Defibrillation – Kardioversija – Cardioversion
Description cardioversion
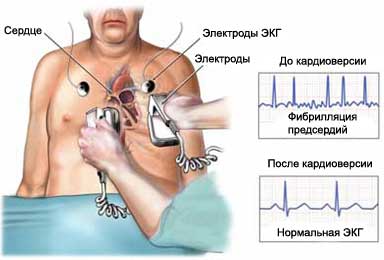
Kardioversija – electric shock through the chest electrodes or pads. Electroshock is performed, to correct a dangerous heart rhythm.
Cardioversion can be It made as planned or emergency procedures, if an abnormal heartbeat to become life-threatening.
When performing cardioversion?
If the heart beats irregularly, it may interfere with normal blood circulation in the body, and deprive various organs, including the brain and heart, oxygen. Without oxygen, bodies can not function properly and, eventually die.
During atrial fibrillation, the electrical signals from the atria rapid and irregular. The atria are shaking, instead of, to completely shrink. Sometimes the signals do not reach the ventricles and the ventricles continue to pump blood, usually, irregularly, sometimes faster.
Planned cardioversion may be used to treat these disorders:
- Atrial fibrillation – very fast, irregular atrial jitter, ventricles pump blood regularly;
- Auricular flutter – a significant acceleration of the atrial contraction (to 200-400 min) while maintaining normal atrial rhythm.
Emergency cardioversion may be used to treat certain types of abnormal heart rhythms, that can lead to death, if a normal heart rhythm is restored:
- Atrial tachycardia – rapid heartbeat, arising in conjunction with atrial ventricular heart palpitations;
- Ventricular tachycardia – rapid heartbeat, arising in the ventricle;
- Ventricular fibrillation – rapid movements of the muscles of the ventricles without effective pumping of blood (It can be deadly).
Possible complications during cardioversion
If you plan to perform a cardioversion, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Inability to stop the abnormal heart rhythm;
- Resumption of the abnormal rhythm after, as a normal heartbeat is restored;
- Development of a more dangerous arrhythmia;
- Damage to the heart muscle;
- Contact of blood clots in the blood circulation, which leads to complications, as stroke or organ damage;
- Burning or irritation to the skin of the breast, at the site of application of the electrodes.
How to conduct cardioversion?
Preparation for the procedure
For a planned cardioversion:
- To diagnose the condition, patient do an electrocardiogram. ECG records the electrical activity of the heart;
- They can be assigned to blood thinners for several weeks before the procedure;
- It may be necessary to undergo transesophageal echocardiography – Ultrasonic detection of blood clots in the heart;
- We need to organize a trip to the hospital and back after the procedure;
- Need to arrange assistance at home after the procedure;
- The night before cardioversion can eat a light meal. You can not eat or drink anything after midnight on the day of the procedure;
- It is necessary to consult a doctor, to determine, Can I take prescribed medications as usual.
When emergency cardioversion time to prepare for the procedure is not.
Anesthesia
The patient is given a potent sedative with a short action time.
Procedure cardioversion
Electrodes are attached to the chest. Electric charge through electrodes applied to the heart. The procedure synchronizes the electrical activity of the heart, and resumes its normal functioning. Electrical shock, perhaps, I have to repeat. The charge may be increased with each attempt.
Immediately after the procedure, cardioversion
While the patient is awake, he was sent to the recovery room. After the procedure, you can go home. If appointed treatment, perhaps, will have to stay in hospital.
How long does cardioversion?
The procedure lasts less 30 minutes.
Kardioversija – Will it hurt?
Sedation prevents pain during the procedure. If carried out an urgent cardioversion, the patient can feel part of its implementation – to feel a boost, that some patients compared with a blow to the chest.
The average time of hospital stay
If carried out a planned cardioversion, the patient can be sent home, as soon as his condition stabilizes.
People, who require cardioversion emergency can be sent to the hospital. This can be done for further observation or because of the underlying disease, application called cardioversion.
Caring for a patient after cardioversion
Home Care
Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions. Maybe, You will need to take blood thinners for several weeks after the procedure. In this case, the levels of these drugs in the blood must be controlled with blood, usually, once a week.
They can be assigned to antiarrhythmic drugs, that will help prevent future improper heartbeat.
Contact your doctor after cardioversion
After discharge from the hospital need to see a doctor, If the following symptoms:
- Blisters, redness, or open sores on the chest;
- Confusion, dizziness;
- Feeling palpitations;
- Feeling skipped heart beats, or irregular heartbeat;
- Cough, labored breathing, breathlessness;
- Severe nausea and vomiting;
- Chest pain or pain in your left arm or jaw;
- Abdominal pain, back, hands or feet;
- Blood in the urine;
- Changes in vision or speech;
- Difficulty by foot;
- Hanging facial muscles.
