Treatment of retinal detachment
Description treat retinal detachment
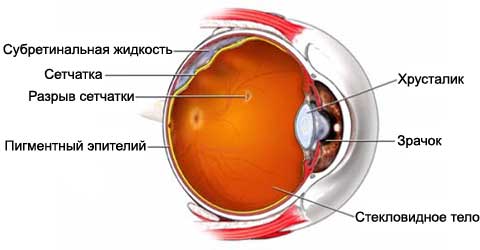
The procedure is performed to restore retinal detachment. The retina is a thin layer of light-sensitive tissue, nerves and blood vessels, located in the back of the eye. Touch retinal layer receives an image and sends it to the brain. This layer may shift from its normal position, which can lead to vision loss. The retina is often separated from the back of the eye, like the wallpaper from the wall. Delamination is usually preceded by the appearance of the hole or tear in the retina.
The reasons for the treatment of retinal detachment
The procedure is performed, to return the retina back into the correct position and try to restore vision.
If the vision was good before the detachment, a successful operation usually restores vision to normal levels. If vision was poor before the detachment of the retina, return view can be slow and incomplete. The peripheral retinal detachment, probably, heal faster, than the detachment of the macula (the central part of the retina) or complete retinal detachment.
The longer the retina was detached, the less likely, that vision will be restored.
Possible complications of the treatment of retinal detachment
Complications are rare, but no procedure does not guarantee the absence of risk. If you plan to treatment, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Repeated retinal detachment – sometimes detached retina again after surgery. In this case, we will need more surgery. In severe cases, this complication may be irreversible;
- Endophthalmitis – an infection inside the eye;
- Prolyferatyvnaya vytreoretynopatyya – this condition causes progressive contraction and scarring of the retina after treatment, which may require surgery. In severe cases, this complication may be irreversible.
Factors, that may increase the risk of complications:
- Poor overall health;
- The high degree of damage to the retina;
- Cataracts;
- Glaucoma.
How is the treatment of retinal detachment?
Preparation for the procedure
There will be a comprehensive eye test, including will be assigned some or all of the following assays:
- Testing of visual acuity – vision will be checked using a chart with letters or numbers;
- Slitlamp – a special tool is used to inspect the front of the eye;
- Tonometry – will be assessed by the pressure inside the eye;
- Examination of the retina – special drops are used for mydriasis, after which the retina is examined with special equipment;
- B-scan – special ultrasound instrument will be used to explore inside the eye.
It can be assigned to a general medical examination. It may include some or all of the tests:
- Blood and urine tests
- Chest X-ray – test, which uses X-rays to study the structures inside the body;
- Electrocardiogram – measurement of the electrical activity of the heart.
In the run-up to the procedure:
- We need to organize a trip for the operation and back home;
- Do not eat or drink anything, at least 8 hours before the procedure.
Consult your doctor about the drugs taken. A week before surgery you may be asked to stop taking some medicines:
- Aspirin or other anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Blood thinners, such as clopidogrel (Plaviks) or warfarin.
Anesthesia
The operation can be performed under local or general anesthesia. Local anesthesia numb the area after the introduction of the operation. General anesthesia puts the patient to sleep. The type of anesthesia depends on the type of procedure, age and other factors.
Description of the procedure for treating retinal detachment
There are several surgical treatment of retinal detachment. The most common are:
Sclerotherapy
Flexible silicone lining is stitched to the outer surface of the back of the eye. This is done under the skin of the eye. You'll never see the lining. Through the eyes and the lining are special loop, which, like the belt is pressed against the retina to the rear wall. This procedure has a high success rate in restoring retinal. It is performed under local or general anesthesia.
Pneumatic retinopexy
A gas bubble will be injected into the eye cavity. The pressure will force the retina into place. You often need to lie in a special position, to maintain the gas bubble in situ. Retina, usually, takes the place for a few days. Using a laser, (heat) or cryotherapy (cold) the retina is attached to the place.
This method generally has a high success rate, but it is not suitable for all types of detachment. Often performed under local or general anesthesia. The main advantage of this procedure is that, that it can be done in the outpatient clinic with anesthetic eye drops.
Vytrэktomyya (removal of the vitreous)
This method may be needed for complex cases of retinal detachment. It may also be used, If the procedure, above, not successful.
The liquid from the eye, as well as any scar tissue will be removed. The fluid will then be replaced with a gas bubble or specialized oil, known as silicone oil. The bubble or oil will help push the retina in the eye. Retinal tears are then closed with a laser or cryotherapy. Often at the same time is hardening. The procedure is performed under local or general anesthesia.
How long will the recovery of the retina?
About 1-4 o'clock.
Will it hurt?
Anesthesia prevents pain during the procedure. During recovery, you may experience some pain or nausea. Your doctor can give you medicine, to reduce pain.
The average hospital stay
Usually you can go home the day of surgery.
Care after treatment retinal detachment
On the eye and the bandage is a metal plate. When you return home, follow these steps:, to ensure the normal recovery:
- Do not remove the bandage to a doctor's permission. Usually, it is removed the next day;
- If your doctor instructs you to keep your head in a certain position, make it as much as possible, even when eating, sleep or bathe;
- Do not allow the eye to come into contact with water, until it is allowed to physician;
- Avoid strenuous physical activity, until it is allowed to physician;
- Your doctor will schedule follow-up meetings, to monitor your recovery;
- You can often return to work within 1-2 weeks after surgery, if the doctor permits it;
- Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions.
The final result of the operation can sometimes be seen only through 1-2 year.
Contact your doctor after treatment retinal detachment
After returning home, you need to see a doctor, If the following symptoms:
- Any change in vision;
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Redness, edema, growing pain, bleeding, or excessive discharge from the eye;
- Cough, shortness of breath or chest pain;
- Other painful symptoms.
