgical treatments, such as bed rest, Wearing supporting brace and taking pain.
Possible complications of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty
Complications are rare, but no procedure does not guarantee the absence of risk. If you plan to vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Leakage of cement into the spinal canal or into adjacent veins;
- Infection;
- Bleeding;
- Increased back pain;
- Vertebral fracture or adjacent edges;
- Numbness, tingling in the spine;
- Paralysis.
In some cases, the physician may decide, the risk of complications after the procedure is too big. Factors include increased risk:
- Vertebral fractures, which spread to the spinal canal;
- Radikulopatiâ – irritation of the nerve roots in the area of the fracture, which often causes numbness, tingling or weakness in the legs;
- The presence of recurrent infection;
- Blood clotting;
- Soft or porous bones.
If there was a fracture of the vertebrae due to osteoporosis, vertebroplasty may not be effective.
Besides, Smoking may increase the risk of complications.
How is the vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty?
Preparation for the procedure
- It is necessary to undergo a full medical examination and blood tests;
- Medical imaging techniques used back, such as:
- Talk to your doctor about taking any medications. You may be asked to stop taking certain medicines a week before the procedure,:
- Aspirin or other anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Blood thinners, such as clopidogrel (Plaviks) or warfarin;
- Do not eat for at least six hours before the procedure. Drink fluids need to stop for 3-6 hours before the procedure.
Anesthesia
- Most of the operations carried out by administering a sedative and local anesthesia. Sedation will help you relax. It is used as a local anesthetic, that numb the area of the operation;
- In some cases, it may be used general anesthesia.
Description of the procedure of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty
Vertebroplasty
You will be asked to lie on your stomach. Around you will be located X-ray cameras, that will show images of bones on a monitor. The doctor will use it, to adjust the position of the needle and the introduction of cement.
The skin over the fractured bone will be anesthetized and sterilized. A hollow needle is inserted into the vertebra. Acrylic cement stirred until the consistency of toothpaste. The cement is added contrast agent, which will improve the X-ray image. When the needle reaches the desired location, cement will be injected into the fractured bone. The doctor will monitor the introduction of cement, its position in the bone bonding strength and check.
Kyphoplasty
The doctor makes a small incision in the back. A tiny drill used to create holes in the bone. Through Hole introduced special air balloon, which then inflates, to open up the space for introducing cement and correct distortion. After, as the balloon is removed, It will be introduced into the cavity of the acrylic cement. This will help maintain the correct position of the vertebra.
Immediately after the procedure, vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty
It may be computed tomography, to determine the correctness of the cement. You will remain lying on his stomach for 10-20 minutes. This will allow the cement to harden. Then you will be moved to the recovery room. You will be asked to lie on your back, and it is in a position for an hour or so.
How long will the vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty?
From 40 minutes before 2 hours.
Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty – Will it hurt?
You may feel some pain, when you lie on your stomach. Many patients notice immediate and significant relief of pain after the procedure.
The average hospital stay
Usually, you need to stay in the hospital for a few hours. Maybe, you have to extend your stay, if complications arise.
Care after vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty
Care in a hospital
You will be under medical supervision for a few hours after the operation, for the early detection of complications.
Home Care
It may feel some discomfort at the injection needle or incision. Reduction of discomfort is achieved using ice (applied only 15 minutes per hour). They can also help paracetamol or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. You can also get medicine to prevent muscle spasm.
It is recommended to stay in bed for 24 hours after treatment. Then you can gradually increase activity to normal levels. Ask the doctor, when it is safe to shower, bathe, or to expose the surgical site to water.
Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions.
Contact your doctor after vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty
After discharge from the hospital need to see a doctor, If the following symptoms:
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Redness, edema, increased pain, bleeding, or discharge from the incision or needle insertion site;
- Severe pain in the back or ribs;
- Cough, shortness of breath or chest pain;
- New numbness, tingling or weakness in the spine.
