Mammary cancer – Breast Cancer
Description of breast cancer
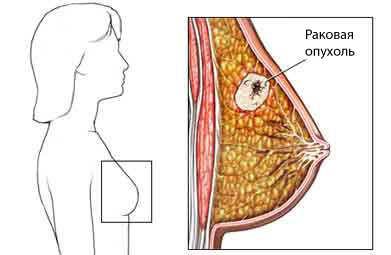
Mammary cancer – disease, whereby at mammary tissue growing cancer cells.
Cancer occurs, when the body's cells start to divide uncontrollably and form weight fabric, which is called a tumor. The term cancer refers to malignant tumors. They may spread to nearby tissue or other parts of the body.
Although most people think that breast cancer is the disease women, Men also can develop them. Breast cancer in men can be more aggressive.
Causes of Breast Cancer
The causes of breast cancer are unknown. Studies show, that there are certain risk factors, Related Disease.
Risk factors for breast cancer
Factors, which increases the risk of breast cancer:
- Paul: female, Although men can also develop breast cancer;
- Age: senior 50 years;
- Breast cancer in the last;
- The presence of family members with breast cancer;
- Changes in breast tissue, such as atypical ductal hyperplasia, dolʹkovaâ carcinoma in situ;
- Changes in certain genes (Krca1, BRCA2, and etc);
- Race: white;
- Increased exposure to estrogen over a lifetime, are caused by:
- Early onset of menstruation;
- Late menopause;
- The absence or late child birth;
- Lack of breastfeeding;
- The use of hormone replacement therapy;
- Tobacco;
- Increased breast density (stronger – lobular and ductal tissue and less – fat tissue);
- Radiotherapy in age 30 years;
- Alcohol abuse.
Studies show, that the majority of women with the above risk factors do not get breast cancer. Many of the sick woman have none of the risk factors, above, except age.
Symptoms of breast cancer
In the initial stage of breast cancer may be no symptoms. But the further development of cancer can lead to the following changes:
- Swelling or thickening in the chest area, in the axillary region or in the neck;
- Change the size or shape of the breast;
- Isolation or high sensitivity of the nipple;
- Pitting the breast skin (skin looks like orange peel);
- Visual and change the sensitivity of the skin of breast, areola or nipple (eg, heat, swelling, redness, or peeling).
These symptoms may be caused by other, less severe disorders. If you have any of them, consult a doctor.
Diagnosis of breast cancer
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, perform a physical examination.
Tests may include:
- Clinical breast exams – examined the size and shape of the breast, to identify, whether its changing the tumor;
- Mammography – X-rays of the breast, to determine the tumor or other changes in breast tissue;
- US – the use of high-frequency sound waves, to find a fluid-filled cyst or abnormal mass of tissue;
- CT scan – X-ray views, which uses computer, to make pictures of organs inside the body;
- PET / CT – type of medical imaging, that combines positron emission tomography (PET) and methods CT;
- Biopsy – removal of the tumor tissue to test for cancer cells. Types of biopsies of breast cancer include:
- Tonkoigolynaya aspiration – removal of fluid and / or cells from a breast tumor with a fine needle;
- With a needle biopsy – removal of tissue with a needle from the field, which is suspicious on a mammogram;
- Hirurgicheskaya biopsy:
- Intsizionnaya biopsy – removing a tissue sample or an entire area of suspicious;
- Эkstsizionnaya biopsy – removing the entire suspicious area and the area of healthy tissue around;
- Evaluation of tissue – the breast tissue is tested for the presence of estrogen and progesterone receptors, as well as the presence of HER2 / neu; used for treatment planning;
- Genetic testing – some patients blood is evaluated for the presence of specific gene mutations.
Treatment of breast cancer
Once detected breast cancer, appointed Tests, allowing to determine the extent of its spread.
Treatment includes:
Operation
- Lumpectomy – removing breast cancer and some normal tissue around the tumor. Often also removed some of the lymph nodes under the arms;
- It may also be called tilektomiya and kvadrantektomiya;
- Segmentectomy – removal of the cancer and a large area of normal breast tissue around it;
- Simple mastectomy – removal of the breast or a greater part of the breast, as much as possible. The surgeon will try not to remove lymph nodes;
- Radical mastectomy – removal of the breast, pectoral muscles, lymph nodes under the arm, and a certain amount of fat and skin. This procedure is performed only rarely, if the cancer has spread to the chest muscles;
- A modified radical mastectomy – removal of the entire breast, lymph nodes under the arms and, often, muscle tissue in the breast;
- Biopsy storozhevogo limfaticheskogo uzla – a small amount of blue dye and / or radioactive isotope is injected into the area, where the tumor is located. Isotope or dye is then transferred into the armpit. The lymph nodes, substances that fall in, removed. The effectiveness of this procedure exceeds 95%. It reliably identifies those lymph nodes, that may contain cancer. If any of guard nodes contain cancer, remaining lymph nodes must also be removed. This method is commonly used for women, which do not have lymph node, that can be felt in the armpit. Possible side effects are much less, than after a standard lymph node dissection.
- Axillary lymph node dissection – removal of the lymph nodes under the arm. This is done, to determine, whether cancer cells have spread to the lymphatic system.
Radiation therapy
Radiation is used, to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. Therapy may be the following types:
- External radiation therapy – radiation is directed at the tumor from a source outside the body;
- Internal radiation therapy – radioactive material placed in the chest near the cancer cells.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy – the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. The formulations may be provided in various forms, including tablets, injection, and catheter. The drugs enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body, killing mostly cancer, and also some healthy cells.
Biological Therapy
Biological therapy involves using medications or substances, produced by the body. They are used to increase or restore the natural defenses against cancer (immunomodulators).
Gormonalynaya therapy
Hormone therapy uses the fact, Many breast cancers “sensitive to estrogen”. Estrogen binds to “estrogen sensitive "cells and stimulates their growth and division. Special drugs prevent the binding of estrogen, that stops the growth of cells, thereby, prevents or delays breast cancer recurrence.
Preventing Breast Cancer
Detection and treatment of breast cancer in the early stages – the best way to prevent death from the disease. Breast cancer does not cause symptoms in the early stages of, therefore it is important to perform regular screening tests and. These steps help detect cancer before symptoms appear. The following recommendations are for women, asymptomatic, who are not at high risk of breast cancer:
- Mammography:
- Age 40-49 – it is recommended to carry out a survey every 1-2 year;
- Age 50-74 – it is recommended to carry out a survey every year, Resolution doctor – every two years;
- Clinical breast exams:
- Age 20-39 – once 1-3 year, on doctor's advice;
- Age 40 and older – Every year;
- Breast self-exam:
- Age 20 and older – optional; talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of this method.
If you have an increased risk of breast cancer, you may need to perform mammograms more often. The doctor can decide on the best screening schedule.
Besides, if there is a very high risk of developing breast cancer, surgery to remove the breast can be done in advance, before the cancer (so-called prophylactic mastectomy).
