The central catheter – Setting central venous catheter
Description of the installation of central venous catheter
Central catheter is a long thin tube, which is entered into a major vein. Central catheter is used for delivery into the bloodstream medication, feeding, intravenous drugs and chemotherapy.
There are different types of central catheters, including:
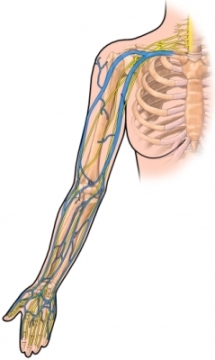
- Peripheral Central catheter – the catheter is inserted through a vein in your arm, until it reaches the veins to heart;
- Netunnel′nyj central venous catheter is inserted into a large vein in the neck or leg; end of the tube is out of the skin.
- Tunnel catheter is a catheter, which is fixed in place, When scar tissue is formed. You can use it for a few weeks or months. The catheter is introduced into a large vein in the neck, which returns blood to the heart. He was then further along the chest wall and through the skin at a distance of about 12 see from the introduction in Vienna.
- Port-catheter – the device is inserted into a vein in the shoulder or neck. Port (Titanium camera) is located under the skin, and the catheter is inserted into the central vein. For the introduction of drugs membrane port Pierce special needle and the following 3-5-7 days through this needle, you can enter any solutions in any quantity.
Causes of Central catheter
Central catheter is inserted, When the patient must:
- Long term enter medications or fluids;
- Chemotherapy;
- For nutrition, If the flow of food through the digestive system cannot;
- Periodic sampling of blood;
- Blood transfusion;
- Intravenous drugs, When the veins on your arm inaccessible;
- For dialysis.
Central catheter usually introduces Interventional Radiologist or vascular surgeon. After the introduction of the catheter can be used for several weeks or months.
Possible complications after the introduction of Central catheter
Complications are rare, but no procedure does not guarantee the absence of risk. Before, How do I install central catheter, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Bloodstream infections, When the bacteria enter the bloodstream through or around a central catheter;
- Bleeding;
- Collapsed lung;
- Arrhythmia (unstable heartbeat);
- Nerve damage;
- An air bubble or a portion of the catheter may block blood vessels, causing chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness and heart palpitations;
- Blood clots in Vienna or in the catheter may block blood flow.
Factors, that may increase the risk of complications include:
- Smoking;
- Difficult access to veins;
- Blood clots;
- Obesity;
- Broken bones;
- Infection;
- Poor blood circulation;
- The tendency to bleeding.
How is the introduction of a central catheter?
Preparation for the procedure
- A blood test can be performed, to check its clotting;
- The doctor may ask about the presence of allergies;
- It is necessary to arrange a ride home after the procedure;
- The patient may be asked to stop taking certain medicines a week before the procedure,:
- Aspirin or other anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Blood-thinning drugs, such as clopidogrel or warfarin;
- If there is suspicion of pregnancy, you need to inform your doctor before treatment.
Anesthesia
Obezbolivaetsâ catheter area using local anesthesia. Depending on, where central catheter is introduced, sedative may be introduced intravenously.
Describes the process of introducing a central catheter
This procedure can be done both in hospital, as part of treatment, and on an outpatient basis.
The presence of the catheter increases the risk of bloodstream infection. The hospital staff should carry out the procedure, Taking the following steps, to reduce this risk:
- Carefully you need to select a safe place, to insert a catheter;
- Thoroughly wash their hands or use hand sanitizer;
- It is necessary to wear surgical gowns, masks, gloves and cover your hair;
- Clean the skin with an antiseptic;
- Use a sterile sheet.
The following steps may vary depending on the type of catheter and its introduction. Generally, staff will do the following:
- The introduction of anaesthesia is performed;
- Runs a small incision;
- To guide the catheter into a vein used x-rays or ultrasound;
- Before installing the catheter will need to cut it to the desired length. The catheter is flushed with saline solution (salt water);
- The catheter is sent using Windows Explorer catheter. Then Windows Explorer is removed;
- The catheter is attached to the skin (usually using tape). At the end of the catheter CAP is installed;
- In place of the catheter bandage. The bandage around her or the date of introduction.
If you entered a port-catheter, under the skin is done a small cavity to accommodate. The incision is sutured, usually, rassasyvaûŝejsâ thread.
Immediately after treatment
Position will be checked for bleeding, fluid leak, and swelling.
How long does it take for the introduction of a central catheter?
30-45 minutes.
Will it hurt?
During the procedure, the patient will feel pain due to narcosis. Maybe a little discomfort at the site of the installation following the procedure.
The average hospital stay after the introduction of Central catheter
This procedure is usually done in the hospital, because it is necessary to treat. Length of stay will depend on the reasons for the introduction of Central catheter. If you are ambulatory treatment course through Central catheter, the patient can be sent home daily procedures.
Patient care after the procedure of introducing a central catheter
Care in a hospital
After the procedure, staff can provide the following assistance, to help rebuild:
- Running X-ray, To make sure, that the catheter is in the correct position;
- Place the insertion of the catheter periodically checked for bleeding;
- Medicines, fluid or nutrient solution is introduced through the catheter;
- Port catheter is washed to help prevent blood clots;
- Measures are being taken, to reduce the risk of infection:
- It should be carefully Wash hands and gloves, before touching the catheter or changing the bandage;
- Use an antiseptic to clean the exposed parts of the catheter;
- Take precautions when handling medicine, fluids or nutrition, which will be introduced through the catheter;
- For patients showed, to identify the signs of infection, which include fever, chills, and problems on site (eg, redness, edema, allocation of extraneous fluid);
- When the bandage is changed, Visitors do not need to be in hospital ward;
- The catheter remains in the injection site as much, as necessary.
There are also steps, you can take, to reduce the risk of infection:
- It is necessary to ask the staff to take every precaution, to prevent infection;
- Staff should immediately tell your doctor, if catheter site redness and pain is felt;
- Before entering the chamber need to wash their hands. You can not let visitors touch the catheter.
Home Care
Upon returning home, you need to perform the following actions, to ensure the normal recovery:
- You want to maintain a place clean, dry and turned. When changing bandages you need to follow the instructions of your doctor;
- Before touching the catheter, You need to wash their hands or use hand sanitizer;
- We need to ask your doctor about, when it is safe to shower, bathe, or to expose the surgical site to water;
- You cannot swim or bathe with an inserted Central catheter;
- To avoid any activities, that could weaken Central catheter;
- No one should touch the catheter;
- Every day you need to check the place for signs of infection (eg, redness, pain);
- You need to rinse the catheter saline or heparin, as indicated by a physician.
Communication with a physician after the procedure of introducing a central catheter
Upon returning home, you need to see a doctor, If the following symptoms:
- Signs of infection, fever and chills, redness or swelling at the site of installation;
- Pain at the site of installation;
- Or leakage of drainage catheter;
- Problems with flushing or the introduction of a fluid into catheter;
- Catheter weakens or falls.
