Prostate cancer
Description of prostate cancer
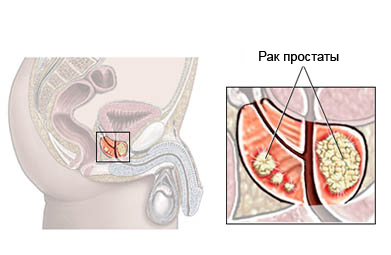
Prostate – iron size of a walnut, located on the neck of the bladder. It surrounds the urethra. Iron is part of the male reproductive system and produces a liquid, which is part of semen. Prostate cancer is a disease, wherein the prostate cancer cells are formed.
The earlier start prostate cancer treatment, the better the result. If you suspect, that you have prostate cancer, consult a doctor.
The causes of prostate cancer
The causes of prostate cancer are unknown.
Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer
Factors, which increase the risk of prostate cancer:
- Age: 55 and older;
- Family history of prostate cancer, especially father or brother;
- Family history of prostate cancer, who are diagnosed at a younger age;
- Consumption of foods high in fat.
Symptoms of prostate cancer
Symptoms of prostate cancer may include:
- The need to urinate more often, especially at night;
- Difficulties with the start of urination or inability to contain urine;
- Inability to urinate;
- A weak flow of urine;
- Painful or burning urination;
- Difficulties with erection;
- Painful ejaculation;
- Blood in urine or semen;
- Frequent pain or stiffness in the lower back, hips or upper thighs.
These symptoms may be caused by other diseases, such as BPH or infection.
Diagnosis of prostate cancer
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical examination. Your doctor may order the following tests:
- Digital rectal examination;
- Analysis of urine;
- Blood tests;
- Other Tests, such as:
- Transrectal ultrasonography;
- Intravenous pyelogram;
- Cystoscopy;
- Biopsy prostatы.
Prostate Cancer Treatment
After prostate cancer detection survey is conducted, allowing to determine the extent and scope of cancer. The treatment method depends on the stage and extent of disease.
Treatments for prostate cancer include:
Vыzhidatelynaya tactics
The method includes monitoring a cancer, to detect the start of the growth or spread of. Watchful waiting may be appropriate in the following cases:
- Prostate cancer is at an early stage and growing slowly;
- Prostate cancer is detected at an advanced age;
- There are serious health problems (risks of treatment outweigh the benefits).
Operation in prostate cancer
Types of operations, which may be implemented in prostate cancer:
- Pelvic lymphadenectomy – removal of the lymph nodes in the pelvis, to determine the presence of cancer;
- Radical retropubic prostatectomy – removal of the entire prostate and surrounding lymph nodes through an incision in the abdominal cavity;
- Radical perineal prostatectomy – removal of the entire prostate through an incision between the scrotum and the anus;
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) – removing a portion of the prostate with the tool, which is introduced through the urethra (It may be carried out to alleviate the symptoms).
Since an operation for prostate cancer may cause side effects, such as erectile dysfunction, incontinence, They may be required and other methods of operation. Some examples include methods, nerve sparing, Robot and Laparoscopic Surgery.
Radiation therapy for prostate cancer
Radiation therapy It involves the use of radiation, to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. Methods of treatment include:
- Conformal Radiotherapy – used in the treatment of three-directional radiation beams, which conform in shape prostate. This treatment spares nearby tissue from the damaging effects of radiation;
- Intensively-modulated radiation therapy – uses radiation beams of different intensities, to achieve higher tumor doses as small as possible and irradiating the surrounding tissue.
Hormone therapy for prostate cancer
If prostate cancer has spread or after treatment there was a recurrence of his, the treatment can be used hormone therapy. The goal of hormone therapy is to reduce the level of male hormones, called androgens. The main androgen is testosterone. Lowering androgen levels can cause a decrease in prostate cancer, reduce or slow the growth of tumors. For hormone replacement therapy can be used following preparations and procedures:
- Analogs (agonistы) luteinizing hormone releasing hormone (LGRG) – These drugs cause a drop in testosterone to very low levels;
- Antagonists lteiniziruyuschego hormone releasing hormone (LGRG) – procedure also reduces testosterone, but it does so faster and without splash testosterone levels, what happens when using LHRH analogues;
- Acceptance of anti-androgens (eg, ʙikalutamid, flutamid, nilutamid) – These drugs block the action of androgens;
- Other hormone therapy:
- Estrogen therapy – now rarely used, If other treatments are ineffective;
- Ketoconazole – It affects the production of androgens;
- Abiraterone – It can be used in cases, When prostate cancer is not responding to other treatments;
- Orteronel (an experimental drug) – It affects the production of androgens;
- Enzalutamid – It affects the production of androgens;
- Abiraterone – It can be used in late stages of prostate cancer.
In some cases, It may be required orchiectomy, which includes the removal of the testicles, that stops the production of androgens.
Other embodiments of the treatment of prostate cancer
Other embodiments may include:
- Krioxirurgija – It involves the use of an instrument to freeze and destroy prostate cancer cells;
- Chemotherapy – if prostate cancer has spread, and other treatments have been ineffective, Chemotherapy may be used. There are a number of chemotherapeutic drugs, is used to treat prostate cancer:
- Docetaxel (This is usually the first drug, used in chemotherapy);
- Cabazitaxel;
- Mytoksantron;
- Estramustine;
- Doxorubicin;
- Immunotherapy – Immunotherapy is a treatment, which is aimed at strengthening the immune system. At the same time the body begins to fight cancer cells. Sipuleutsel-T (Sipuleucel-T) It is a type of immunotherapy, which is approved for the treatment of prostate cancer;
- Targetnaya therapy – Treatment focuses on the cause of the cancer cells:
- Selective antagonists of endothelin receptors – It interferes with the growth of cancer cells, after which they cease to grow;
- Anti-angiogenic drugs block the formation of new blood vessels, that stops the growth of cancer cells;
- Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (eg, Imatinib) – blocking protein, which causes the multiplication of cancer cells;
- Application of high intensity focused ultrasound – the procedure involves the use of endorectal probe (probe, which is introduced into the rectum) to kill cancer cells by ultrasonic energy.
Prevention of Prostate Cancer
To reduce the risk of prostate cancer, proceed as follows:
- Eat a healthy diet. It is recommended to have a diet high in fruits, vegetables and fish, and low in red meat;
- Ask your doctor about taking certain medications. For Example, daily aspirin and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors may reduce the risk of prostate cancer.
