Spiral intrauterine – setting – Set Navy
Description of IUD insertion
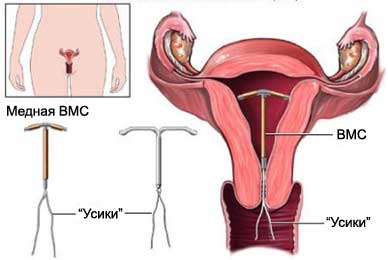
Intrauterine device (Navy) is one method of contraception for women. She introduced the doctor into the uterus, It is located in the fetus during pregnancy.
There are two Navy Type:
- Gormonosoderzhaschaya Navy;
- Copper IUD.
Both of them are shaped “T” with two threads (“Usyk”) at the end.
Gormonosoderzhaschaya IUD releases the hormone progestin, while copper ions releasing copper IUDs.
Gormonosoderzhaschaya IUDs can remain in the body for five. Copper IUDs can remain for 10 years. After removal of an intrauterine device Most women can get pregnant again.
IUDs do not protect against sexually transmitted diseases.
Reasons to Install Navy
This procedure is performed for preventing pregnancy. In addition to birth control, gormonosoderzhaschaya IUD may also have other applications, such as the treatment of the following diseases:
- Heavy menstruation;
- Pelvic pain;
- Early endometrial cancer or precancerous conditions.
Possible complications of installing intrauterine device
Serious complications are rare, but no procedure does not guarantee the absence of risk. If you plan to install an intrauterine device, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Spasms;
- Abnormal bleeding and spotting for a few months after installation;
- Pain during menstruation;
- IUD falls out of uterus into the vagina or completely out of the body;
- Infertility;
- Pelvic infection;
- Damage to the uterus or other pelvic organs;
- Neregulyarnaya menstruation or absence of menstruation (gormonosoderzhaschaya Navy);
- Heavy menstruation (Copper IUD).
Even with the Navy a chance, that you can get pregnant. If this is to happen, there is a risk of ectopic pregnancy. This condition, when the fetus develops outside the uterus. Other complications include:
- Miscarriage;
- Early childbirth;
- Pelvic infection.
Navy is not suitable for all women. IUD is contraindicated in pregnant women or women, having these disorders:
- Vaginal bleeding of unknown etiology;
- Deformirovannaя uterus;
- Family history of ectopic pregnancy;
- Pelvic infection after childbirth or abortion in the last three months;
- History of pelvic inflammatory disease, if it has not been a normal pregnancy;
- The presence of sexually transmitted diseases or other infections in the pelvic area;
- Increased risk of pelvic infection (eg, having more than one sexual partner, Problems with the immune system);
- Cervical cancer or cervical cancer;
- Liver disease or liver cancer (gormonosoderzhaschih for Navy);
- Mammary cancer (gormonosoderzhaschih for Navy);
- Allergy to copper (for copper IUDs);
- Wilson's disease (for copper IUDs).
We need to discuss these risks with your doctor before you install Navy.
How is the installation of an intrauterine device?
Preparation for the procedure
Before installing the Navy doctor will prescribe the following:
- The test for sexually transmitted diseases and pregnancy;
- The study of history;
- Inspection of the uterus, vagina and other organs;
- We consider the risks and benefits of IUD insertion, and determines the type of intrauterine device, preferred to install;
Before installing intrauterine device you need to sign a consent form.
You also need to arrange a ride home after the procedure.
Anesthesia
In most cases, anesthesia is not used. Some doctors use the gel for pain cervix. It can also be done the injection of anesthetic into the area of the cervix, to block pain and discomfort during the procedure.
Installation procedures IUD
This procedure is usually performed in an outpatient setting without the need to stay in hospital.
You lie on a table for inspection and place your feet in nogoderzhateli. Will be inserted into the vagina and the doctor extender can locate the cervix. The cervix and vagina will be treated with an antiseptic. Another tool, called holder will be used for cervical dilatation and retaining it in the open position. The doctor inserts a special instrument to measure the depth of the uterus, To make sure, that it would match the size of the Navy.
T-shaped spiral is folded and inserted into the tube. The doctor inserts a tube into the uterus through the vagina and cervix. As soon as the doctor inserted a tube, He pulls it back a bit, allowing IUD accept original T-shaped intrauterine. The tube holder and then are deleted. “Antennae” Navy will play from the cervix into the vagina. They are shortened to a length 2-3 cm. At the end of procedure dilator removed.
How long will the installation of an intrauterine device?
The procedure for the introduction takes about five minutes.
Installation of an intrauterine device – Will it hurt?
You may feel cramping or mild discomfort during or directly after the installation of the Navy. They can be administered painkillers, to reduce discomfort during the procedure.
Care after the installation of an intrauterine device
Care in a hospital
Immediately after the procedure, the staff may give pain medicine, to ease the discomfort.
Nursing homes
When you return home, Follow these steps:, to ensure the normal recovery:
- Get plenty of rest;
- Typically, you can resume daily activities, Once you feel comfortable;
- Visit your doctor about a month after IUD insertion, To make sure, that the IUD is in the correct position;
- Each month, check with your fingers, To make sure, what “mustache” in the rear of the vagina;
- Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions.
Contact your doctor after you install an intrauterine device
After returning home, you need to see a doctor, If the following symptoms:
- Change the length “usikov”;
- It is impossible to find “mustache” fingers;
- The sense of loss of the Navy of the cervix;
- Suspected pregnancy;
- Heavy menstruation or increase the length of the menstrual period;
- Missed, later, or short menstrual period;
- Signs of sexually transmitted disease you or your partner;
- Severe cramps, pain or tenderness in the abdomen;
- Pain or bleeding during sex;
- Unexplained fever or chills;
- Flu-like symptoms, such as muscle pain and fatigue;
- Vaginal discharge or sores on the genitals;
- Unexplained vaginal bleeding;
- Severe headache and migraine;
- Evidence heart attack or stroke.
