Ovarian Cancer
Description of ovarian cancer
Ovarian Cancer – formation of cancerous cells in the ovaries. The ovaries produce eggs and female hormones. The most common type of ovarian cancer is epithelial cancer.
Cancer there, when the body's cells divide uncontrollably and form a build-up (weight) of cloth, called tumor. The term cancer refers to malignant tumors, that can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body. Benign tumors do not spread to other organs.
Many of these tumors can grow to a large size, not showing symptoms. They are also quite difficult to find during a physical exam. As a result,, at about 70% cancer patients detected at a late stage of the disease.
Germ cell tumors also arise from reproductive tissues. They account 20% tumors.
Stromal tumors are a rare type of cancer. They arise from connective tissue cells of the ovary. Usually, They produce hormones, which causes symptoms, allowing to detect them early.
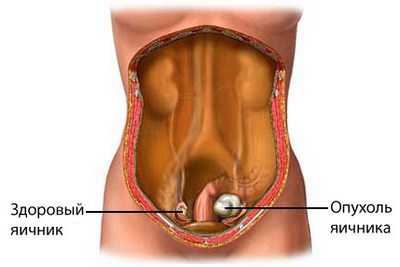
Causes of ovarian cancer
The causes of ovarian cancer are not known. Studies show, that there are certain risk factors, Related Disease.
Risk factors for ovarian cancer
Factors, which increases the risk of ovarian cancer:
- Family history of ovarian cancer, especially the mother, sister or daughter;
- Age: senior 50 years;
- Menstrual cycle – first menstrual period was up 12 years; after the birth of their first child 30 years; late menopause;
- Availability Breast Cancer or endometrial cancer;
- Mutations of certain genes, including BRCA1, BRCA2.
Using birth control pills for more than five years reduces the risk of ovarian cancer.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
Symptoms of ovarian cancer are often only appear in the later stages of the disease.
Symptoms include:
- The discomfort and / or pain in the abdomen;
- Gas, indigestion, pressure, swelling, bloating or cramps;
- Ascites;
- Nausea, diarrhea, constipation, frequent urination;
- Loss of appetite;
- Fullness of the stomach even after consuming a small amount of food;
- Unexplained weight gain or loss;
- Abnormal bleeding from the vagina;
- Hair growth, deepening of the voice, acne, absence of menstruation – in certain types of stromal tumors.
These symptoms, in addition to ovarian cancer, They may be caused by other, less serious diseases. If you experience any of them, consult a doctor.
Diagnosis of ovarian cancer
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical examination.
Tests may include:
Gynecological examination
Doctor, using a gloved finger examined the following organs:
- Uterus;
- Vagina;
- Ovaries;
- Fallopian tubes;
- Urinary bladder;
- Rectum.
The doctor will look for the presence of tumors or change the size and shape of.
Diagnostic tests
Doctor prescribes tests,that can help diagnose disease:
- US – examination, that uses sound waves, to examine the internal organs;
- Biopsy tissue or cell;
- Computed tomography of the abdomen (CT) – type of X-ray, which uses computer, to make pictures of organs inside the body;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRT) – test, which uses magnetic waves, to make pictures of structures inside the body;
- Barium enema – introduction of contrast fluid into the rectum. This allows you to perform X-rays, in which the doctor can find abnormal tissue changes;
- Test CA-125 – blood test, to measure the level of CA-125 substance. When ovarian cancer its level can be increased;
- Test OVA1 – blood test, performed after the detection of anomalies in the pelvic area. Specific protein levels in the blood may indicate, whether the tumor in the pelvis is cancerous.
Treatment of ovarian cancer
The treatment method depends on the stage of the disease and the patient's health.
The general approach to the treatment of ovarian cancer
Once detected ovarian cancer, appointed Tests, allowing to determine the extent of its spread.
The more developed a tumor, the worse the prognosis. About 75% all epithelial ovarian tumors are detected in the late stages. Overall five-year survival rate is about 50%.
The first step of treatment is often surgery, then receive chemotherapy. Sometimes it is also used for the treatment of radiation therapy.
Treatment of ovarian cancer include:
Operation
A cancerous tumor and nearby tissue will be removed. It may also be removed nearby lymph nodes.
Chemotherapy in ovarian cancer
Chemotherapy – the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. Preparations for the chemotherapy may be given in various forms: tablets, injection, the introduction of a catheter. The drugs enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body, killing mostly cancer, and also some healthy cells.
Radiation therapy in ovarian cancer
Radiation is used, to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. Therapy may be the following types:
- External radiation therapy – radiation is directed at the tumor from a source outside the body;
- Internal radiation therapy – radioactive material placed in the chest near the cancer cells.
The greater the development of tumors at diagnosis, the worse the prognosis. Unfortunately, 75% of all epithelial tumors are detected 3 or 4 stage at diagnosis. Overall five-year survival rate is about 50%.
Prevention of ovarian cancer
There are no methods to prevent ovarian cancer, as the cause of its occurrence is unknown. In the early stages of ovarian cancer symptoms it does not appear. If you think, that the risk of cancer of the ovaries, consult a doctor. If necessary, the doctor will schedule inspections. Also, all women should have regular pelvic examination, including vaginal examination and palpation of the ovaries.
