Hip fracture
Description of hip fracture
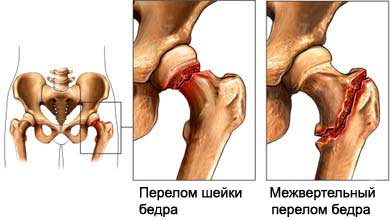
Hip fracture – the destruction of the femur just below the hip joint. The hip joint consists of a ball at the top of the femur and the rounded socket (acetabulum) in the pelvis. Most hip fractures occur in the neck of the femur 1-2 cm below the ball portion of the hip.
Causes of hip fracture
The reason hip fracture is a bone injury, the cause of which can be:
- Fall (The most common cause of hip fractures);
- Osteoporosis – bone disease, that weakens all bones, including hip;
- Car accidents and other serious injuries;
- Fatigue fractures (rarely) athletes;
- Bone Diseases, such as osteomalacia (rarely);
- Bone tumors (rarely).
Risk factors for hip fracture
Factors, increase the risk of hip fracture include:
- Previous hip fracture or frequent falls;
- Age: 65 and older;
- Paul: female (particularly after menopause);
- Heredity:
- Family history of fractures;
- Thin bones, slender body (low body weight);
- Race: white or Asian;
- Other:
- Poor diet;
- Inadequate intake or absorption of calcium and vitamin D;
- Low body weight;
- Lack of physical activity;
- Weakness;
- Poor balance and coordination;
- Smoking;
- Excessive alcohol consumption;
- Chronic illness or poor health;
- Irregular heartbeat or low blood pressure;
- Arthritis;
- Parkinson's Disease;
- History stroke;
- Mental disorders, including Alzheimer's disease;
- Vision problems;
- Taking certain medications, that cause dizziness, drowsiness or weakness;
- Systemic administration of cortisone or other steroids;
- Thyroid problems;
- Heart failure.
Symptoms of hip fracture
Symptoms include:
- Pain in the hip;
- Difficulty or inability to stand, walk or move the hip;
- Abnormal appearance broken leg:
- The leg looks shorter;
- The foot turned inside out.
Diagnosis of hip fracture
The doctor will ask about your symptoms, recent physical activity, About, how the accident occurred, will examine the fracture.
Tests may include:
- Roentgen – to pinpoint, where the broken bone and how strongly it budged;
- X-ray bone scan or MRT – Used, if the fracture does not show up on x-ray, but the symptoms point to its presence.
Treatment of hip fracture
The goal is, as quickly as possible to get to his feet, while until a broken bone heals. For elderly patients staying in bed for a few days may even lead to serious complications.
Treatment includes:
Fast emergency treatment of hip fracture
- Removing the load with foot injuries and the immobilization of fractures;
- Checking vital signs, such as blood pressure;
- Troubleshooting, life-threatening, such as internal blood loss;
- Pain relief using painkillers and other drugs.
Surgery for hip fracture
The operation is performed, to set the broken bone in place and hold it in the correct position. Operation can include:
- Installation plates and screws at the fracture site;
- Hip replacement metal implant (prosthesis) c layer, which is set in the acetabulum.
Physical help with femoral neck fracture
The recovery period may be required:
- Exercises or therapy, help strengthen the muscles;
- A cane or walker as recommended by your doctor – to assist with walking;
- Assistance in daily activities, until complete bone healing.
If you are diagnosed with hip fracture, Follow your doctor's instructions.
Prevention of hip fracture
Corrective actions can reduce many of the factors, which may lead to fracture of the femoral neck. Recommendations include the following:
- Eat a diet with nutrients for strong bones:
- Calcium – about 1000 mg per day (check with your doctor);
- Vitamin D – 400-800 units per day;
- Adequate intake of protein;
- Exercise (check with your doctor):
- Exercises with the load on the hip joint, eg, walking;
- Strengthening exercises for the upper and lower extremities;
- Consult your doctor, if you are at risk for osteoporosis. Prophylactic treatment may include:
- Hormone replacement therapy for women after menopause;
- Bifosfonatы;
- Calcitonin;
- Ask the doctor, whether taken drugs cause various disorders, including:
- Loss of bone mass;
- Dizziness, drowsiness, or confusion;
- To reduce the risk of falling at work and home:
- Immediately clean spills on the floor;
- Use non-slip mats in the bathtub and shower;
- Install handrails next to the toilet and shower or bath;
- Ustonovil handrails on both sides of the stairs;
- Keep a flashlight in case of power outage;
- Get regular eye checkups.
