BPH, prostatic hyperplasia: what is this, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
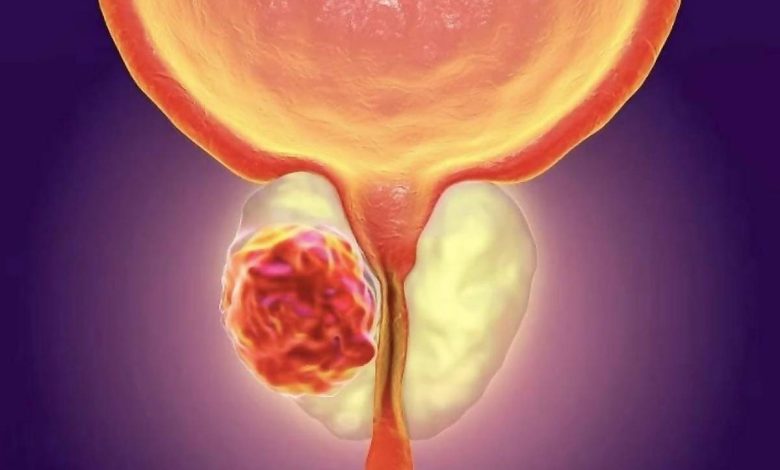
Description BPH
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (DGPŽ) – increasing the size of the prostate (Prostate). Prostate – iron size of a walnut, located on the neck of the bladder. It surrounds the urethra. Iron is part of the male reproductive system. Increased prostate cancer not associated with.
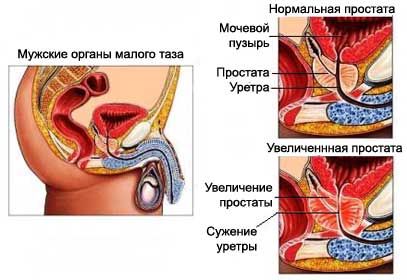
The reasons for increasing the size of the prostate
The exact cause of BPH is unknown. It is assumed that this may be due to changes in hormone levels with age. Eventually becomes so enlarged prostate, that exerts pressure on the urethra. This leads to a narrowing or blockage of the urethra.
Risk factors for benign prostatic hyperplasia
Risk factors increase the likelihood of prostate adenoma. The main risk factor for BPH is age over 50 years.
Symptoms of BPH
Symptoms of BPH causes constriction of urethra, caused by the growth of the prostate. The severity of symptoms usually increases over time.
Symptoms include:
- Pain with urination;
- A weak flow of urine;
- Dribbling of urine after urination;
- The feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- Frequent urination, especially at night;
- Discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- Urinary incontinence.
Diagnosis of prostate adenoma
BPH diagnosis is made by:
- The patient's age;
- Symptoms of the disorder;
- Digital rectal examination – the doctor inserts a gloved finger into the rectum, to explore the area of the prostate.
Other tests may include:
- Research urination;
- Cystometrogram (functional study of bladder);
- Roentgen urinary tract;
- Transrectal ultrasonography;
- Determining the degree of voiding;
- Cystoscopy – test allows the doctor to examine the urethra and bladder inside.
- Testing for prostate specific antigen (PSA) It is often used to detect prostate cancer. Nonetheless, BPH can also lead to a decrease in PSA. This may cause false suspicions about the presence of cancer.
Treatment of BPH
For mild cases of treatment of prostate adenoma is not required. However, most men, BPH, may require medical intervention.
Treatment of BPH include:
Medication
Drugs, for treating BPH include:
- Inhibitors of 5-alpha-reductase (finasteride, dutasterid) – These drugs are taken to reduce the symptoms, such as frequent urination and difficulty beginning to urinate;
- Alpha-blockers (eg, tamsulozin, alьfuzozin, doksazozin, terazosin) – preparations, taken to relax the bladder and increase urine flow;
- Antimuscarinics (oxybutynin, solifenacin, tolterodine, darifenaцin, trospyy, fesoterodine) – drugs help relax the muscles of the bladder, which helps to reduce frequent urination;
- An inhibitor of the enzyme phosphodiesterase-5 (tadalafil [Cialis]) – a drug to treat erectile dysfunction may reduce symptoms of BPH;
- Attention: You should not take tadalafil together with nitrate medications (eg, nitroglycerin), since blood pressure may become dangerously low. Besides, tadalafil should not be taken in combination with an alpha-blocker.
Each group of medicines have different side effects. Enzyme inhibitors may cause decreased sexual desire and problems with erection. Alpha-blockers may cause decreased blood pressure, dizziness, nasal congestion. Antimuscarinic drugs can cause dry mouth, constipation, dry eyes, problems emptying the bladder, perplexity.
If you have BPH, you should not take decongestants drugs, containing alpha-agonists (eg, Pseudoephedrine). These drugs can worsen the symptoms of BPH.
Minimally invasive interventions
They are used, when drugs are ineffective, but the patient is not ready for operation. Nonsurgical treatment includes:
- Transurethral microwave thermotherapy – It uses microwaves, to destroy excess prostate tissue;
- Transurethral needle ablation – It uses low levels of radio frequency energy, to cauterize the part of the enlarged prostate;
- Transurethral laser therapy – to remove excess prostate tissue using highly directional laser.
Prostate surgery
Surgical procedures include:
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) – through the penis are special tools, to remove the enlarged portion of the prostate;
- Transurethral incision of the prostate (TUYP) – in the neck of the bladder makes a small incision, that allows you to expand the urethra;
- Open surgery to remove the enlarged portion of the prostate through an incision – usually, performed through an incision in the lower abdomen and much more invasive than the TOUR or TUIP;
- Stenting the prostate – inserted into the urethra tiny metal rings, to expand and maintain it open;
- Usually used for men, who do not want to take medicine or perform surgery;
- It is not a long-term treatment.
Alternative methods of treatment of prostate adenoma
Herbal products, which have been studied as a possible treatment for BPH include:
- Saw palmetto extract – Sometimes the drug can reduce symptoms of BPH;
- Beta-sitosterol – some studies show, that his technique can help reduce the symptoms;
- African plum (Pygeum) – Some researchers suggest, that supplementation reduces symptoms.
If you were diagnosed with BPH, Follow your doctor's instructions.
Prevention of prostate adenoma
Prostate enlargement occurs naturally with age. There is no specific prevention of disorder.
