Cystoscopy – Cystourethroscopy
Description cystoscopy
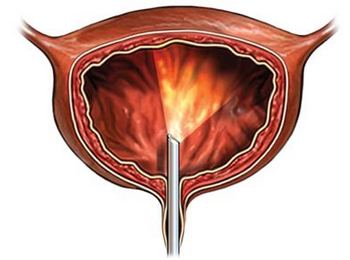
Cystoscopy – inspection of the bladder. The procedure is performed by a special device with a camera and a light source at the end of, called a cystoscope. The device allows the doctor to examine the urethra and bladder.
Reasons for cystoscopy
Cystoscopy may be done, to investigate the following symptoms:
- Urinary tract infections;
- Blood in the urine;
- Urinary incontinence;
- Frequent urination;
- Dribbling after urination;
- Pain;
- Difficulty urinating.
Infringement, which can be identified through cystoscopy:
- Tumors;
- Bladder stones;
- Inflammation;
- Cysts;
- Protrusion of the bladder wall (diverticulum);
- Open wounds (ulcers);
- Polyps;
- The narrowing of the urethra;
- Increased prostate (males).
Possible complications cystoscopy
Complications are rare, but no procedure does not guarantee the absence of risk. Before, how to perform cystoscopy, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Infection;
- Bleeding;
- Accidental damage to the bladder wall cystoscope (rarely);
Factors, that may increase the risk of complications:
- Active infection;
- Diabetes;
- Coagulation failure.
How is cystoscopy?
Preparation for the procedure
Cystoscopy usually performed in a doctor's office. In some cases, a cystoscopy may be done in conjunction with another procedure. If you plan general anesthesia, your doctor may recommend:
- Arrange a ride home from the procedure;
- Do not eat or drink in the evening and the night before the procedure.
Anesthesia
It can be used in the following types of anesthesia:
- Local anesthesia – anesthetized area procedures. It may be given as a gel, which is inserted into the urethra. They can be used sedatives, to help relax;
- Regional anesthesia – blocks pain in most of the body. It may be used, if the procedure is carried out in a hospital;
- General anesthesia – during the procedure the patient will sleep. It is inserted through an IV in the arm or shoulder. This type can be used, if the procedure is carried out in a hospital.
Description of the procedure
You will lie on the examination table. The doctor inserts the cystoscope through the urethra, and supplies it to the bladder. Because the bladder is drained urine. Further, the bladder is filled with clean water, which will allow a better view of its walls. We study the bladder, urethra and prostate (males).
How much time will it take cystoscopy?
5-10 minutes.
Cystoscopy – Will it hurt?
You may feel a tingling or burning sensation when urinating. The doctor may give pain medicine.
Aftercare cystoscopy
When you return home, Follow these steps:, to ensure the normal recovery:
- Keep in mind, you can see a little blood in the urine for several days after the procedure;
- Take prescribed medications, including antibiotics;
- Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions.
Contact your doctor after cystoscopy
Returning home, consult a doctor, if there was any of the following symptoms of:
- Pain, burning, frequent urination or persistent bleeding in the urine;
- You are unable to urinate or empty the bladder completely;
- Blood in the urine 24 an hour after the examination;
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Abdominal pain, back or side;
- Nausea and / or vomiting;
- Cough, shortness of breath or chest pain.
