Bladder Cancer
Description of bladder cancer
Bladder cancer is a disease, where in bladder cancer cells grow. The bladder is located in the lower abdomen and is a hollow organ with flexible muscular wall. Its main function is to store urine before urination.
Cancer occurs, when the cells of the organism (In this case, the cells of the bladder) divide without control and order. Usually, cells divide chaotically. If cells keep dividing uncontrollably, when the body does not need new cells, excrescent (weight) of cloth, called a growth or tumor. The term cancer refers to malignant tumors, that can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body. Benign tumors do not spread throughout the body.
There are three main types of bladder cancer. They are classified by the type of cell, which become cancerous:
- Urotelialʹnaâ cancer – it accounts for more 90% bladder cancer;
- Ploskokletochnыy cancer – is about 4% cases of bladder cancer;
- Adenocarcinoma – about 1% -2% bladder cancer.
Causes of bladder cancer
The cause of bladder cancer is unknown. But, identified several risk factors.
Risk factors for bladder cancer
Factors, which increase the likelihood of bladder cancer:
- Smoking;
- Age: Most cases of bladder cancer is recorded in 65-85 years;
- Occupation (due to occupational exposure to certain substances);
- The risk group includes:
- People, working with rubber, leather and textile;
- Artists;
- Parikmaxerы;
- Train drivers;
- Truck Drivers;
- Oil Industry Workers;
- The risk group includes:
- Race: white;
- Paul: male;
- Genetics;
- Chronic bladder inflammation or infection (eg, schistosomiasis, infection, caused parasitic worms);
- Personal or family history of bladder cancer;
- The application of some chemotherapy drugs: cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide;
- Exposure to arsenic;
- Radiation therapy pelvic;
- Birth defects of the bladder;
- Chemical substances (eg, nitrozaminы, ʙenzidin);
- Urinary stones for many years;
- Prolonged use of a catheter to drain urine (for many years);
- Bladder diverticula – protrusion of the bladder wall;
- Metastasis of cancer from another species.
Symptoms of bladder cancer
Symptoms include:
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Frequent urination or a strong urge to urinate without voiding;
- Urodynia;
- Lower back pain;
- Weight loss, bone pain, stomach ache – in advanced cases of cancer.
These symptoms may be caused by other, less severe disorders, such as bladder stones or infection. If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a doctor.
Diagnosis of bladder cancer
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical examination. During the examination, the doctor will examine the abdomen and tazaovuyu region to search for abnormalities. It may also be carried out rectally or vaginally examination.
Assays include:
- Urinary cytology – a urine sample is examined under a microscope to look for cancerous or precancerous cells;
- Urine culture – to search for signs of infection (eg, bacteria);
- Cystoscopy – procedure, in which the doctor examines the bladder through the urethra using a cystoscope and (a thin tube with a camera and light source);
- Intravenous pyelogram – X-rays of the bladder, kidney, ureters after entering the bloodstream radiopaque substance;
- Computed tomography of the abdomen – such as X-rays, wherein the computer is used, to take pictures inside of the bladder and surrounding organs;
- Magnetic resonance imaging – test, which uses magnetic waves, to take pictures inside of the bladder and surrounding organs;
- Ultrasonography – test, which uses sound waves to study the bladder;
- A bone scan – type of survey, which uses a computer and a special gamma-ray, to make pictures of bones with suspected metastasis;
- Biopsy – removal of a sample of tissue of the bladder, to check for cancer cells.
Treatment of bladder cancer
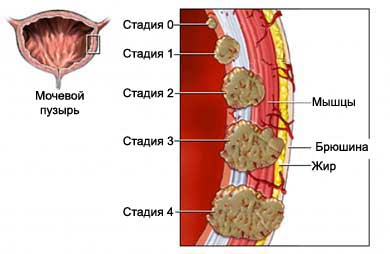
If diagnosed with cancer of the bladder, assigned survey, to determine the extent of its spread. Treatment of bladder cancer depends on the stage. The stages of bladder cancer:
- Stage 0: cancer cells are found only on the surface of the inner membrane of the urinary bladder;
- Stage 1: cancer cells are found in the interior of the bladder inside the shell; lymph nodes are not affected with cancer;
- Stage 2: cancer cells have spread to the muscle of the bladder; lymph nodes are not affected with cancer;
- Stage 3: cancer cells have spread the muscular wall of the bladder to the layer of tissue, surrounding the bladder or reproductive organs, including prostate, lymph nodes are not affected;
- Stage 4: cancer cells, spread beyond the bladder to the abdominal wall or the wall of the pelvis without lymph node involvement or spread on one or more of the lymph nodes and other parts of the body.
Treatment options include the following:
Operation bladder
The operation involves the removal of cancerous cells and surrounding tissue. Operations for the treatment of bladder cancer include transurethral resection and cystectomy.
- Transurethral resection – It is performed at an early stage or superficial bladder cancer. Through the urethra into the bladder introduced cystoscope. At the end of the cystoscope is a small wire loop, which is used to remove cancer cells. Besides, during this procedure can be carried out glare (burning by means of electric current remaining cancer cells);
- Cystectomy (surgical removal of all or part of the bladder) – runs when invasive bladder cancer. Partial cystectomy – removing a portion of the bladder, while at radical cystectomy removes the entire bladder and nearby lymph nodes. Men, usually, also removes the prostate gland. Women have a uterus may be removed, ovary, part of the vagina and the fallopian tubes. When the bladder is removed, for the accumulation of urine should be a special bag.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy – Use of radiation, allowing to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. Radiation therapy may be:
- External radiation therapy – radiation is directed at the tumor from a radiation source outside the body;
- Internal radiation therapy – Radioactive materials are placed near the cancer cells of the bladder. Are introduced through the urethra or through an incision in the abdominal cavity.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy – the use of medical drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs may be administered in various forms, including tablets, injection or administration through the catheter. The drugs enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body, killing mostly cancer cells, and also some healthy cells. When bladder cancer chemotherapy drugs are often administered directly into the bladder – this is called intravesical chemotherapy.
Biological Therapy (immunotherapy)
Biological Therapy – using the immune system to fight cancer. Substances, vyrabytyvaemye in the body or in the laboratory are administered directly into the bladder, to help improve or restore the body's defenses against cancer. This type of therapy is used only for superficial cancers, which was removed transurethrally.
Prevention of bladder cancer
Steps, which can reduce the risk of bladder cancer:
- Do not smoke or use tobacco products. If you smoke, to throw;
- It is necessary to avoid or minimize occupational exposure to chemicals; Follow safe work practices;
- Eat a diet, rich in fruits and vegetables;
- Avoid excessive consumption of foods high in fat and high cholesterol;
- Minimize the use of phenacetin, medication.
